转载:http://blog.csdn.net/hengzo/article/details/49689725
The linear feedback shift register is implemented as a series of Flip-Flops inside of an FPGA that are wired together as a shift register. Several taps off of the shift register chain are used as inputs to either an XOR or XNOR gate. The output of this gate is then used as feedback to the beginning of the shift register chain, hence the Feedback in LFSR.

- LFSR patterns are pseudo-random.
- Output patterns are deterministic. You can figure out the next state by knowing the position of the XOR gates as well as the current pattern.
- A pattern of all 0's cannot appear when the taps use XOR gates. Since 0 XORed with 0 will always produce 0, the LFSR will stop running.注意初始化种子
- A pattern of all 1's cannot appear when the taps use XNOR gates. Since 1 XNORed with 1 will always produce 1, the LFSR will stop running.
- The maximum possible number of iterations of any LFSR = 2Bits-1
产生伪随机数的方法最常见的是利用一种线性反馈移位寄存器(LFSR)。它是由n个D触发器和若干个异或门组成的,如图:
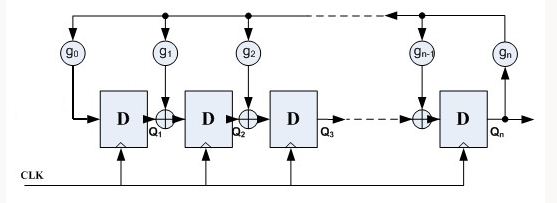
其中,gn为反馈系数,取值只能为0或1,取为0时表明不存在该反馈之路,取为1时表明存在该反馈之路;n个D触发器最多可以提供2^n-1个状态(不包括全0的状态),为了保证这些状态没有重复,gn的选择必须满足一定的条件。下面以n=3,g0=1,g1=1,g2=0,g3=1为例,说明LFSR的特性,具有该参数的LFSR结构如下图:
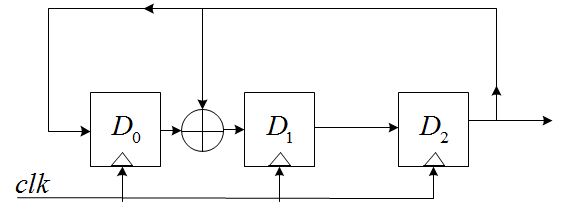
假设在开始时,D2D1D0=111(seed),那么,当时钟到来时,有:
D2=D1_OUT=1;
D1=D0_OUT^D2_OUT=0;
D0=D2_OUT=1;
即D2D1D0=101;同理,又一个时钟到来时,可得D2D1D0=001. ………………
画出状态转移图如下:
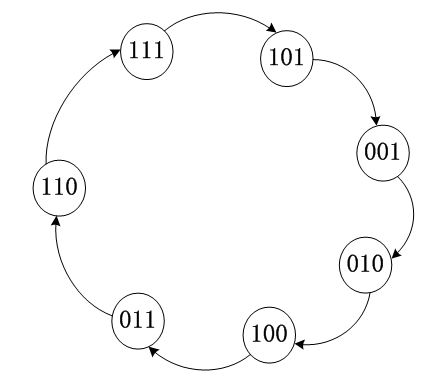
从图可以看出,正好有2^3-1=7个状态,不包括全0;
如果您理解了上图,至少可以得到三条结论:
1)初始状态是由SEED提供的;
2)当反馈系数不同时,得到的状态转移图也不同;必须保证gn===1。
3)D触发器的个数越多,产生的状态就越多,也就越“随机”;
verilog实现
1 <pre name="code" class="plain">//文章地址:http://www.nandland.com/vhdl/modules/lfsr-linear-feedback-shift-register.html 2 //程序地址:http://www.nandland.com/verilog/modules/code/LFSR.v 3 4 5 /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 6 // File downloaded from http://www.nandland.com 7 /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 8 // Description: 9 // A LFSR or Linear Feedback Shift Register is a quick and easy way to generate 10 // pseudo-random data inside of an FPGA. The LFSR can be used for things like 11 // counters, test patterns, scrambling of data, and others. This module 12 // creates an LFSR whose width gets set by a parameter. The o_LFSR_Done will 13 // pulse once all combinations of the LFSR are complete. The number of clock 14 // cycles that it takes o_LFSR_Done to pulse is equal to 2^g_Num_Bits-1. For 15 // example setting g_Num_Bits to 5 means that o_LFSR_Done will pulse every 16 // 2^5-1 = 31 clock cycles. o_LFSR_Data will change on each clock cycle that 17 // the module is enabled, which can be used if desired. 18 // 19 // Parameters: 20 // NUM_BITS - Set to the integer number of bits wide to create your LFSR. 21 /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 22 module LFSR #(parameter NUM_BITS) 23 ( 24 input i_Clk, 25 input i_Enable, 26 27 // Optional Seed Value 28 input i_Seed_DV, 29 input [NUM_BITS-1:0] i_Seed_Data, 30 31 output [NUM_BITS-1:0] o_LFSR_Data, 32 output o_LFSR_Done 33 ); 34 35 reg [NUM_BITS:1] r_LFSR = 0; 36 reg r_XNOR; 37 38 39 // Purpose: Load up LFSR with Seed if Data Valid (DV) pulse is detected. 40 // Othewise just run LFSR when enabled. 41 // 初始化seed值可以选择载入, 42 always @(posedge i_Clk) 43 begin 44 if (i_Enable == 1'b1) 45 begin 46 if (i_Seed_DV == 1'b1) 47 r_LFSR <= i_Seed_Data; 48 else 49 r_LFSR <= {r_LFSR[NUM_BITS-1:1], r_XNOR}; 50 end 51 end 52 53 // Create Feedback Polynomials. Based on Application Note: 54 // http://www.xilinx.com/support/documentation/application_notes/xapp052.pdf 55 //使用同或运算,初始化种子不能全1 56 57 58 always @(*) 59 begin 60 case (NUM_BITS) 61 3: begin 62 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[3] ^~ r_LFSR[2]; 63 end 64 4: begin 65 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[4] ^~ r_LFSR[3]; 66 end 67 5: begin 68 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[5] ^~ r_LFSR[3]; 69 end 70 6: begin 71 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[6] ^~ r_LFSR[5]; 72 end 73 