一、基本介绍
一个类对另一个类的依赖应该建立在最小的接口上
二、应用实例
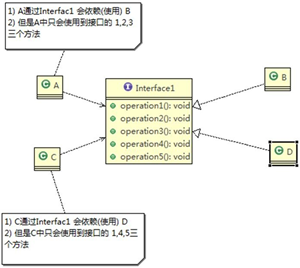
分析以上类图:
首先有四个类,分别是A,B,C,D,以及一个接口Interface1,其中有五个抽象方法,分别是operation1,operation2,operation3,operation4,operation5
类B和类D都会实现Interface1接口
类A通过Interface1接口依赖类B,但是类A中只会使用到接口的operation1,operation2,operation3三个方法
类C通过Interface1接口依赖类D,但是类C中只会使用到接口的operation1,operation4,operation5三个方法
编写程序如下:
1 public class Segregation1 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 A a = new A(); 4 //类A通过接口依赖类B 5 a.depend1(new B()); 6 a.depend2(new B()); 7 a.depend3(new B()); 8 9 C c = new C(); 10 //类C通过接口依赖类D 11 c.depend1(new D()); 12 c.depend4(new D()); 13 c.depend5(new D()); 14 } 15 } 16 17 interface Interface1 { 18 void operation1(); 19 void operation2(); 20 void operation3(); 21 void operation4(); 22 void operation5(); 23 } 24 25 class B implements Interface1 { 26 @Override 27 public void operation1() { 28 System.out.println("B中实现了operation1"); 29 } 30 @Override 31 public void operation2() { 32 System.out.println("B中实现了operation2"); 33 } 34 @Override 35 public void operation3() { 36 System.out.println("B中实现了operation3"); 37 } 38 @Override 39 public void operation4() { 40 System.out.println("B中实现了operation4"); 41 } 42 @Override 43 public void operation5() { 44 System.out.println("B中实现了operation5"); 45 } 46 } 47 48 class D implements Interface1 { 49 @Override 50 public void operation1() { 51 System.out.println("D中实现了operation1"); 52 } 53 @Override 54 public void operation2() { 55 System.out.println("D中实现了operation2"); 56 } 57 @Override 58 public void operation3() { 59 System.out.println("D中实现了operation3"); 60 } 61 @Override 62 public void operation4() { 63 System.out.println("D中实现了operation4"); 64 } 65 @Override 66 public void operation5() { 67 System.out.println("D中实现了operation5"); 68 } 69 } 70 71 //类A通过接口Interface1依赖类B,但是只会用到1,2,3方法 72 class A { 73 public void depend1(Interface1 interface1) { 74 interface1.operation1(); 75 } 76 public void depend2(Interface1 interface1) { 77 interface1.operation2(); 78 } 79 public void depend3(Interface1 interface1) { 80 interface1.operation3(); 81 } 82 } 83 84 //类C通过接口Interface1依赖类B,但是只会用到1,4,5方法 85 class C { 86 public void depend1(Interface1 interface1) { 87 interface1.operation1(); 88 } 89 public void depend4(Interface1 interface1) { 90 interface1.operation4(); 91 } 92 public void depend5(Interface1 interface1) { 93 interface1.operation5(); 94 } 95 }
输出结果:
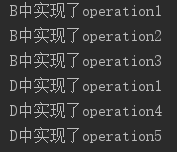
类A和类C都通过Interface1接口分别依赖类B和类D
但是由于类A和类C只需要使用Interface1接口中的部分方法,造成了类B和类D中方法的冗余
-
类A通过接口Interface1依赖类B,类C通过接口Interface1依赖类D,如果接口Interface1对于类A和类C来说不是最小接口,那么类B和类D必须去实现他们不需要的方法
-
将接口Interface1拆分为独立的几个接口,类A和类C分别与他们需要的接口建立依赖关系。也就是采用接口隔离原则
-
接口Interface1中出现的方法,根据实际情况拆分为三个接口
解决方案:将Interface1接口的粒度进一步细化,分解为Interface1,Interface2,Interface3三个接口
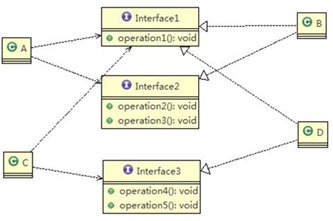
代码实现:
1 public class Segregation1 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 A a = new A(); 4 //类A通过接口依赖类B 5 a.depend1(new B()); 6 a.depend2(new B()); 7 a.depend3(new B()); 8 9 C c = new C(); 10 //类C通过接口依赖类D 11 c.depend1(new D()); 12 c.depend4(new D()); 13 c.depend5(new D()); 14 } 15 } 16 17 interface Interface1 { 18 void operation1(); 19 } 20 21 interface Interface2 { 22 void operation2(); 23 24 void operation3(); 25 } 26 27 interface Interface3 { 28 void operation4(); 29 30 void operation5(); 31 } 32 33 class B implements Interface1, Interface2 { 34 @Override 35 public void operation1() { 36 System.out.println("B中实现了operation1"); 37 } 38 39 @Override 40 public void operation2() { 41 System.out.println("B中实现了operation2"); 42 } 43 44 @Override 45 public void operation3() { 46 System.out.println("B中实现了operation3"); 47 } 48 } 49 50 class D implements Interface1, Interface3 { 51 @Override 52 public void operation1() { 53 System.out.println("D中实现了operation1"); 54 } 55 56 @Override 57 public void operation4() { 58 System.out.println("D中实现了operation4"); 59 } 60 61 @Override 62 public void operation5() { 63 System.out.println("D中实现了operation5"); 64 } 65 } 66 67 //类A通过接口Interface1,2依赖类B 68 class A { 69 public void depend1(Interface1 interface1) { 70 interface1.operation1(); 71 } 72 73 public void depend2(Interface2 interface2) { 74 interface2.operation2(); 75 } 76 77 public void depend3(Interface2 interface2) { 78 interface2.operation3(); 79 } 80 } 81 82 //类C通过接口Interface1,3依赖类B 83 class C { 84 public void depend1(Interface1 interface1) { 85 interface1.operation1(); 86 } 87 88 public void depend4(Interface3 interface3) { 89 interface3.operation4(); 90 } 91 92 public void depend5(Interface3 interface3) { 93 interface3.operation5(); 94 } 95 }
输出结果:
与实现接口隔离原则之前的输出结果相同,但是在接口的粒度上进行了细化,降低了代码的耦合度