title: Java nio
date: 2017-08-08 07:05:48
tags: [Java]
转载自http://ifeve.com/overview/
原始英文地址: http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-nio/overview.html
Java NIO 由以下几个核心部分组成:
- Channels
- Buffers
- Selectors
虽然Java NIO 中除此之外还有很多类和组件,但在我看来,Channel,Buffer 和 Selector 构成了核心的API。其它组件,如Pipe和FileLock,只不过是与三个核心组件共同使用的工具类。因此,在概述中我将集中在这三个组件上。其它组件会在单独的章节中讲到。
Channel 和 Buffer
基本上,所有的 IO 在NIO 中都从一个Channel 开始。Channel 有点象流。 数据可以从Channel读到Buffer中,也可以从Buffer 写到Channel中。这里有个图示:
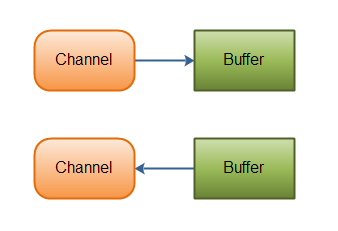
Channel和Buffer有好几种类型。下面是JAVA NIO中的一些主要Channel的实现:
- FileChannel
- DatagramChannel
- SocketChannel
- ServerSocketChannel
正如你所看到的,这些通道涵盖了UDP 和 TCP 网络IO,以及文件IO。
与这些类一起的有一些有趣的接口,但为简单起见,我尽量在概述中不提到它们。本教程其它章节与它们相关的地方我会进行解释。
以下是Java NIO里关键的Buffer实现:
- ByteBuffer
- CharBuffer
- DoubleBuffer
- FloatBuffer
- IntBuffer
- LongBuffer
- ShortBuffer
这些Buffer覆盖了你能通过IO发送的基本数据类型:byte, short, int, long, float, double 和 char。
Java NIO 还有个 MappedByteBuffer,用于表示内存映射文件, 我也不打算在概述中说明。
Selector
Selector允许单线程处理多个 Channel。如果你的应用打开了多个连接(通道),但每个连接的流量都很低,使用Selector就会很方便。例如,在一个聊天服务器中。
这是在一个单线程中使用一个Selector处理3个Channel的图示:
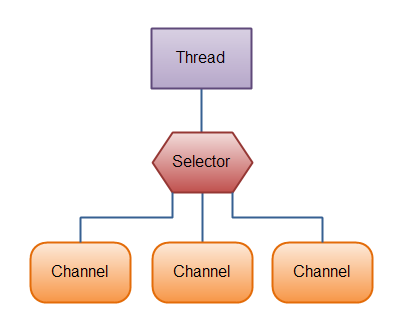
下面是NIO的一些代码
public void testNio() throws IOException {
// 打开文件
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("data/uid.txt", "rw");
// 获取Channel
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel();
// 得到一个大小为48的Buffer
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
// Channel开始向Buffer添加数据, byteCount返回的为byteBuffer真实读取到的大小,此时 postion =
// byteCount
int byteCount = channel.read(byteBuffer);
while (byteCount != -1) {
System.out.println("read:" + byteCount);
// buffer 启动写模式 limit=position, position=0,
// buffer只能从postion~limit(不包含limit)之间读取数据
byteBuffer.flip();
// hasRemaining()方法判断position<limit
while (byteBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
// get()方法返回position所对应的值,position++;
System.out.println((char) byteBuffer.get());
}
byteBuffer.clear();
byteCount = channel.read(byteBuffer);
}
file.close();
}
public void testTransfer() throws IOException {
// fromChannel打开fromFile.txt
RandomAccessFile fromFile = new RandomAccessFile("fromFile.txt", "rw");
FileChannel fromChannel = fromFile.getChannel();
// toChannel打开toFile.txt
RandomAccessFile toFile = new RandomAccessFile("toFile.txt", "rw");
FileChannel toChannel = toFile.getChannel();
long position = 0;
//Returns the current size of this channel's file.
long count = fromChannel.size();
// 開始Channel之間的轉化
toChannel.transferFrom(fromChannel, position, count);
fromFile.close();
toFile.close();
}
ifeve NIO系列教程地址
Java NIO系列教程(一) Java NIO 概述
Java NIO系列教程(二) Channel
Java NIO系列教程(三) Buffer
Java NIO系列教程(四) Scatter/Gather
Java NIO系列教程(五) 通道之间的数据传输
Java NIO系列教程(六) Selector
Java NIO系列教程(七) FileChannel
Java NIO系列教程(八) SocketChannel
Java NIO系列教程(九) ServerSocketChannel
Java NIO系列教程(十) Java NIO DatagramChannel
Java NIO系列教程(十一) Pipe
Java NIO系列教程(十二) Java NIO与IO