bitset作为C++一个非常好用的STL,在一些题目中巧妙地使用会产生非常不错的效果。今天扶苏来分享一点bitset的基础语法和应用
本文同步发布于个人其他博客,同时作为P3674题解发布。
本文感谢@burnside和@ddosvoid神仙帮助审稿。
注意:以下内容均按照C++98语法书写,可以在C++98下编译通过。
bitset是一个01串,每一位是占一个字节,可以进行单点0/1修改,左移右移以及按位运算操作。一个非常好用的用法是统计某个数是否出现过,类似一个桶。同时两个bitset取或可以在优秀的常数下获得两个集合是否有重复元素的信息。
声明与初始化
使用bitset需要引用
其声明方法为
std::bitset<N>s;
其中N为s的长度。
对于s的初始化,开在全局默认为全0。如果开在局部可以使用下面的reset函数置零。
同时bitset资瓷以下赋值姿势:可以使用一个同长度的std::string型01串对其进行赋值,bitset内部与string对应位相同:
// The default is that N is 8.
std::bitset<N> s (std::string("00110101"));
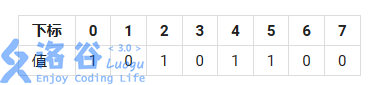
需要注意的是集合内部的下标是从右向左单调递增的,即字符串的第一位代表set的第7位(从0编号)。上面的赋值方法对应s的值如下表:
修改与运算
bitset中每一个元素可以通过下标的方式访问。一个长度为(N)的bitset下标编号为([0,N))。
进行单点修改时,直接访问位置然后赋值即可:
s[pos] = x;
单点修改的复杂度为(O(1))。
左移右移的写法与整形类似,移动后返回一个bitset,例如左移(x)位:
std::bitset<N> k = s << x;
同时资瓷<<=和>>=操作:
s <<= x;
如果将字长放在RAM模型中,约定计算机字长为(w)的话,一次左右移的复杂度为(O(frac{N}{w}))。其中在32位系统上,(w~=~32),64位系统上(w~=~64)。由于bitset的绝大部分操作的复杂度都为(O(frac{N}{w})),以下内容中,若不特殊说明,则默认操作的复杂度同上。
如果仅仅考察运算量同输入规模的增长关系或不将字长纳入RAM模型,则可认为一次操作的复杂度为(O(N)),常数为(frac{1}{32})或(frac{1}{64}),这两种说法在文献上都有出现,在OI中为了方便计算运算量,一般使用第一种表达方法。以下内容一律使用(O(frac{N}{w}))的表示法。
同时bitset资瓷二元按位运算,即资瓷与、或、异或三个运算符:返回值为一个bitset。结果为运算符两侧的bitset按位运算的结果。
std::bitset<N> k = s & s0;
输入输出与转换
bitset重载了<<和>>输入输出流,可以使用std::cin和std::cout来读入和输出一个bitset的所有元素。
当读入的长度小于bitset的位数时,会从第0位开始赋值直到字符串结束。当读入长度大于bitset的位数时,在扶苏的MinGW编译器上会截取前【位数】个进行赋值。未尝试过在其他环境下的结果。
注意,输出时bitset是反着输出的,即第0位是从右向左数第1个:
std::cin >> s; // 1101
std::cout << s << std::endl; // 000001101
从上述例子中可以看出,输入字符串的第【长度】位是集合的第1位。注意事项和使用std::string进行初始化的一致。
bitset提供两个转换函数,可以转换为std::string型,unsigned long int型(即unsigned int)。函数名为别为to_string()和to_ulong();
在C++11标准下可以转换为unsigned long long int型,函数名为to_llong()
其中转换成std::string型会转换成01串,其他两个类型会按照二进制位转换成十进制数字。
当bitset大小大于32位时,转换成unsigned long int会导致RE,大于64位时,转换成unsigned long long int会产生RE:
// The default is that N is 8.
