为什么要用numpy
Python中提供了list容器,可以当作数组使用。但列表中的元素可以是任何对象,因此列表中保存的是对象的指针,这样一来,为了保存一个简单的列表[1,2,3]。就需要三个指针和三个整数对象。对于数值运算来说,这种结构显然不够高效。
Python虽然也提供了array模块,但其只支持一维数组,不支持多维数组(在TensorFlow里面偏向于矩阵理解),也没有各种运算函数。因而不适合数值运算。
NumPy的出现弥补了这些不足。
(——摘自张若愚的《Python科学计算》)
import numpy as np
数组创建
## 常规创建方法
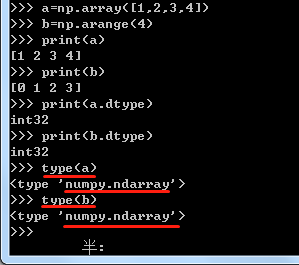
a = np.array([2,3,4])
b = np.array([2.0,3.0,4.0])
c = np.array([[1.0,2.0],[3.0,4.0]])
d = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]],dtype=complex) # 指定数据类型
print a, a.dtype
print b, b.dtype
print c, c.dtype
print d, d.dtype
[2 3 4] int32
[ 2. 3. 4.] float64
[[ 1. 2.]
[ 3. 4.]] float64
[[ 1.+0.j 2.+0.j]
[ 3.+0.j 4.+0.j]] complex128
数组的常用函数
print np.arange(0,7,1,dtype=np.int16) # 0为起点,间隔为1时可缺省(引起歧义下不可缺省)
print np.ones((2,3,4),dtype=np.int16) # 2页,3行,4列,全1,指定数据类型
print np.zeros((2,3,4)) # 2页,3行,4列,全0
print np.empty((2,3)) #值取决于内存
print np.arange(0,10,2) # 起点为0,不超过10,步长为2
print np.linspace(-1,2,5) # 起点为-1,终点为2,取5个点
print np.random.randint(0,3,(2,3)) # 大于等于0,小于3,2行3列的随机整数
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6]
[[[1 1 1 1]
[1 1 1 1]
[1 1 1 1]]
[[1 1 1 1]
[1 1 1 1]
[1 1 1 1]]]
[[[ 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0.]]
[[ 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0.]
[ 0. 0. 0. 0.]]]
[[ 1.39069238e-309 1.39069238e-309 1.39069238e-309]
[ 1.39069238e-309 1.39069238e-309 1.39069238e-309]]
[0 2 4 6 8]
[-1. -0.25 0.5 1.25 2. ]
[[1 0 1]
[0 1 0]]
类型转换
print float(1)
print int(1.0)
print bool(2)
print float(True)
1.0
1
True
1.0
数组输出
从左到右,从上向下
一维数组打印成行,二维数组打印成矩阵,三维数组打印成矩阵列表
print np.arange(1,6,2)
print np.arange(12).reshape(3,4) # 可以改变输出形状
print np.arange(24).reshape(2,3,4)# 2页,3行,4页
[1 3 5]
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
[[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
[[12 13 14 15]
[16 17 18 19]
[20 21 22 23]]]
基本运算
## 元素级运算
a = np.array([1,2,3,4])
b = np.arange(4)
print a, b
print a-b
print a*b
print a**2
print 2*np.sin(a)
print a>2
print np.exp(a) # 指数
[1 2 3 4] [0 1 2 3]
[1 1 1 1]
[ 0 2 6 12]
[ 1 4 9 16]
[ 1.68294197 1.81859485 0.28224002 -1.51360499]
[False False True True]
[ 2.71828183 7.3890561 20.08553692 54.59815003]
## 矩阵运算(二维数组)
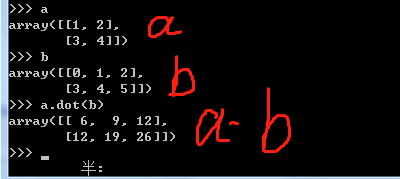
a = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]]) # 2行2列
b = np.arange(6).reshape((2,-1)) # 2行3列
print a,b
print a.dot(b) # 2行3列
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/fu6543210/article/details/83240024