Linux系统在启动的时候就已经启动了很多的进程信息。
root@ubuntu:/# ps -ef (系统启动就有了,相当于windows的服务)
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 1 0 0 04:27 ? 00:00:01 /sbin/init auto noprompt
root 4 2 0 04:27 ? 00:00:00 [kworker/0:0H]
root 6 2 0 04:27 ? 00:00:00 [mm_percpu_wq]
root 7 2 0 04:27 ? 00:00:00 [ksoftirqd/0]
root 8 2 0 04:27 ? 00:00:00 [rcu_sched]
守护进程是后台运行的,随着操作系统的启动而启动。相当于windows的服务。
守护进程分为2大类:1.系统级守护进程(硬件管理级的,登陆级的)。2.网络级的守护进程(蓝牙,拨号,web服务器,应用服务器,ftp服务器,邮件服务器,)。
(ps是查看进程信息)
root@ubuntu:/# ps -ef | grep init
root 1 0 0 04:27 ? 00:00:01 /sbin/init auto noprompt (init进程)
root 5177 5136 0 05:12 pts/2 00:00:00 grep --color=auto init (这个是当前查找进程)
root@ubuntu:/# ps -ef | grep ftp
root 1390 1 0 04:27 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/vsftpd /etc/vsftpd.conf (ftp进程)
root 5285 5136 0 05:16 pts/2 00:00:00 grep --color=auto ftp (这个是当前查找进程)
(pstree是查看守护进程信息,守护进程树)
root@ubuntu:/# pstree
(第一个运行的是systemd进程,)
systemd─┬─ManagementAgent───6*[{ManagementAgent}]
├─ModemManager─┬─{gdbus}
│ └─{gmain}
├─NetworkManager─┬─dnsmasq
│ ├─{gdbus}
│ └─{gmain}
├─VGAuthService
├─accounts-daemon─┬─{gdbus}
│ └─{gmain}
├─lightdm─┬─Xorg───{InputThread}
│ ├─lightdm─┬─upstart─┬─at-spi-bus-laun─┬─dbus-daemon
│ │ │ │ ├─{dconf worker}
│ │ │ │ ├─{gdbus}
│ │ │ │ └─{gmain}
│ │ │ ├─at-spi2-registr─┬─{gdbus}
│ │ │ │ └─{gmain}
├─rtkit-daemon───2*[{rtkit-daemon}]
├─snapd───6*[{snapd}]
├─systemd-timesyn───{sd-resolve}
├─systemd-udevd
├─udisksd─┬─{cleanup}
│ ├─{gdbus}
│ ├─{gmain}
│ └─{probing-thread}
├─upowerd─┬─{gdbus}
│ └─{gmain}
├─vmtoolsd───{vmtoolsd}
├─vmware-vmblock-───2*[{vmware-vmblock-}]
├─vsftpd
└─whoopsie─┬─{gdbus}
└─{gmain}
守护进程操作:
service crond stop
service crond start
service crond restart : 修改配置文件要重启。
service crond reload : 重新读取配置文件,进程不会停。
root@ubuntu:/# sysv-rc-conf (守护进程列表,相当于windows的服务列表,查看守护进程的启动方式)
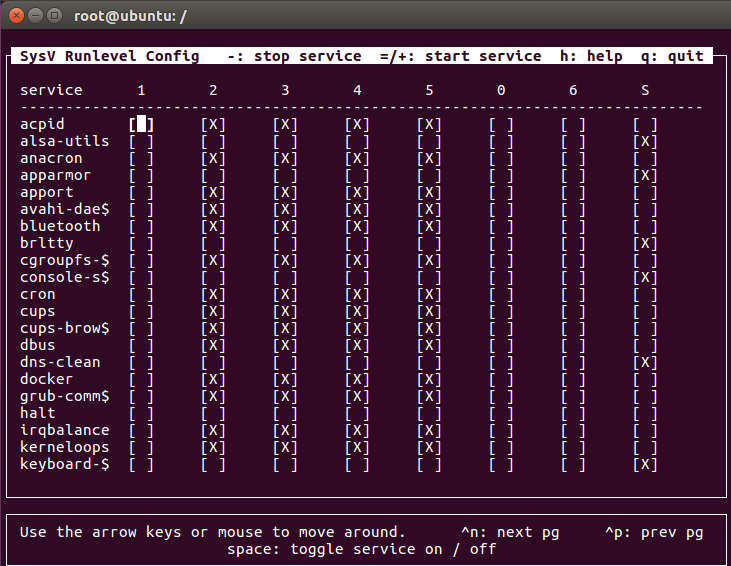
(0:关机,1:单用户,2: 多用户模式,没有NFS网络支持,3:多用户模式,有NFS,登录后进入控制台命令行模式,4:备用,自定义模式,5:有图形界面模式,6:重启)
(0,6是关机和重启,都是要关闭的。1是单用户不支持网络功能,所以网络功能的进程不需要启动,也会有一个功能限制,所以有些不启动。2,3,4,5可以随便定制)
root@ubuntu:/# sysv-rc-conf --list
acpid 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on
alsa-utils 0:off 1:off 6:off S:on
anacron 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on
apparmor S:on
apport 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on
avahi-daemon 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
bluetooth 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
