咕bye 2018,因为我这场又咕咕咕了
时间过得真快啊
A.New Year and the Christmas Ornament
分类讨论后等差数列求和

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 int a,b,c; 6 int main() 7 { 8 scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c); 9 printf("%d",min(min((a+1)*3,b*3),(c-1)*3)); 10 return 0; 11 }
B.New Year and the Treasure Geolocation
坐标分别加起来除个$n$,没了

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 long long n,a,b,t1,t2; 6 int main() 7 { 8 scanf("%lld",&n); 9 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%lld%lld",&t1,&t2),a+=t1,b+=t2; 10 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%lld%lld",&t1,&t2),a+=t1,b+=t2; 11 printf("%lld %lld",a/n,b/n); 12 return 0; 13 }
C.New Year and the Sphere Transmission
分解因数后变成了等差数列求和

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int N=1000005; 6 int n,cnt,facs[N]; 7 long long ans[N]; 8 int gcd(int a,int b) 9 { 10 return b?gcd(b,a%b):a; 11 } 12 int main() 13 { 14 scanf("%d",&n); 15 for(int i=1;i*i<=n;i++) 16 if(n%i==0) 17 { 18 facs[++cnt]=i; 19 if(i*i!=n) 20 facs[++cnt]=n/i; 21 } 22 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 23 { 24 int g=gcd(facs[i],n),tot=n/g; 25 ans[i]=1ll*(n-g+2)*tot/2; 26 } 27 sort(ans+1,ans+1+cnt); 28 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 29 printf("%lld ",ans[i]); 30 return 0; 31 }
D.New Year and the Permutation Concatenation
不错的题
考虑容斥,计算不合法的方案数,这里我们要讲一讲如何实现next_permutation,是这样的:
以 1 3 5 4 2 为例
1.从序列末尾向前扫,直到一个位置pos序列开始下降 1 3 5 4 2
2.从后面这段递减的序列里找到第一个大于*pos的数,将pos位置的数与它交换 1 4 5 3 2
3.排序— —即翻转后面这段原来递减的序列 1 4 2 3 5
这样我们发现后面原来长度为n-pos的这段递减的序列被破坏了,而它原来是可以跟后面的一个排列配对的
那么显然对每个长度$len$统计有长度为$len$的递减序列的排列去掉即可(除了一种情况— —len==n,这时候没有排列能和它配对)
这样一来对每个$len$前$n-len$个可以随便排,后面$len$个又有$C_n^{len}$种选法,所以总方案数就是$sumlimits_{len=1}^{n-1}frac{n!}{len!}$,然后从总数里把这个容斥掉即可

1 #include<cstdio> 2 const int N=1000005,mod=998244353; 3 int n,x,y,ans,fac[N],inv[N]; 4 void exGCD(int &x,int &y,int a,int b) 5 { 6 if(!b) x=1,y=0; 7 else exGCD(y,x,b,a%b),y-=a/b*x; 8 } 9 int Inv(int nm,int md) 10 { 11 exGCD(x,y,nm,md); 12 return (x%md+md)%md; 13 } 14 int main() 15 { 16 scanf("%d",&n),fac[0]=inv[0]=1; 17 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) fac[i]=1ll*fac[i-1]*i%mod; 18 inv[n]=Inv(fac[n],mod),ans=1ll*n*fac[n]%mod; 19 for(int i=n-1;i;i--) inv[i]=1ll*inv[i+1]*(i+1)%mod; 20 for(int i=1;i<=n-1;i++) ans-=1ll*fac[n]*inv[i]%mod,ans=(ans+mod)%mod; 21 printf("%d",ans); 22 return 0; 23 }
E.New Year and the Acquaintance Estimation
观察样例/仔细分析/动手推理可以发现答案是一段隔2连续的区间!(我是第一种
所以只要求上下界就好了,怎么求呢?二分
怎么想到二分的呢?没想到,但是题目贴心地给了一个wiki的链接,里面有这样一个东西

