2018年存在我手机里的这2张图片
图片来自这篇博客
图片
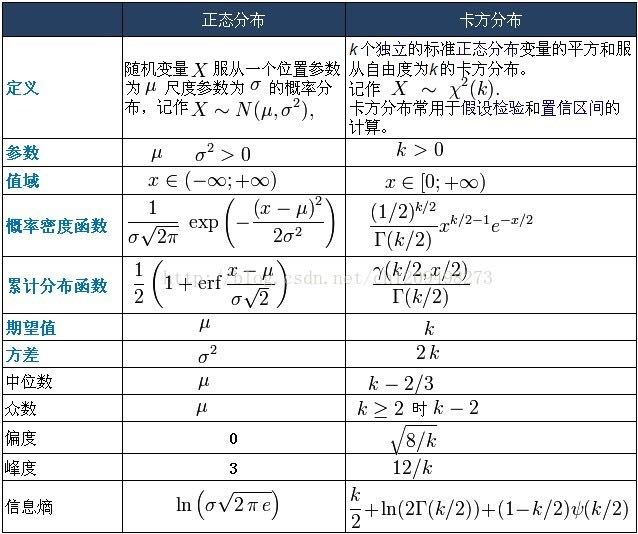
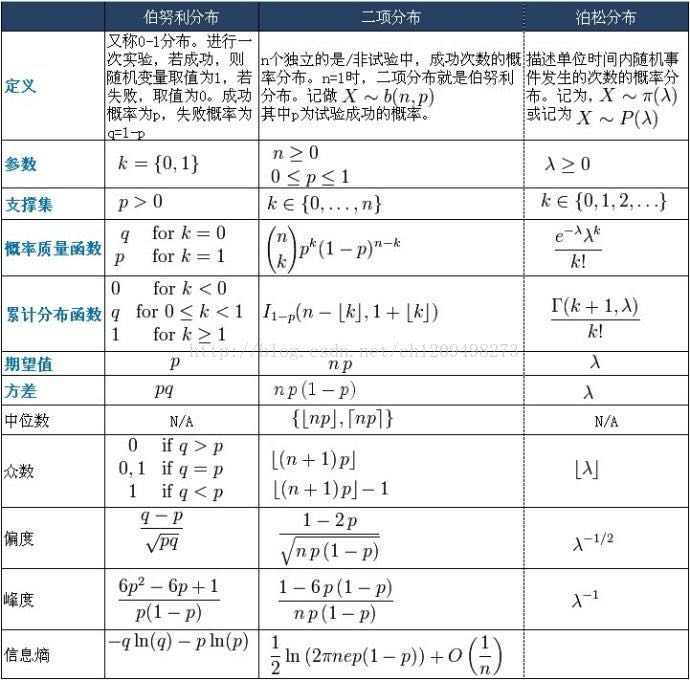
一些概念
偏度
皮尔逊偏度系数把偏度定义为
[ ilde{mu}_{3}=mathrm{E}left[left(frac{X-mu}{sigma}
ight)^{3}
ight]=frac{mu_{3}}{sigma^{3}}=frac{mathrm{E}left[(X-mu)^{3}
ight]}{left(mathrm{E}left[(X-mu)^{2}
ight]
ight)^{3 / 2}}=frac{kappa_{3}}{kappa_{2}^{3 / 2}}
]
其中(kappa_i)是累积量
Skewness indicates the direction and relative magnitude of a distribution's deviation from the normal distribution.
PDF曲线面积一半对应的位置
众数 mode
PDF曲线最大值对应的位置
峰度
皮尔逊峰度系数把峰度(kurtosis)定义为
[operatorname{Kurt}[X]=mathrm{E}left[left(frac{X-mu}{sigma}
ight)^{4}
ight]=frac{mathrm{E}left[(X-mu)^{4}
ight]}{left(mathrm{E}left[(X-mu)^{2}
ight]
ight)^{2}}=frac{mu_{4}}{sigma^{4}}
]
峰度是描述总体中所有取值分布形态陡缓程度的统计量。 这个统计量需要与正态分布相比较,峰度为3表示该总体数据分布与正态分布的陡缓程度相同;峰度大于3表示该总体数据分布与正态分布相比较为陡峭,为尖顶峰;峰度小于3表示该总体数据分布与正态分布相比较为平坦,为平顶峰。
信息熵
连续分布 (应该叫做差熵)
[h(X)=-int p(x) ext{log}(p(x))dx
]
离散分布
[H(X)=-sumlimits_{i}[p_i(x) ext{log}(p_i(x))]
]
PDF
probability density function概率密度函数(f(x))
或者叫 probability mass function
CDF
累计分布函数 cumulative distribution function
[F(x)=P(Xleq x )
]
the survivor function
[S(x)=P(Xgeq x)
]
the hazard function
[h(x)=frac{f(x)}{S(x)}
]
the cumulative hazard funciton
符号别和信息熵弄混了。。。
[H(x)=-ln S(x)
]
the moment generating function矩生成函数 MGF
随机变量(X)的矩生成函数定义为
[M(t)=E[e^{tX}]
]
矩生成函数可用于计算分布的矩:
[�egin{aligned}
M_{X}(t)=mathrm{E}left(e^{t X}
ight) &=1+t mathrm{E}(X)+frac{t^{2} mathrm{E}left(X^{2}
ight)}{2 !}+frac{t^{3} mathrm{E}left(X^{3}
ight)}{3 !}+cdots+frac{t^{n} mathrm{E}left(X^{n}
ight)}{n !}+cdots \
&=1+t m_{1}+frac{t^{2} m_{2}}{2 !}+frac{t^{3} m_{3}}{3 !}+cdots+frac{t^{n} m_{n}}{n !}+cdots
end{aligned}
]
the characteristic function特征函数 CF
随机变量(X)的特征函数定义为
[Phi(t)=E[e^{jtX}]
]
在概率论和统计学中,任何实值随机变量的特征函数完全定义了其概率分布。
[left{�egin{array}{l}
varphi_{X}: mathbb{R}
ightarrow mathbb{C} \
varphi_{X}(t)=mathrm{E}left[e^{i t X}
ight]=int_{mathbb{R}} e^{i t x} d F_{X}(x)=int_{mathbb{R}} e^{i t x} f_{X}(x) d x
end{array}
ight.