brltty S:on
cgroupfs-mou 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
console-setu S:on
cron 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on
cups 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on
cups-browsed 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
dbus 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on
dns-clean S:on
docker 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
grub-common 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on
halt 0:off
irqbalance 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
kerneloops 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
keyboard-set S:on
root@ubuntu:/# man runlevel
┌─────────┬───────────────────┐
│Runlevel │ Target │
├─────────┼───────────────────┤
│0 │ poweroff.target │
├─────────┼───────────────────┤
│1 │ rescue.target │
├─────────┼───────────────────┤
│2, 3, 4 │ multi-user.target │
├─────────┼───────────────────┤
│5 │ graphical.target │
├─────────┼───────────────────┤
│6 │ reboot.target │
└─────────┴───────────────────┘
root@ubuntu:/# sysv-rc-conf --level 2345 crond off (把crond在2345模式下都设置成off)
root@ubuntu:/# sysv-rc-conf --list crond
crond 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off
root@ubuntu:/# sysv-rc-conf --level 213465 crond on (把crond全部设置成on)
root@ubuntu:/# sysv-rc-conf --list crond
crond 1:on 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:on
时间同步
windows服务器和linux服务器都有时钟同步,生产环境,需要经常与互联网时钟同步。windows每7天同步一次。
windows的时间只有一个系统时间。linux的时钟有2种,一种是系统时间,一种是硬件时钟。
yw1989@ubuntu:~$ date :系统时间
2018年 02月 15日 星期四 16:53:02 PST
yw1989@ubuntu:~$ time :硬件时钟,硬件时钟和系统时间不一致也会形成冲突。
real 0m0.000s
user 0m0.000s
sys 0m0.000s
root@ubuntu:/# hwclock :硬件时间,和系统时间一样的。
2018年02月15日 星期四 16时57分12秒 .337802 seconds
root@ubuntu:/# date -s '2018-02-16 08:59:00' :手动调整系统时间,硬件时钟没变。
2018年 02月 16日 星期五 08:59:00 PST
系统时间来源于硬件时钟,重启后系统时间又变了。
root@ubuntu:/# hwclock --systohc :系统时间同步到硬件时间
网络时间同步:安装ntp
root@ubuntu:/# ntpdate time.windows.com :同步
15 Feb 20:34:31 ntpdate[10354]: adjust time server 52.163.118.68 offset -0.033132 sec
root@ubuntu:/etc# vim ntp.conf
pool 0.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst :同步的时间服务器地址
pool 1.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
pool 2.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
pool 3.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst
(时间服务器的守护进程启动起来,并且加入开机启动服务)
root@ubuntu:/etc# service ntp start

