package com.lanhuigu.nio.selector; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; import java.nio.channels.Selector; import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.util.Iterator; public class NIOServer { private Selector selector; public void initServer(int port) throws Exception { ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); // 设置通道为非阻塞 serverChannel.configureBlocking(false); serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port)); this.selector = Selector.open(); /* * 当事件到达的时候,selector.select()会返回, * 如果事件没有到达selector.select()会一直阻塞 */ SelectionKey selectionKey1 = serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);//感兴趣事件是16,准备好的事件是0。 int interestSet = selectionKey1.interestOps();//感兴趣事件是16 boolean isInterestedInAccept = (interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT) == SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT;//true int isInterestedInConnect = interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;//0 int isInterestedInRead = interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_READ;//0 int isInterestedInWrite = interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE;//0 int readySet = selectionKey1.readyOps();//0 } /** * 采用轮训的方式监听selector上是否有需要处理的事件,如果有,进行处理 */ public void listen() throws Exception { System.out.println("start server"); while (true) { // 当注册事件到达时,方法返回,否则该方法会一直阻塞 selector.select();//客户端条用connect方法接触阻塞。这个selector的channelArray数组里面绑定了一个ServerSocketChannelImpl和 n 个SocketChannel。接收客户端的事件,有连接事件和传递数据过来事件,就会解除阻塞分别调用Accept和read方法。 // 获得selector中选中的相的迭代器,选中的相为注册的事件 Iterator ite = this.selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (ite.hasNext()) { SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) ite.next();//客户端条用connect方法,key的感兴趣是16,准备好是16,不准备好select()就会一直阻塞, // 删除已选的key以防重负处理 ite.remove(); // 客户端请求连接事件 if (key.isAcceptable()) { ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();//接收连接的channel SocketChannel channel = server.accept();//处理客户端数据的channel // 设置成非阻塞 channel.configureBlocking(false); // 在这里可以发送消息给客户端 channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(new String("hello client").getBytes())); // 在客户端连接成功之后,为了可以接收到客户端的信息,需要给通道设置读的权限 SelectionKey selectionKey2 = channel.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); //这个selector绑定了2个channel,分别是服务端和客户端channel,分别关心OP_ACCEPT和OP_READ事件。 //这个客户端channel感兴趣是1准备好是0, int interestSet = selectionKey2.interestOps(); boolean isInterestedInAccept = (interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT) == SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT; int isInterestedInConnect = interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT; int isInterestedInRead = interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_READ; int isInterestedInWrite = interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE; int readySet = selectionKey2.readyOps(); // 获得了可读的事件 } else if (key.isReadable()) { read(key); } } } } private void read(SelectionKey key) throws Exception { // 服务器可读消息,得到事件发生的socket通道 SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); // 读取的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10); channel.read(buffer); byte[] data = buffer.array(); String msg = new String(data).trim(); System.out.println("server receive from client: " + msg); ByteBuffer outBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes()); channel.write(outBuffer); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable { NIOServer server = new NIOServer(); server.initServer(8989); server.listen(); } }