s.reset();
s[2] = true;
unsigned int s1 = s.to_ulong();
std::cout << s1 << std::endl; //4
unsigned long long int s2 = s.to_ullong(); //C++11
std::cout << s2 << std::endl; //4
std::string ss = s.to_string();
std::cout << ss << std::endl; //00000100
成员函数
reset
bitset的清空操作为reset。将集合内元素全部置零:
s.reset();
set
set有两种用法,第一种是直接调用set不带参数,会将bitset内所有元素置1,另一种是set后加两个参数,分别是pos和val,意为将bitset中第pos个元素的值置为v。当v为true时可以省略不写。
s.reset();
s.set() //11111111
s.set(3,false) //11110111
s.set(3) //11111111
test
test有一个参数pos,返回一个bitset内第pos位的值。
s.reset();
s.set(7);
int k = s.test(7); // k is true
k = s.test(6); // k is false
any
bitset有一个成员函数为any,返回一个布尔量。若bitset内部存在一位的值为1,则返回true,否则返回false:
s.clear();
bool k = s.any(); //k is false
s[1] = true;
k = s.any() //k is true
复杂度同上。按照不同编译器版本的实现方法,.any()的常数甚至有可能小于理论值。
none
与any相对,返回一个布尔量,不存在任何一个位置的值为1则返回true,否则返回false。
s.clear();
bool k = s.none(); //k is true
s[1] = true;
k = s.none() //k is false
count
count返回一个bitset内1的个数,是一个无符号整形:
s.reset();
int k = s.count(); // k is 0
s[1] = true;
k = s.count(); // k is 1
需要注意的是目前扶苏已知的资料中,count的复杂度也是(O(frac{N}{w}))。
当然想知道0的个数可以用总长度减去count喽
flip
flip函数类似于按位取反,它的两个声明如下:
bitset& flip();
bitset& flip (size_t pos);
当调用s.flip()且括号内无参数时,会将集合内所有元素取反(0变1,1变0)
当调用s.flip(x)时,会将第x位取反(从0编号)
s.reset();
s[1] = true; //s is "01000000"
s.flip(); //s is "10111111"
s.flip(1); //s is "11111111"
手写一个bitset
注意,以下手写bitset内容因为时间紧迫,部分函数未进行单元测试,经测试仅仅A掉P3674 小清新人渣的本愿。如果您发现代码错误请在评论区发表评论或者私信联系@一扶苏一。在此表示感谢qwq
bitset的过度封装导致bitset的一些操作不能实现,比如两个二进制数求lowbit。怎么办呢,我们可以手写一个bitset!
一个bitset的显然可以用一堆unsigned long long拼成的数组实现,一些简单的位运算和成员函数实现十分简单,会在下方直接给出代码,现在我们考虑左移和右移怎么实现。
以下不妨设bitset字长BitNum为64。
不妨设进行左移,如果左移位数v小于64,那么可以单个数字直接移动,我们考虑两个数字之间移动的部分,就是左侧数字的最高v位成为了右侧数字的最低v位,于是我们记录一下这最高的v位就可以迭代了。
考虑左移位数大于64的情况,我们发现这种情况等价于先整个数组左移(frac{v}{BitNum})位置,然后做模意义下的移动即可。
然后考虑仅仅这么做的话,因为我们的bitset不一定是严格【位数】长度的,可能一个数字左移以后再右移会爆炸。比如一个长度为 (3) 的二进制串 (s~=~111) ,对 (s) 先左移一位(110)再右移一位应该得到011,但是因为我们的单个字符一存就是64位,这么做会让答案得到111。具体的解决方法是每次操作结束以后把最高位应该是 (0) 的位置全部截掉。
具体位移部分代码如下
注意代码中_Ary的下标越大代表的二进制位越小。即_Size-1的下标代表二进制串的 (0~sim~63) 位,以此类推
Bitset() { //constructed function of std::string is left out because i dont know how to implement it
memset(_Ary, 0, sizeof _Ary);
int _firstsize = _len % _BitNum;
for (rg int i = 0; i < _firstsize; ++i) _upceil |= 1ull << i;
if (!_firstsize) _upceil = _INF;
}
void reset() {*this = Bitset();}
//operators
void rtmve(const int &_v) {
for (rg int i = _Size - 1; i >= _v; --i) this->_Ary[i] = this->_Ary[i - _v];
for (rg int i = _v - 1; ~i; --i) this->_Ary[i] = 0;
}
void lftmve(const int &_v) {
for (rg int i = 0; (i + _v) < _Size; ++i) this->_Ary[i] = this->_Ary[i + _v];
