1.线程的创建
新建线程通常分为两种:带参数的线程和不带参数的线程,不过建立起来都很简单:
//不带参数 public static void SetUpThread() { Thread t = new Thread(new ThreadStart(() => { Console.WriteLine("====="); })); t.Start(); } //带参数 public static void SetupParameterThread(string id) { Thread t = new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(obj=> { var tmp = Convert.ToString(obj); Console.WriteLine("The parameter is:{0}",tmp); })); t.Start(id); }
Main:static void Main(string[] args) { SetUpThread(); SetupParameterThread("Jack");//传入参数Jack Console.Read(); }
Console:
2.线程等待
在多线程运行中,比如有2个线程A和B,有时候需要A线程停下来,把CPU资源让给B线程,让B线程先执行,这就需要A线程的暂停等待了:
Thread tA = new Thread(()=> { Thread.Sleep(1000); Console.WriteLine("Thread A is running"+DateTime.Now); }); Thread tB = new Thread(() => { Console.WriteLine("Thread B is running"+DateTime.Now); }); tA.Start(); tB.Start();
A线程调用Thread.Sleep(1000); 进入休眠状态,这时候系统就执行B线程,所以可以看到B线程先执行完,等待1s然后A线程继续执行:
Console:
3.线程的终止
当线程运行的时候,有时候必要的要把线程抛弃终止,则需要调用Abort方法:
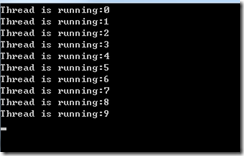
public static void ThreadAbort() { Thread t = new Thread(() => { for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) { if (i >= 10) Thread.CurrentThread.Abort(); Console.WriteLine("Thread is running:"+i); } }); t.Start(); }
本例在i为10的时候终止线程,线程不会在继续执行余下的20次循环:
4.线程状态
在线程执行过程中,我们可以查看线程的状态
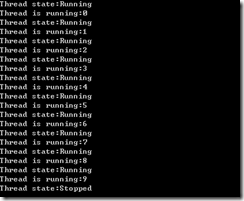
public static void ThreadStates() { Thread t = new Thread(()=> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { var state = Thread.CurrentThread.ThreadState; Console.WriteLine("Thread state:"+state); Console.WriteLine("Thread is running:" + i); } }); t.Start(); t.Join(); Console.WriteLine("Thread state:" + t.ThreadState); }
从结果就看到线程的状态,有时候还可以通过属性 IsAlive来检测线程是否还存活
5.线程的调度
多线程编程中,线程的调度是很常见的,特别是有的线程需要另外一个线程的执行结果作为参数,这时候线程的调度就体现出来了,假设AB两线程,线程A的参数为B的执行结果:
public static void Threaddispatch() { int sharedValue = 10; Thread tb = new Thread(()=> { Console.WriteLine("Thread B is launched"); sharedValue += 20;//对sharedValue 进行加法计算 }); Thread ta = new Thread((obj) => { Console.WriteLine("Thread A is launched"); var arg = Convert.ToInt32(obj); arg += 10; Console.WriteLine("the calculation is:{0}",arg); }); tb.Start(); tb.Join(); ta.Start(sharedValue); //传入线程B计算的结果 }
线程启动后,线程A等待线程B的计算完成,线程B计算完结果sharedValue为30,然后此寄过作为参数直接启动线程A进行最后的计算:
6.线程的优先级
在多线程系统中,在线程并发执行的过程中,需要赋予线程相应的优先级级别,这样优先级别高的线程这同样的系统资源准备下,可以获得优先执行的权利:
可以通过线程的属性Priority来设置线程的优先级;
public enum ThreadPriority { Lowest = 0, BelowNormal = 1, Normal = 2, AboveNormal = 3, Highest = 4 }
7.前台 后台线程
前台线程:在线程创建的时候默认是前台程序,即只有在前台程序结束后,程序才能结束;
后台线程:在程序结束的时候,如果只剩下后台线程,则后台线程将不会再继续执行,程序直接响应结束;
线程的前后台切换可以通过属性IsBackground来设置