1、nextTick调用方法
首先看nextTick的调用方法:
https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#Vue-nextTick
// 修改数据
vm.msg = 'Hello'
// DOM 还没有更新
Vue.nextTick(function () {
// DOM 更新了
})
// 作为一个 Promise 使用 (2.1.0 起新增,详见接下来的提示)
Vue.nextTick()
.then(function () {
// DOM 更新了
})
即:既可以支持回调函数,也可以支持then方法(即Promise)。
2、vue nextTick源码分析
https://github.com/vuejs/vue/blob/dev/src/core/util/next-tick.js
核心代码--nextTick函数:
export function nextTick (cb?: Function, ctx?: Object) {
let _resolve
callbacks.push(() => {
if (cb) {
try {
cb.call(ctx)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick')
}
} else if (_resolve) {
_resolve(ctx)
}
})
if (!pending) {
pending = true
if (useMacroTask) {
macroTimerFunc()
} else {
microTimerFunc()
}
}
// $flow-disable-line
if (!cb && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
return new Promise(resolve => {
_resolve = resolve
})
}
}
更核心的代码:
if (!pending) {
pending = true
if (useMacroTask) {
macroTimerFunc()
} else {
microTimerFunc()
}
}
即:nextTick既可以是宏任务,又可以是微任务!
接着看微任务的定义:
// Determine microtask defer implementation.
/* istanbul ignore next, $flow-disable-line */
if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) {
const p = Promise.resolve()
microTimerFunc = () => {
p.then(flushCallbacks)
// in problematic UIWebViews, Promise.then doesn't completely break, but
// it can get stuck in a weird state where callbacks are pushed into the
// microtask queue but the queue isn't being flushed, until the browser
// needs to do some other work, e.g. handle a timer. Therefore we can
// "force" the microtask queue to be flushed by adding an empty timer.
if (isIOS) setTimeout(noop)
}
} else {
// fallback to macro
microTimerFunc = macroTimerFunc
}
即:vue环境支持Promis的话,使用Promise。否则microTimerFunc 被定义为宏任务macroTimerFunc。
接着看macroTimerFunc的定义:
// Determine (macro) task defer implementation.
// Technically setImmediate should be the ideal choice, but it's only available
// in IE. The only polyfill that consistently queues the callback after all DOM
// events triggered in the same loop is by using MessageChannel.
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) {
macroTimerFunc = () => {
setImmediate(flushCallbacks)
}
} else if (typeof MessageChannel !== 'undefined' && (
isNative(MessageChannel) ||
// PhantomJS
MessageChannel.toString() === '[object MessageChannelConstructor]'
)) {
const channel = new MessageChannel()
const port = channel.port2
channel.port1.onmessage = flushCallbacks
macroTimerFunc = () => {
port.postMessage(1)
}
} else {
/* istanbul ignore next */
macroTimerFunc = () => {
setTimeout(flushCallbacks, 0)
}
}
优先使用setImmediate(只有ie浏览器10以上支持),其次是MessageChannel,最后是setTimeout。以上三个都属于宏任务。
HTML5中规定setTimeout的最小时间延迟是4ms,也就是说理想环境下异步回调最快也是4ms才能触发。Vue使用这么多函数来模拟异步任务,其目的只有一个,就是让回调异步且尽早调用。而 MessageChannel 和 setImmediate 的延迟明显是小于 setTimeout的。
$nextTick属于宏任务还是微任务,你会了吗?
3、那什么时候使用宏任务,什么时候使用微任务呢?
在 Vue 2.4 之前都是使用的
microtasks(微任务),但是 microtasks 的优先级过高,在某些情况下可能会出现比事件冒泡更快的情况,但如果都使用 macrotasks(宏任务) 又可能会出现渲染的性能问题。所以在新版本中,会默认使用 microtasks,但在特殊情况下会使用 macrotasks。比如 v-on。下图是使用v-on时,源码调试截图:
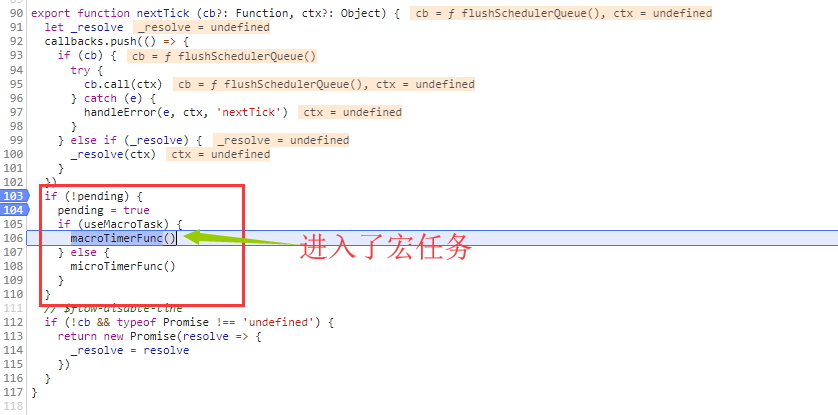
在chrome下使用了MessageChannel实现的宏任务。

4、宏任务和微任务执行顺序
for (macroTask of macroTaskQueue) {
// 1. Handle current MACRO-TASK
handleMacroTask();
// 2. Handle all MICRO-TASK
for (microTask of microTaskQueue) {
handleMicroTask(microTask);
}
}