7: begin 74 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[7] ^~ r_LFSR[6]; 75 end 76 8: begin 77 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[8] ^~ r_LFSR[6] ^~ r_LFSR[5] ^~ r_LFSR[4]; 78 end 79 9: begin 80 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[9] ^~ r_LFSR[5]; 81 end 82 10: begin 83 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[10] ^~ r_LFSR[7]; 84 end 85 11: begin 86 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[11] ^~ r_LFSR[9]; 87 end 88 12: begin 89 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[12] ^~ r_LFSR[6] ^~ r_LFSR[4] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; 90 end 91 13: begin 92 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[13] ^~ r_LFSR[4] ^~ r_LFSR[3] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; 93 end 94 14: begin 95 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[14] ^~ r_LFSR[5] ^~ r_LFSR[3] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; 96 end 97 15: begin 98 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[15] ^~ r_LFSR[14]; 99 end 100 16: begin 101 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[16] ^~ r_LFSR[15] ^~ r_LFSR[13] ^~ r_LFSR[4]; 102 end 103 17: begin 104 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[17] ^~ r_LFSR[14]; 105 end 106 18: begin 107 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[18] ^~ r_LFSR[11]; 108 end 109 19: begin 110 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[19] ^~ r_LFSR[6] ^~ r_LFSR[2] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; 111 end 112 20: begin 113 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[20] ^~ r_LFSR[17]; 114 end 115 21: begin 116 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[21] ^~ r_LFSR[19]; 117 end 118 22: begin 119 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[22] ^~ r_LFSR[21]; 120 end 121 23: begin 122 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[23] ^~ r_LFSR[18]; 123 end 124 24: begin 125 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[24] ^~ r_LFSR[23] ^~ r_LFSR[22] ^~ r_LFSR[17]; 126 end 127 25: begin 128 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[25] ^~ r_LFSR[22]; 129 end 130 26: begin 131 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[26] ^~ r_LFSR[6] ^~ r_LFSR[2] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; 132 end 133 27: begin 134 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[27] ^~ r_LFSR[5] ^~ r_LFSR[2] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; 135 end 136 28: begin 137 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[28] ^~ r_LFSR[25]; 138 end 139 29: begin 140 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[29] ^~ r_LFSR[27]; 141 end 142 30: begin 143 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[30] ^~ r_LFSR[6] ^~ r_LFSR[4] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; 144 end 145 31: begin 146 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[31] ^~ r_LFSR[28]; 147 end 148 32: begin 149 r_XNOR = r_LFSR[32] ^~ r_LFSR[22] ^~ r_LFSR[2] ^~ r_LFSR[1]; 150 end 151 152 endcase // case (NUM_BITS) 153 end // always @ (*) 154 155 156 assign o_LFSR_Data = r_LFSR[NUM_BITS:1]; 157 158 // Conditional Assignment (?) 159 //一个循坏结束,数据个数2^NUM_BITS -1 160 assign o_LFSR_Done = (r_LFSR[NUM_BITS:1] == i_Seed_Data) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0; 161 162 endmodule // LFSR
`timescale 1ns / 100ps `define N_BITS 4 module tb_lfsr; reg i_Clk; reg i_Enable; // Optional Seed Value reg i_Seed_DV; reg [`N_BITS-1:0] i_Seed_Data; wire [`N_BITS-1:0] o_LFSR_Data; wire o_LFSR_Done; LFSR #(.NUM_BITS(`N_BITS)) dut( .i_Clk(i_Clk), .i_Enable(i_Enable), .i_Seed_DV(i_Seed_DV), .i_Seed_Data(i_Seed_Data), .o_LFSR_Data(o_LFSR_Data), .o_LFSR_Done(o_LFSR_Done)); always #10 i_Clk = ~i_Clk; initial begin i_Clk = 0; i_Enable = 0; i_Seed_DV = 0; i_Seed_Data = 0; #15; i_Enable = 1; i_Seed_DV = 1; @(posedge i_Clk); #5; i_Seed_DV = 0; end endmodule
//参考程序地址:http://www.nandland.com/verilog/modules/code/LFSR.v