for (rg int i = _Size - _v; i < _Size; ++i) this->_Ary[i] = 0;
}
Bitset& operator<<=(int _v) {
if (_v < 0) {
*this >>= -_v;
return *this;
}
this->lftmve(_v / _BitNum);
_v %= _BitNum;
ull _tp = 0, _Pos = _BitNum - _v;
for (rg int i = 1; i <= _v; ++i) _tp |= 1ull << (_BitNum - i);
ull _Lstv = 0;
for (rg int i = _Size - 1; ~i; --i) {
ull _Tp_Lstv = (_Ary[i] & _tp) >> _Pos;
_Ary[i] <<= _v;
_Ary[i] |= _Lstv;
_Lstv = _Tp_Lstv;
}
this->_Ary[0] &= _upceil; // cut off redundant digit
return *this;
}
Bitset& operator>>=(int _v) {
if (_v < 0) {
*this <<= -_v;
return *this;
}
this->rtmve(_v / _BitNum);
_v %= _BitNum;
ull _tp = (1ull << _v)- 1;
ull _Lstv = 0, __Pos = _BitNum - _v;
for (rg int i = 0; i < _Size; ++i) {
ull _Tp_Lstv = (_Ary[i] & _tp) << __Pos;
_Ary[i] >>= _v;
_Ary[i] |= _Lstv;
_Lstv = _Tp_Lstv;
}
this->_Ary[0] &= _upceil; //// cut off redundant digit
return *this;
}
考虑set和test操作,我们需要定位这一位在数组中的位置,如果按照上面所述的方法存二进制串的话,第二进制串第v个位置应该对应的数组位置__Pos和这一个数上的二进制位置_v应该按照如下方法寻找
inline void __GetPos(const ull &_pos, int &__Pos, int &_v) {
__Pos = _Size - _pos / _BitNum - 1;
_v = _pos % _BitNum;
}
考虑我们如何修改一个位置的值:如果修改为true,则可以直接与1ull<<v取或,如果修改为false,则可以先修改为true,然后与1ull<<v取异或
void set(const ull &_pos, const bool val = true) {
int __Pos , _v;
__GetPos(_pos,__Pos,_v);
if(val) {
this->_Ary[__Pos] |= (1ull << (_v));
} else {
this->_Ary[__Pos] |= (1ull << (_v));
this->_Ary[__Pos] ^= (1ull << (_v));
}
}
剩下的部分就很简单辣,这里直接给出代码,这份代码中实现了大部分bitset的操作,因为我不会对单个bit取值,所以没有重载[]运算符,对集合的修改需要使用set和test函数。
#define Fusu_Bitset
#ifdef Fusu_Bitset
#include <cstddef> //size_t used
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#endif
namespace Fusu {
template <size_t _len>
struct Bitset {
#define rg register
#define ci const int
#define cl const long long
typedef long long int ll;
typedef unsigned long long int ull;
const static int _BitNum = 64;
const static int _Size = _len / _BitNum + ((_len % _BitNum) == 0 ? 0 : 1);
ull _Ary[_Size];
ull _upceil;
const static ull _INF = (1ull << 63) - 1 + (1ull << 63);
Bitset() { //constructed function of std::string is left out because i dont know how to implement it
memset(_Ary, 0, sizeof _Ary);
int _firstsize = _len % _BitNum;
for (rg int i = 0; i < _firstsize; ++i) _upceil |= 1ull << i;
if (!_firstsize) _upceil = _INF;
}
void reset() {*this = Bitset();}
//operators
void rtmve(const int &_v) {
for (rg int i = _Size - 1; i >= _v; --i) this->_Ary[i] = this->_Ary[i - _v];
for (rg int i = _v - 1; ~i; --i) this->_Ary[i] = 0;
}
void lftmve(const int &_v) {
for (rg int i = 0; (i + _v) < _Size; ++i) this->_Ary[i] = this->_Ary[i + _v];
for (rg int i = _Size - _v; i < _Size; ++i) this->_Ary[i] = 0;
