JDBC(Java Data Base Connectivity,java数据库连接),由一些类和接口构成的API,它是J2SE的一部分,由java.sql,javax.sql包组成。
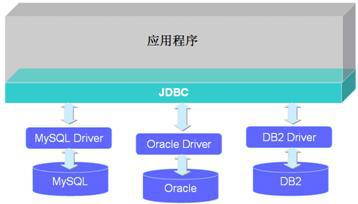
应用程序、JDBC API、数据库驱动及数据库之间的关系:
连接数据的步骤:
-
注册驱动 (只做一次)。
- 建立连接(Connection)。
-
创建执行SQL的语句(Statement)。
- 执行语句。
-
处理执行结果(ResultSet)。
- 释放资源。
快速起步示例:
导包(如果是使用eclipse等IDE工具,无须担心,只是要注意导入的是java.sql,javax.sql的类或接口)
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement;
static void test() throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException { //1.注册驱动 //DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver()); //System.setProperty("jdbc.drivers", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//将com.mysql.jdbc.Driver加载到虚拟机,推荐方式 //2.建立连接 /* * jdbc(协议名):子协议(mysql):子名称(无)//主机名:端口号(主机名:端口号可以缺省)/数据库名?属性名=属性值&.... */ String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc"; String user = "root"; String password = "yezi"; Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); //3.创建语句 Statement st = conn.createStatement(); //4.执行语句 ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery("select * from user"); //5.处理结果 while(rs.next()) { System.out.println(rs.getObject(1)+" "+rs.getObject(2)+ " "+rs.getObject(3)+" "+rs.getObject(4)); } //6.释放资源(注意顺序) rs.close(); st.close(); conn.close(); }
注册驱动(3种方式):
-
Class.forName(“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”);——将驱动类com.mysql.jdbc.Driver加载到虚拟机中。推荐这种方式,不会对具体的驱动类产生依赖。
- DriverManager.registerDriver(com.mysql.jdbc.Driver);——会造成DriverManager中产生两个一样的驱动,并会对具体的驱动类产生依赖。
-
System.setProperty(“jdbc.drivers”, “driver1:driver2”);——虽然不会对具体的驱动类产生依赖,但注册不太方便,所以很少使用。
建立连接:
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
url格式:
JDBC:子协议:子名称//主机名:端口/数据库名?属性名=属性值&…
user,password可以用“属性名=属性值”方式告诉数据库。
其他参数如:useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=GBK。
释放资源:
释放ResultSet, Statement,Connection。
数据库连接(Connection)是非常稀有的资源,用完后必须马上释放,如果Connection不能及时正确的关闭将导致系统宕机(?)。Connection的使用原则是尽量晚创建,尽量早的释放。
以上代码还需要进行优化,优化后的代码如下:
首先建立一个工具类(JdbcUtils),用于注册驱动、建立连接、释放资源:
public final class JdbcUtils { private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc"; private static String user = "root"; private static String password = "yezi"; private JdbcUtils() { } /* * 静态代码块 * 随着类的加载而执行,只执行一次,并优先于主函数。用于给类进行初始化。 */ static { try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e); } } public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { return DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); } public static void free(ResultSet rs, Statement st, Connection conn) { //比较规范的释放方式,比较麻烦 try { if(rs != null) rs.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if(st != null) st.close(); } catch(SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(conn != null) try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
/* * JDBC访问数据库的模板 */ static void template() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //2.建立连接 conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); //单例模式 //conn = JdbcUtilsSing.getInstance().getConnection(); //3.创建语句 st = conn.createStatement(); //4.执行语句 rs = st.executeQuery("select * from user"); //5.处理结果 while(rs.next()) { System.out.println(rs.getObject(1)+" "+rs.getObject(2)+ " "+rs.getObject(3)+" "+rs.getObject(4)); } } finally { JdbcUtils.free(rs, st, conn); } }
当然还可以使用单例模式(开发原则:定义单例,建议使用饿汉式)来建立连接。
只要在JdbcUtils类中加入以下三句(懒汉式在此就不赘述):
private static JdbcUtilsSing instance = new JdbcUtilsSing(); private JdbcUtilsSing() { } public static JdbcUtilsSing getInstance() { return instance; }
基本的CRUD(创建、读取、更新、删除)模板代码:
增加对应SQL的INSERT,返回增加成功的行(记录)数 。
更新(修改)对应SQL的UPDATE,返回被修改的行(记录)数。
删除对应SQL的DELETE,返回被删除的行(记录)数 。