这个定理可以在图的度数降序排好序的情况下检查图是否可行,这明摆着是告诉我们二分啊=。=
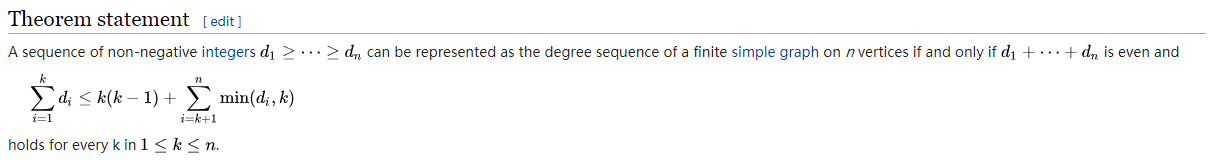
我们发现这个式子别的都好说,就是这个
$sumlimits_{i=k+1}^{n}min(d_i,k)$
边扫边维护还未出现过的度数小于当前的$k$的点数的和sum即可,说白了就是前缀和,然后每次用$n-i-sum$更新。为什么?因为这就是后面那个式子里$k$的的贡献的增加量(未出现过的大于等于$k$的数)
注意二分+检查之后偏移的方向

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<vector> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 const int N=500005; 7 int mem[N],tmp[N],bkt[N]; 8 int n,l,r,rd,ld,hd,sum,odd; 9 bool cmp(int a,int b) 10 { 11 return a>b; 12 } 13 int check(int x) 14 { 15 int p=0,pos=0; 16 memset(bkt,0,sizeof bkt); 17 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 18 { 19 if(mem[i]<x&&p<i) 20 pos=++p,tmp[pos]=x; 21 tmp[++p]=mem[i]; 22 } 23 if(!pos) pos=++p,tmp[pos]=x; 24 for(int i=1;i<=p;i++) bkt[tmp[i]]++; 25 long long lsum=0,rsum=0,fsum=0; 26 for(int i=1;i<=p;i++) 27 { 28 lsum+=tmp[i],bkt[tmp[i]]--; 29 rsum+=2*(i-1),rsum-=min(tmp[i],i-1); 30 fsum+=bkt[i-1],rsum+=n-i+1-fsum; 31 if(lsum>rsum) return i>=pos?1:-1; 32 } 33 return 0; 34 } 35 int main() 36 { 37 scanf("%d",&n); 38 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 39 scanf("%d",&mem[i]),sum+=mem[i]; 40 odd=sum%2,sort(mem+1,mem+1+n,cmp); 41 l=0,r=(n-odd)/2,ld=rd=-1; 42 while(l<=r) 43 { 44 int mid=(l+r)/2; 45 if(check(2*mid+odd)<0) l=mid+1; 46 else ld=mid,r=mid-1; 47 } 48 l=ld,r=(n-odd)/2; 49 while(l<=r) 50 { 51 int mid=(l+r)/2; 52 if(check(2*mid+odd)>0) r=mid-1; 53 else rd=mid,l=mid+1; 54 } 55 if(ld==-1||rd==-1) printf("-1"); 56 else for(int i=ld;i<=rd;i++) printf("%d ",2*i+odd); 57 return 0; 58 }
F.New Year and the Mallard Expedition

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 const int N=100005; 6 char mapp[N]; long long len[N]; 7 long long n,wat,spa,ans,sta; 8 int main() 9 { 10 scanf("%lld",&n); 11 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 12 scanf("%lld",&len[i]); 13 scanf("%s",mapp+1); 14 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 15 { 16 if(mapp[i]=='G') 17 { 18 ans+=len[i]*5; 19 spa+=len[i]*2; 20 sta+=len[i]; 21 } 22 else if(mapp[i]=='W') 23 { 24 wat=true; 25 ans+=len[i]*3; 26 sta+=len[i]; 27 } 28 else if(mapp[i]=='L') 29 { 30 if(sta<len[i]) 31 { 32 ans+=(wat?3:5)*(len[i]-sta); 33 sta=len[i]; 34 } 35 ans+=len[i]; 36 sta-=len[i]; 37 } 38 spa=min(spa,sta); 39 } 40 if(sta) ans-=sta+spa;//ans-=(5-1)*spa/2,ans-=(3-1)*(sta-spa)/2; 41 printf("%lld",ans); 42 return 0; 43 }
首先模拟,草地先走路,水里游泳,岩浆飞过去。在这个过程中我们记录一下是否遇到了水,因为如果遇到岩浆飞不过去的情况,需要在之间走来走去/游来游去积攒体力。模拟的同时记录一个“可以用飞行代替行走”的路程的消耗,这个东西步步和你的耐力取min,最后如果它小于耐力就把它代表的行走换成飞行,如果还剩下一些就把一些游泳也换成飞行