}
Bitset& operator<<=(int _v) {
if (_v < 0) {
*this >>= -_v;
return *this;
}
this->lftmve(_v / _BitNum);
_v %= _BitNum;
ull _tp = 0, _Pos = _BitNum - _v;
for (rg int i = 1; i <= _v; ++i) _tp |= 1ull << (_BitNum - i);
ull _Lstv = 0;
for (rg int i = _Size - 1; ~i; --i) {
ull _Tp_Lstv = (_Ary[i] & _tp) >> _Pos;
_Ary[i] <<= _v;
_Ary[i] |= _Lstv;
_Lstv = _Tp_Lstv;
}
this->_Ary[0] &= _upceil;
return *this;
}
Bitset& operator>>=(int _v) {
if (_v < 0) {
*this <<= -_v;
return *this;
}
this->rtmve(_v / _BitNum);
_v %= _BitNum;
ull _tp = (1ull << _v)- 1;
ull _Lstv = 0, __Pos = _BitNum - _v;
for (rg int i = 0; i < _Size; ++i) {
ull _Tp_Lstv = (_Ary[i] & _tp) << __Pos;
_Ary[i] >>= _v;
_Ary[i] |= _Lstv;
_Lstv = _Tp_Lstv;
}
this->_Ary[0] &= _upceil;
return *this;
}
Bitset operator&(const Bitset &_others) const {
Bitset _ret;
for (rg int i = _Size - 1; ~i; --i) {
_ret._Ary[i] = this->_Ary[i] & _others._Ary[i];
}
return _ret;
}
Bitset operator|(const Bitset &_others) const {
Bitset _ret;
for (rg int i = _Size - 1; ~i; --i) {
_ret._Ary[i] = this->_Ary[i] | _others._Ary[i];
}
return _ret;
}
Bitset operator^(const Bitset &_others) const {
Bitset _ret;
for (rg int i = _Size - 1; ~i; --i) {
_ret._Ary[i] = this->_Ary[i] ^ _others._Ary[i];
}
return _ret;
}
Bitset operator~() const {
Bitset _ret;
for (rg int i = _Size - 1; ~i; --i) {
_ret._Ary[i] = ~this->_Ary[i];
}
return _ret;
}
Bitset operator<<(const int &_v) const {
Bitset x = *this;
x <<= _v;
return x;
}
Bitset operator>>(const int &_v) const {
Bitset x = *this;
x >>= _v;
return x;
}
//member functions
inline void __GetPos(const ull &_pos, int &__Pos, int &_v) {
__Pos = _Size - _pos / _BitNum - 1;
_v = _pos % _BitNum;
}
void set() {
for (rg int i = 0; i < _Size; ++i) this->_Ary[i] = _INF;
}
void set(const ull &_pos, const bool val = true) {
int __Pos , _v;
__GetPos(_pos,__Pos,_v);
if (val) {
this->_Ary[__Pos] |= (1ull << (_v));
} else {
this->_Ary[__Pos] |= (1ull << (_v));
this->_Ary[__Pos] ^= (1ull << (_v));
}
}
int test(const ull &_pos) {
int __Pos , _v;
__GetPos(_pos,__Pos,_v);
return this->_Ary[__Pos] & (1ull << (_v)) ? 1 : 0;
}
bool any() {
for (rg int i = _Size - 1; ~i; --i) if (this->_Ary[i]) return true;
return false;
}
bool none() {
return !this->any();
}
ull conut() {
ull _cnt = 0;
for (rg int i = _Size - 1; ~i; --i) _cnt += __builtin_popcount(this->_Ary[i]);
/*
*if u cant used double_underlined functions,
*u can set a val to maintain the num of true
*and change it in other operators which would change the num of true
*/
return _cnt;
}
void flip() {
*(this) = ~(*this);
}
void flip(const ull &_pos) {
if(this->test(_pos)) this->set(_pos, false);
