一.异常的分类
1.由Java虚拟机抛出的异常(Error):程序无法处理的问题,用户不用去进行处理(虚拟机错误丶内存溢出错误丶线程死锁)
2.Exception异常:程序本身可以进行处理的异常
1.非检查异常(Unchecked Exception):编译器不需要强制处理的异常(空指针异常丶数组下标越界异常丶算数异常丶类型转换异常)
2.检查异常(checked Exception):编译器需要强制处理的异常(IOException丶SQLException)
二.异常处理的两种方法
1.通过try丶catch和finally关键字在当前位置进行异常处理
public static void main(String[] a){ int sum = 0; while(true){ try { //以两数相除除数不能为0进行举例 System.out.println("请依次输入两个数值进行除法操作:"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); int one =scanner.nextInt(); int two =scanner.nextInt(); sum = one/two; System.out.println("最终结果为:"+sum); } catch (Exception e) { //用catch将错误进行捕捉,这里可以使用多重catch,对于不同的错误进行捕捉,但最后的catch建议为Exception。 // TODO Auto-generated catch block //显示错误堆栈信息 e.printStackTrace(); }finally{
System.out.print("无论有没有错误我都会执行");
} } } }
输出:

2.通过try丶catch丶finally丶throw和throws抛出异常给函数调用者进行处理
public class Try {
public static void main(String[] a){
try{
Function(); //在函数调用者处对异常进行处理
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static void Function() throws Exception{ //通过throws将异常进行抛出
System.out.println("请输入一个数值进行判断:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int one =scanner.nextInt();
if(one<100)
{
throw new Exception(); //若输入的数值小于100则抛出异常
}
}
}
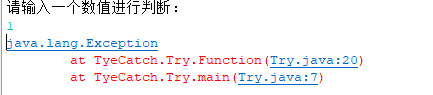
输出:
3.自定义异常进行处理
class MyException extends Exception{ //自定义异常,通过super方法传递异常信息给父级
public MyException(){
super("这是我自定义的异常");
}
}
public class Try {
public static void main(String[] a){
try{
Function();
}catch(MyException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static void Function() throws MyException{
System.out.println("请输入一个数值进行判断:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int one =scanner.nextInt();
if(one<100)
{
throw new MyException(); //将自定义异常进行抛出
}
}
}
输出:

三.异常链
有的时候我们会在处理一个异常的时候抛出一个新的异常,也就是异常的嵌套,但是最后我们得到的异常信息却只有一个。
示例:
public class Try {
public static void main(String[] a){
try{
Function1();
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static void Function1() throws Exception{
try{
Function2();
}catch(Exception e){
throw new Exception();
}
}
static void Function2() throws Exception{
try{
Function3();
}catch(Exception e){
throw new Exception();
}
}
static void Function3() throws Exception{
throw new Exception();
}
}
输入结果:

这样的话显示出的异常就只有一个了,那我们如果想让这条异常链中的所有异常信息全部输出该怎么办呢?方法很简单,我们在抛出异常的时候将异常对象也当作参数进行抛出就行了。
示例:
public class Try {
public static void main(String[] a){
try{
Function1();
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static void Function1() throws Exception{
try{
Function2();
}catch(Exception e){
throw new Exception("异常2",e);
}
}
static void Function2() throws Exception{
try{
Function3();
}catch(Exception e){
throw new Exception("异常2",e);
}
}
static void Function3() throws Exception{
throw new Exception("异常3");
}
}
运行结果:

到此,我们Java中的异常便是描述完了。