]
[f_{X}(x)=frac{1}{2pi}int_{mathbb{R}}varphi_X(t)e^{-jtx}dt
]
利用随机变量X的特征函数CF求X的k阶矩
[mathrm{E}left[X^{k}
ight]=i^{-k} varphi_{X}^{(k)}(0)
]
[mathrm{E}left[X^{1}
ight]=i^{-1} varphi_{X}^{(1)}(0)=-j varphi_{X}^{(1)}(0)
]
[mathrm{E}left[X^{2}
ight]=i^{-2} varphi_{X}^{(2)}(0)=-varphi_{X}^{(2)}(0)
]
例子
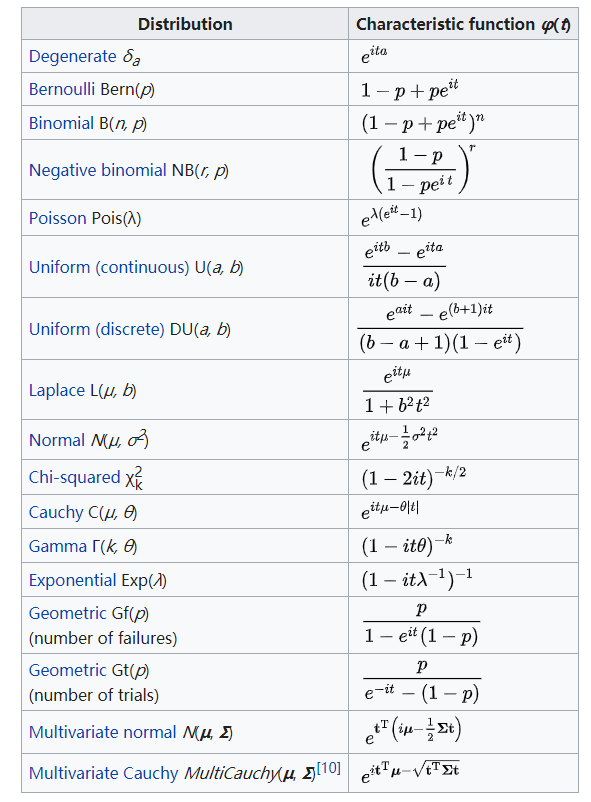
这个积分建议背一下
[intlimits_{-infty}^{infty} e^{i t x} frac{1}{sqrt{2pi}sigma} e^{-frac{(x-mu)^2}{2sigma^2}} d x=e^{i t mu-frac{1}{2} sigma^{2} t^{2}}
]
inverse distribution
逆分布是随机变量的倒数服从的分布
让随机变量(Y=frac{1}{X})
[G(y)=operatorname{Pr}(Y leq y)=operatorname{Pr}left(X geq frac{1}{y}
ight)=1-operatorname{Pr}left(X<frac{1}{y}
ight)=1-Fleft(frac{1}{y}
ight)
]
式子两边再对(y)求导
[g(y)=frac{1}{y^{2}} fleft(frac{1}{y}
ight)
]
正交、不相关、独立
首先拿随机变量举例子
从上往下分别是:正交、不相关、独立
[E[XY]=0\
Cov[X,Y]=E[XY]-E[X]E[Y]=0quad ext{i.e.} quad
ho_{XY}=frac{Cov[X,Y]}{sigma_Xsigma_Y}=0\
p_{XY}(x,y)=p_X(x)p_Y(y)
]
下面拿随机过程为例子

常见的概率分布总结及它们间的联系
http://www.math.wm.edu/~leemis/chart/UDR/UDR.html
APPL: A Probability Programming Language
http://www.math.wm.edu/~leemis/2001amstat.pdf
http://mtholyoke.edu/~mpeterso/classes/math342/appl.html