else this->set(_pos, true);
}
//changing functions
std::string to_string() {
std::string _ret;
_ret.clear();
for (rg int i = 0; i < _Size; ++i) {
for (rg int j = _BitNum - 1; ~j; --j) _ret += (this->_Ary[i] & (1ull << j)) ? '1' : '0';
}
return _ret;
}
unsigned int to_ulong() {
return this->_Ary[_Size - 1];
}
};
} //namespace
Samples
这是非常显然的一个布尔背包问题,因为数据规模比较小,可以直接把多重背包拆分成01背包做。
考虑朴素的做法显然是设(f_{i,j})为前(i)个中,第(j)的价值能否拼出来,转移方程显然:
复杂度(O(nsum~w_i)),考虑可以滚动掉第一维,然后考察转移,实质上是将原数组的01串左移了(w_i)位与原串取或。
于是如果设(f)是一个bitset,则转移可以写成
复杂度(O(n~sum~w_i~ imes~frac{1}{w})),实际效率十分优秀。
使用bitset优化01bool背包的转移是bitset一个比较常见的用法。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <bitset>
#include <iostream>
#ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE
#define freopen(a, b, c)
#endif
#define rg register
#define ci const int
#define cl const long long
typedef long long int ll;
namespace IPT {
const int L = 1000000;
char buf[L], *front=buf, *end=buf;
char GetChar() {
if (front == end) {
end = buf + fread(front = buf, 1, L, stdin);
if (front == end) return -1;
}
return *(front++);
}
}
template <typename T>
inline void qr(T &x) {
rg char ch = IPT::GetChar(), lst = ' ';
while ((ch > '9') || (ch < '0')) lst = ch, ch=IPT::GetChar();
while ((ch >= '0') && (ch <= '9')) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48), ch = IPT::GetChar();
if (lst == '-') x = -x;
}
template <typename T>
inline void ReadDb(T &x) {
rg char ch = IPT::GetChar(), lst = ' ';
while ((ch > '9') || (ch < '0')) lst = ch, ch = IPT::GetChar();
while ((ch >= '0') && (ch <= '9')) x = x * 10 + (ch ^ 48), ch = IPT::GetChar();
if (ch == '.') {
ch = IPT::GetChar();
double base = 1;
while ((ch >= '0') && (ch <= '9')) x += (ch ^ 48) * ((base *= 0.1)), ch = IPT::GetChar();
}
if (lst == '-') x = -x;
}
namespace OPT {
char buf[120];
}
template <typename T>
inline void qw(T x, const char aft, const bool pt) {
if (x < 0) {x = -x, putchar('-');}
rg int top=0;
do {OPT::buf[++top] = x % 10 + '0';} while (x /= 10);
while (top) putchar(OPT::buf[top--]);
if (pt) putchar(aft);
}
const int maxn = 7;
const int maxt = 20010;
int MU[maxn], kase;
std::bitset<maxt>frog;
void clear();
int main() {
freopen("1.in", "r", stdin);
while (true) {
clear();
for (rg int i = 1; i < 7; ++i) qr(MU[i]);
int sum = 0;
for (rg int i = 1; i < 7; ++i) sum += MU[i] * i;
if (!sum) return 0;
printf("Collection #%d:
", ++kase);
if (sum & 1) {
puts("Can't be divided.
");
continue;
}
frog.set(0);
for (rg int i = 1; i < 7; ++i) {
for (rg int j = 1; j <= MU[i]; ++j)
frog |= (frog << i);
}
if (frog.test(sum >> 1)) puts("Can be divided.
");
else puts("Can't be divided.
