1、监听器实现
实现ApplicationListener接口:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
System.out.println("事件"+event);
}
}
使用@EventListener注解
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyServiceListener {
@EventListener(classes = ApplicationEvent.class)
public void myService(ApplicationEvent event){
System.out.println("MyServiceListener类接收事件:"+ event);
}
}
2、源码解析前需要了解的事件发布工具类:ApplicationEventMulticaster接口
ApplicationEventMulticaster接口的实现类可以管理大量ApplicationListener对象并向其发布事件。
相关方法:
void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener); (添加一个侦听器以通知所有事件。)
void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName);(添加一个侦听器以通知所有事件。)
void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event);(将给定的应用程序事件多播到适当的侦听器。)
void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType);
该工具类注入方式:refresh(); --> initApplicationEventMulticaster();
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME=“applicationEventMulticaster”)
3、实现ApplicationListener接口方式注入监听器相关源码解析:
1)、向ApplicationEventMulticaster接口(AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster实现类)添加实现ApplicationListener接口的监听器
refresh(); (AnnotationConfigApplicationContext.java)
registerListeners(); (AbstractApplicationContext.java)
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames){
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
2)spring框架注入的内部类:ApplicationListenerDetector.java (添加实现ApplicationListener接口的监听器)
注入位置:refresh(); ---->prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);------->beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
作用:创建实现ApplicationListener接口的监听器时,需遍历已经注入的后置处理器(beanPostProcessors),该后置处理器向applicationContext类注入该监听类
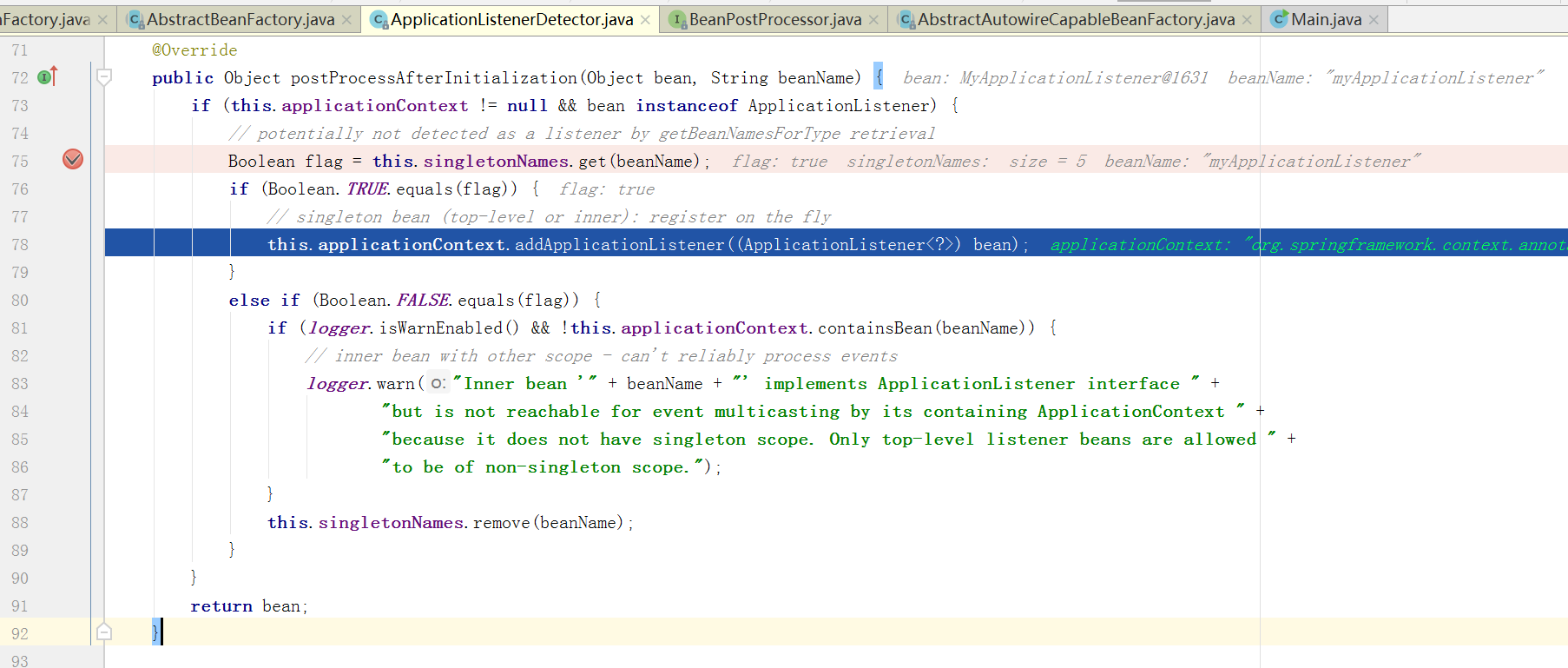
即:ApplicationListenerDetector.java:this.applicationContext.addApplicationListener((ApplicationListener<?>) bean);
--->AbstractApplicationContext.java:this.applicationEventMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
---->AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster.java:this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
3、使用@EventListener注解的注入监听器相关源码解析
相关知识点:Class类中的getMethods(),该方法是获取本类以及父类或者父接口中所有的公共方法(public修饰符修饰的)。
Class类中的getDeclaredMethods(),该方法是获取本类中的所有方法,包括私有的(private、protected、默认以及public)的方法。
Class类中的getInterfaces(),能够获得这个对象所实现的所有接口。
Method类中getModifiers(),返回此类或接口以整数编码的 Java 语言修饰符。如需要知道返回的值所代表的意思,则需要用到 java.lang.reflect.Modifier 这个类,这个类提供了 static 方法和常量,可以对类和成员访问修饰符进行解码。
Method.getAnnotation(Class <T> annotationClass)方法如果存在这样的注释,则返回指定类型的元素的注释,否则为null。
Class1.isAssignableFrom(Class2),是用来判断一个类Class1和另一个类Class2是否相同或者Class1类是不是Class2的父类。
关键类:org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor(实现类:org.springframework.context.event.EventListenerMethodProcessor)
注入位置:
this(); (AnnotationConfigApplicationContext.java)
----> this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this); (AnnotationConfigApplicationContext.java)
----->this(registry, getOrCreateEnvironment(registry)); (AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader.java)
----->AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry); (AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader.java)
----->registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(registry, null); (AnnotationConfigUtils.java)
(在给定的注册表中注册所有相关的注释后处理器)

EventListenerMethodProcessor作用:
使用EventListenerMethodProcessor处理器来解析方法上的@EventListener:
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated()
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
EventListenerMethodProcessor.java------> smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated() :
@Override
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
List<EventListenerFactory> factories = getEventListenerFactories();
String[] beanNames = this.applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!ScopedProxyUtils.isScopedTarget(beanName)) {
Class<?> type = null;
try {
type = AutoProxyUtils.determineTargetClass(this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory(), beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
}
if (type != null) {
try {
processBean(factories, beanName, type);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Failed to process @EventListener " +
"annotation on bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
}
}
EventListenerMethodProcessor.java------>processBean(factories, beanName, type)。
覆写了MetadataLookup对象的inspect(Method method)方法。
inspect(Method method)方法:AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, EventListener.class);改操作判断方法是否有@EventListener注解。如果存在这样的注释,则返回指定类型的元素的注释,否则为null。