package com.lanhuigu.nio.selector; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; import java.nio.channels.Selector; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.util.Iterator; public class NIOClient { private Selector selector; public void initClient(String ip, int port) throws IOException { SocketChannel channel = SocketChannel.open(); // 设置通道为非阻塞 channel.configureBlocking(false); this.selector = Selector.open(); // 客户端连接服务器,其实方法执行并没有实现连接,需要在listen()方法中调用channel.finishConnect();才能完成连接 channel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(ip, port)); //channel连接通了,传统IO是连接上了之后就通过IO流来传输数据。服务端selector就会得到OP_ACCEPT事件select方法就会返回。 // 将通道管理器和该通道绑定,并为该通道注册SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT事件 SelectionKey selectionKey1 = channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT); // channel和selector绑定,这个selector关心这个channel的OP_CONNECT事件,selector的通道数组里面只有一个。 int interestSet = selectionKey1.interestOps();//感兴趣的是8,准备好的是0, boolean isInterestedInAccept = (interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT) == SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT;//false int isInterestedInConnect = interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;//8 int isInterestedInRead = interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_READ;//0 int isInterestedInWrite = interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE;//0 int readySet = selectionKey1.readyOps();//0 } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void listen() throws Exception { while (true) { /* * 选择一组可以进行I/O操作的事件,放在selector中,客户端的该方法不会阻塞, * selector的wakeup方法被调用,方法返回,而对于客户端来说,通道一直是被选中的 * 这里和服务端的方法不一样,查看api注释可以知道,当至少一个通道被选中时。 */ int I = selector.select();//OP_CONNECT事件已有,不会阻塞 // 获得selector中选中的项的迭代器 Iterator ite = this.selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (ite.hasNext()) { SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) ite.next(); // 删除已选的key,以防重复处理 ite.remove(); // 连接事件发生 if (key.isConnectable()) { // 如果正在连接,则完成连接 SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); if (channel.isConnectionPending()) {//该方法返回true表示连接成功 channel.finishConnect(); } // 设置成非阻塞 channel.configureBlocking(false); // 在这里可以给服务端发送信息哦 channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(new String("hello server!").getBytes())); // 在和服务端连接成功之后,为了可以接收到服务端的信息,需要给通道设置读的权限。 SelectionKey selectionKey2 = channel.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); // 获得了可读的事件,此时感兴趣是1准备好是8,selector数组里面还是只有一个SelectionKeyImpl //这个selctor关心这个channel的OP_READ和OP_CONNECT事件,并且只有这一个channel. int interestSet = selectionKey2.interestOps();//1 boolean isInterestedInAccept = (interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT) == SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT;//fasle int isInterestedInConnect = interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;//0 int isInterestedInRead = interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_READ;//1 int isInterestedInWrite = interestSet & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE;//0 int readySet = selectionKey2.readyOps(); } else if (key.isReadable()) { read(key); } } } } private void read(SelectionKey key) throws Exception { SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); // 分配缓冲区 ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10); channel.read(buffer); byte[] data = buffer.array(); String msg = new String(data).trim(); System.out.println("client receive msg from server:" + msg); ByteBuffer outBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes()); channel.write(outBuffer); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { NIOClient client = new NIOClient(); client.initClient("localhost", 8989); client.listen(); } }
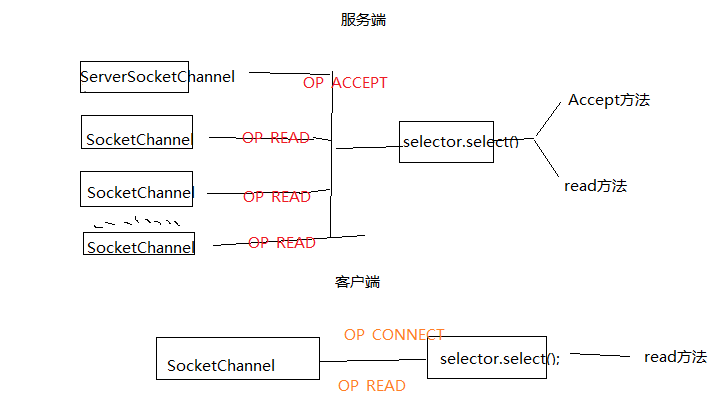
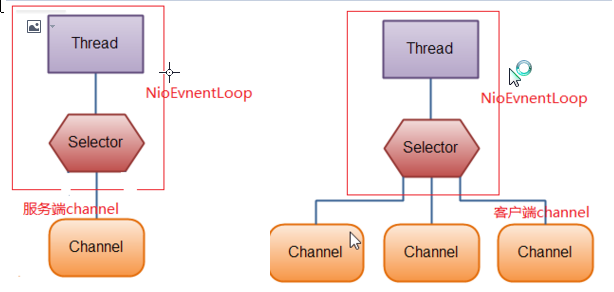
netty的服务端是有2个NioEventLoop,2个线程,2个selector的。 这里服务端只有一个selector既处理服务端channel也处理客户端channel。