public class CRUD { public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { //create(); //read(); //update(); delete(); } static void create() throws SQLException { Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //2.建立连接 conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); //3.创建语句 st = conn.createStatement(); //4.执行语句 String sql = "insert into user (name,birthday,money) values ('name1','1987-01-01',400)"; int i = st.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println("i="+i); } finally { JdbcUtils.free(rs, st, conn); } } static void read() throws SQLException { Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //2.建立连接 conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); //3.创建语句 st = conn.createStatement(); //4.执行语句 rs = st.executeQuery("select id,name,birthday,money from user"); //5.处理结果 while(rs.next()) { System.out.println(rs.getObject("id")+" "+rs.getObject("name")+ " "+rs.getObject("birthday")+" "+rs.getObject("money")); } } finally { JdbcUtils.free(rs, st, conn); } } static void update() throws SQLException { Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //2.建立连接 conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); //3.创建语句 st = conn.createStatement(); //4.执行语句 String sql = "update user set money = money + 10"; int i = st.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println("i="+i); } finally { JdbcUtils.free(rs, st, conn); } } static void delete() throws SQLException { Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //2.建立连接 conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); //3.创建语句 st = conn.createStatement(); //4.执行语句 String sql = "delete from user where id > 4"; int i = st.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println("i="+i); } finally { JdbcUtils.free(rs, st, conn); } } }
CRUD总结:
增、删、改用Statement.executeUpdate来完成,返回整数(匹配的记录数),这类操作相对简单。
查询用Statement.executeQuery来完成,返回的是ResultSet对象,ResultSet中包含了查询的结果;查询相对于增、删、改要复杂一些,因为有查询结果要处理。
SQL注入,PreparedStatement和Statement
在SQL中包含特殊字符或SQL的关键字(如:' or 1 or ')时Statement将出现不可预料的结果(出现异常或查询的结果不正确),可用PreparedStatement来解决。
PreperedStatement(从Statement扩展而来)相对Statement的优点:
- 没有SQL注入的问题。
- Statement会使数据库频繁编译SQL,可能造成数据库缓冲区溢出。
-
数据库和驱动可以对PreperedStatement进行优化(只有在相关联的数据库连接没有关闭的情况下有效)。
代码如下:
static void read(String name) throws SQLException { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //2.建立连接(最耗时) conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); //3.创建预处理sql语句,在构造时就给它sql语句 String sql = "select id,name,birthday,money from user where name = ?"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, name); //4.执行语句 //rs = ps.executeQuery(sql);//注意此次调用的是Statement接口里的方法 rs = ps.executeQuery(); //5.处理结果 while(rs.next()) { System.out.println(rs.getInt("id")+" "+rs.getString("name")+ " "+rs.getDate("birthday")+" "+rs.getFloat("money")); } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("read:"+(end-start)); } finally { JdbcUtils.free(rs, ps, conn); } }
JDBC读写日期类型
jdbc通常处于数据访问层,主要是和数据库打交道,所用到的一般日期类型都是java.sql.Date,而在业务层我们使用的日期类型一般都是java.util.Date。两者的关系是:java.sql.Date继承java.util.Date。我们在插入的时候传递的是java.util.Date,而ps.setDate()方法要求的是java.sql.Date,所以要进行一下转化。
例(insert):
static void create(String name, Date birthday, float money) throws SQLException { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //2.建立连接 conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); //3.创建语句 String sql = "insert into user (name,birthday,money) values (?,?,?)"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, name); /* * birthday.getTime()返回的是从1970-01-01 00:00:00到birthday的毫秒数 */ ps.setDate(2, new java.sql.Date(birthday.getTime())); ps.setFloat(3, money); //4.执行语句 int i = ps.executeUpdate(); System.out.println("i="+i); } finally { JdbcUtils.free(rs, ps, conn); } }
例(read):
static Date read(int id) throws SQLException { Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet rs = null; Date birthday = null; try { //2.建立连接 conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); //3.创建语句 st = conn.createStatement(); //4.执行语句 rs = st.executeQuery("select birthday from user where id = " + id); //5.处理结果 while(rs.next()) { //取值的时候是java.sql.Date赋值给一个父类类型java.util.Date是没有问题的 //birthday = rs.getDate("birthday");//输出2016-03-23 /* * 当然也可以像insert的时候那样转换一下 * 不过好麻烦,而且输出的没有格式化哟! */ birthday = new Date(rs.getDate("birthday").getTime());//输出Wed Mar 23 00:00:00 CST 2016 } return birthday; } finally { JdbcUtils.free(rs, st, conn); } }
JDBC读写Clob(大文本数据类型)
因为数据库产品不一样,所以表示大文本数据类型的字段也不一样,mysql:text,oracle:Clob。
写(insert):