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(registry, null)方法会为容器注入名为org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory,类型为DefaultEventListenerFactory.java,该类的方法:public ApplicationListener<?> createApplicationListener(String beanName, Class<?> type, Method method),其根据类名,类的class,方法(有@EventListener注解),来构建一个监听器。
protected void processBean(final List<EventListenerFactory> factories, final String beanName, final Class<?> targetType) {
//.........................
Map<Method, EventListener> annotatedMethods = null;//存放所有有@EventListener注解的方法
annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetType,
new MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<EventListener>() {
@Override
public EventListener inspect(Method method) {
return AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, EventListener.class);
}
});
//.......................................
// Non-empty set of methods
for (Method method : annotatedMethods.keySet()) {
for (EventListenerFactory factory : factories) {
if (factory.supportsMethod(method)) {
Method methodToUse = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(
method, this.applicationContext.getType(beanName));
ApplicationListener<?> applicationListener =
factory.createApplicationListener(beanName, targetType, methodToUse);
if (applicationListener instanceof ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) {
((ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) applicationListener)
.init(this.applicationContext, this.evaluator);
}
this.applicationContext.addApplicationListener(applicationListener);
break;
}
}
}
}
MethodIntrospector.java ---------> selectMethods()
覆写了MethodCallback对象的doWith(Method method)方法。
在doWith方法中,T result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod); 会调用上面被覆写的inspect方法来判断方法是否有@EventListener注解。
public static <T> Map<Method, T> selectMethods(Class<?> targetType, final MetadataLookup<T> metadataLookup) {
final Map<Method, T> methodMap = new LinkedHashMap<Method, T>();//存放所有有@EventListener注解的方法
Set<Class<?>> handlerTypes = new LinkedHashSet<Class<?>>();
handlerTypes.addAll(Arrays.asList(targetType.getInterfaces()));
for (Class<?> currentHandlerType : handlerTypes) {//遍历本类或父接口
final Class<?> targetClass = (specificHandlerType != null ? specificHandlerType : currentHandlerType);
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(currentHandlerType, new ReflectionUtils.MethodCallback() {
@Override
public void doWith(Method method) {
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
T result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod);
if (result != null) {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
if (bridgedMethod == specificMethod || metadataLookup.inspect(bridgedMethod) == null) {
methodMap.put(specificMethod, result);
}
}
}
}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);
}
return methodMap;
}
void doWithMethods(Class<?> clazz, MethodCallback mc, MethodFilter mf),循环遍历该类的全部方法,将method当做方法参数调用dowith方法。
public static void doWithMethods(Class<?> clazz, MethodCallback mc, MethodFilter mf) {
// Keep backing up the inheritance hierarchy.
Method[] methods = getDeclaredMethods(clazz);//获取该类的全部方法
for (Method method : methods) {
if (mf != null && !mf.matches(method)) {
continue;
}
try {
mc.doWith(method);
}
catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Not allowed to access method '" + method.getName() + "': " + ex);
}
}
if (clazz.getSuperclass() != null) {
doWithMethods(clazz.getSuperclass(), mc, mf);
}
else if (clazz.isInterface()) {
for (Class<?> superIfc : clazz.getInterfaces()) {
doWithMethods(superIfc, mc, mf);
}
}
}
4、发布事件相关源码解析:
annotationConfigApplicationContext.publishEvent(new MyApplicationEvent("yhq"));
----> publishEvent(event, null); (AbstractApplicationContext.java)
----->getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType); (AbstractApplicationContext.java)
------>(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.java):
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
for (final ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
});
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
------> getApplicationListeners(event, type) (AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster.java)//获取全部类型匹配的listener
------> Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners = retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, retriever); //检查listener是否匹配。
------>invokeListener(listener, event);
------>listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
----->this.bridgedMethod.invoke(bean, args);