");
}
return 0;
}
void clear() {
frog.reset();
memset(MU, 0, sizeof MU);
}
既然bitset可以优化01背包,那么可不可以优化完全背包呢?事实上完全是可以的,比如这道题。
本题是一个bool完全背包的递推,不会做请右转题解区。考虑这题布尔背包的朴素转移(O(n~ imes~max{a_i}))的,但是可以通过bitset来降低运算量。
具体的,我们发现一个位置(x)能被表示出来当且仅当(f_{x-k~ imes~a_i}~= true),其中(f)为布尔数组。即(f_x~|=~f_{x-k~ imes~a_i})。我们用bitset来作为这个布尔数组,于是发现上式等价于(f~|=~f~<<(k~ imes~a_i))。枚举一下(k)即可转移。
接着发现当(k~=~3)时的结果等价于(k~=~1)再(k~=~2)的结果叠加,于是(3)是不需要枚举的。(k~=~5)时的结果与(k~=~1)再(k~=~4)的的结果是相同的,也不需要枚举。同理可以发现非二的幂次的(k)都不需要枚举,于是可以只枚举2的幂次。
考虑复杂度,一共枚举(n)个值,每次枚举从(a_i)逐次乘二到(max{a_i}),一共乘(log (max{a_i}))次。一次bitset的操作复杂度为(O(frac{max{a_i}}{w})),于是总复杂度(O(n~max{a_i}~log (max{a_i})~ imes~frac{1}{w}))。实际运算量不增反降。
Code
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE
#define freopen(a, b, c)
#endif
#define rg register
#define ci const int
#define cl const long long
typedef long long int ll;
namespace IPT {
const int L = 1000000;
char buf[L], *front=buf, *end=buf;
char GetChar() {
if (front == end) {
end = buf + fread(front = buf, 1, L, stdin);
if (front == end) return -1;
}
return *(front++);
}
}
template <typename T>
inline void qr(T &x) {
rg char ch = IPT::GetChar(), lst = ' ';
while ((ch > '9') || (ch < '0')) lst = ch, ch=IPT::GetChar();
while ((ch >= '0') && (ch <= '9')) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48), ch = IPT::GetChar();
if (lst == '-') x = -x;
}
namespace OPT {
char buf[120];
}
template <typename T>
inline void qw(T x, const char aft, const bool pt) {
if (x < 0) {x = -x, putchar('-');}
rg int top=0;
do {OPT::buf[++top] = x % 10 + '0';} while (x /= 10);
while (top) putchar(OPT::buf[top--]);
if (pt) putchar(aft);
}
const int maxn = 110;
const int maxt = 25010;
int t,n;
int MU[maxn];
std::bitset<maxt>s;
void clear();
int main() {
freopen("1.in", "r", stdin);
qr(t);
while(t--) {
clear();
qr(n);
for (rg int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) qr(MU[i]);
std::sort(MU + 1, MU + 1 + n);
s[0] = true;
rg int ans = 0;
for (rg int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) if(!s[MU[i]]) {
++ans;
int x = MU[i];
while(x <= MU[n]) {
s |= s << x;
x <<= 1;
}
}
qw(ans, '
' ,true);
}
return 0;
}
void clear() {
n = 0;
memset(MU, 0, sizeof MU);
s.reset();
}
这是一个标准的bieset题目。
不带修改,资瓷离线,而且还是dllxl大爷的题,于是考虑使用莫队解决。
考虑在查询时如何维护答案:
如果当前序列中
移项得
(a~=~x~+~b)
即这个序列中同时出现了一个数(y)和(y~+~x)。
即(s[y]~=~true)且(s[y+x]~=~true)
这等价于 (s~|~(s<<x)) 存在一个1。于是用bitset维护出现的数字即可。
考虑加法:
若
我们令(b'~=~n~-~b),则
移项得
于是按照减法的方式,再维护一个bitset表示n-y是否出现即可,
对于乘法的情况,因为枚举一个数的因数只需要(O(sqrt{n})),于是直接暴力枚举因数即可。
于是查询的复杂度(O(frac{nm}{w})),可以通过本题。
Code
#prag
ma GCC optimize(3)
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE
#define freopen(a, b, c)
#endif
#define rg register
#define ci const int
#define cl const long long
typedef long long int ll;
namespace IPT {
const int L = 1000000;
char buf[L], *front=buf, *end=buf;
char GetChar() {