public static void create() throws SQLException, IOException { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into clob_test (big_text) values (?)"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); File file = new File("src/cn/itcast/jdbc/CRUD.java"); BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); //使用字符流 ps.setCharacterStream(1, reader, file.length()); /* * 字符读取流将读取出来的文件放到一个String里 * 原因:String在java是没有大小限制的,关键是看你的内存大小 * ps.setString(1, x); */ int i = ps.executeUpdate(); System.out.println("i="+i); reader.close(); } finally { JdbcUtils.free(rs, ps, conn); } }
第1次读取时出现异常:java.sql.SQLException: Before start of result set(异常:在结果及开始之前)
public static void read(int id) throws SQLException, IOException { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "select big_text from clob_test where id = ?"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setInt(1, id); rs = ps.executeQuery();//---->java.sql.SQLException: Before start of result set(异常:在结果及开始之前) Clob clob = rs.getClob(1); File file = new File("CRUD_bak.java"); BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(clob.getCharacterStream()); BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file)); String line = null; while((line = bufr.readLine()) != null) { bufw.write(line); bufw.newLine(); bufw.flush(); } bufw.close(); bufr.close(); } finally { JdbcUtils.free(rs, ps, conn); } }
出现异常的原因:ResultSet对象代表SQL语句执行的结果集,维护指向其当前数据行的光标。每调用一次next()方法,光标向下移动一行。最初它位于第一行之前,因此第一次调用next()应把光标置于第一行上,使它成为当前行。随着每次调用next()将导致光标向下移动一行。在ResultSe对象及其父辈Statement对象关闭之前,光标一直保持有效。
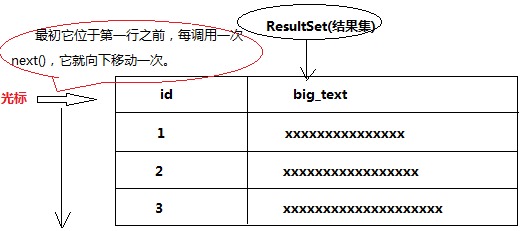
解决办法:使用rs取数据之前,一定要加上rs.next();语句。
public static void read(int id) throws SQLException, IOException { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "select big_text from clob_test where id = ?"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setInt(1, id); rs = ps.executeQuery(); while(rs.next()) { /* * 1.第一种方式 * Clob clob = rs.getClob(1); * BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(clob.getCharacterStream()); */ //Clob clob = rs.getClob(1); //BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(clob.getCharacterStream()); /* * 2.第二种方式,显然这种方式更简单 * BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(rs.getCharacterStream(1)); */ BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(rs.getCharacterStream(1)); /* * 3.第三种方式 * String str = rs.getString(1); */ File file = new File("CRUD_bak.java"); BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file)); String line = null; while((line = bufr.readLine()) != null) { bufw.write(line); bufw.newLine(); bufw.flush(); } bufw.close(); bufr.close(); } } finally { JdbcUtils.free(rs, ps, conn); } }
JDBC读写Blob(大字节数据类型)
写(insert):
public static void create() throws SQLException, IOException { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "insert into blob_test (big_bit) values (?)"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); File file = new File("guan.jpg"); BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream(file)); ps.setBinaryStream(1, in, file.length()); int i = ps.executeUpdate(); in.close(); System.out.println("i="+i); } finally { JdbcUtils.free(rs, ps, conn); } }
读(read):
public static void read(int id) throws SQLException, IOException { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); String sql = "select big_bit from blob_test where id = ?"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setInt(1, id); rs = ps.executeQuery(); while(rs.next()) { /* * 1.第一种方式 * Blob blob = rs.getBlob(1); * BufferedInputStream bfIn = new BufferedInputStream(blob.getBinaryStream()); */ //Blob blob = rs.getBlob(1); //BufferedInputStream bfIn = new BufferedInputStream(blob.getBinaryStream()); /* * 2.第二种方式 * */ BufferedInputStream bfIn = new BufferedInputStream(rs.getBinaryStream(1)); BufferedOutputStream bfOut = new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream(new File("guan_bak.jpg"))); byte[] buff = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; while((len = bfIn.read(buff)) != -1) { bfOut.write(buff, 0, len); } bfOut.close(); bfIn.close(); } } finally { JdbcUtils.free(rs, ps, conn); } }