if (front == end) {
end = buf + fread(front = buf, 1, L, stdin);
if (front == end) return -1;
}
return *(front++);
}
}
template <typename T>
inline void qr(T &x) {
rg char ch = IPT::GetChar(), lst = ' ';
while ((ch > '9') || (ch < '0')) lst = ch, ch=IPT::GetChar();
while ((ch >= '0') && (ch <= '9')) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48), ch = IPT::GetChar();
if (lst == '-') x = -x;
}
template <typename T>
inline void ReadDb(T &x) {
rg char ch = IPT::GetChar(), lst = ' ';
while ((ch > '9') || (ch < '0')) lst = ch, ch = IPT::GetChar();
while ((ch >= '0') && (ch <= '9')) x = x * 10 + (ch ^ 48), ch = IPT::GetChar();
if (ch == '.') {
ch = IPT::GetChar();
double base = 1;
while ((ch >= '0') && (ch <= '9')) x += (ch ^ 48) * ((base *= 0.1)), ch = IPT::GetChar();
}
if (lst == '-') x = -x;
}
namespace OPT {
char buf[120];
}
template <typename T>
inline void qw(T x, const char aft, const bool pt) {
if (x < 0) {x = -x, putchar('-');}
rg int top=0;
do {OPT::buf[++top] = x % 10 + '0';} while (x /= 10);
while (top) putchar(OPT::buf[top--]);
if (pt) putchar(aft);
}
const int maxn = 100010;
std::bitset<maxn>s1,s2;
int n, m;
int MU[maxn], belong[maxn], oc[maxn];
struct Ask {
int opt, l, r, v, id;
bool ans;
inline bool operator<(const Ask &_others) const {
if (belong[this->l] != belong[_others.l]) return this->l < _others.l;
if (belong[this->l] & 1) return this->r < _others.r;
return this->r > _others.r;
}
};
Ask ask[maxn];
inline bool cmp(const Ask &_a,const Ask &_b) {
return _a.id < _b.id;
}
void add(int);
void dlt(int);
int main() {
freopen("1.in", "r", stdin);
qr(n); qr(m);
for (rg int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) qr(MU[i]);
for (rg int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
Ask &now = ask[i];
qr(now.opt); qr(now.l); qr(now.r); qr(now.v); now.id = i;
}
for (rg int i = 1, sn = sqrt(n); i <= n; ++i) belong[i] = i / sn;
std::sort(ask + 1, ask + 1 + m);
int prel = ask[1].l, prer = prel - 1;
for (rg int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
int l = ask[i].l, r = ask[i].r;
while (prel < l) dlt(prel++);
while (prel > l) add(--prel);
while (prer < r) add(++prer);
while (prer > r) dlt(prer--);
int op = ask[i].opt, x = ask[i].v;
if (op == 1) {
ask[i].ans = (s1 & (s1 << x)).any();
} else if (op == 2) {
ask[i].ans = (s1 & (s2 >> (n - x))).any();
} else {
for (rg int j = 1; (j * j) <= x; ++j) if(!(x % j)) {
if(s1[j] && s1[x / j]) {ask[i].ans = true; break;}
}
}
}
std::sort(ask + 1, ask + 1 + m, cmp);
for (rg int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) puts(ask[i].ans ? "hana" : "bi");
return 0;
}
inline void add(int x) {
x = MU[x];
if (!(oc[x]++)) s1[x] = s2[n - x] = true;
}
inline void dlt(int x) {
x = MU[x];
if (!(--oc[x])) s1[x] = s2[n - x] = false;
}
Summary
bitset是C++中十分灵活的一个STL,在许多题目中可以起到优化常数乃至复杂度、降低代码难度的效果。你学会了嘛~