xpath入门
在上次我详细的讲了一下什么是xpath,具体了解可以先看下面这篇博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/yanjiayi098-001/p/12009963.html
使用xpath之前先安装lxml库
pip install lxml
先看一段简单的示例:
from lxml import etree
text = '''
<div>
<ul>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link1.html">first</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second</a>
<li class="item-2"><a href="link3.html">third</li>
<li class="item-3"><a href="link4.html">fourth</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
'''
html = etree.HTML(text)
result = etree.tostring(html)
print(result.decode('utf-8'))
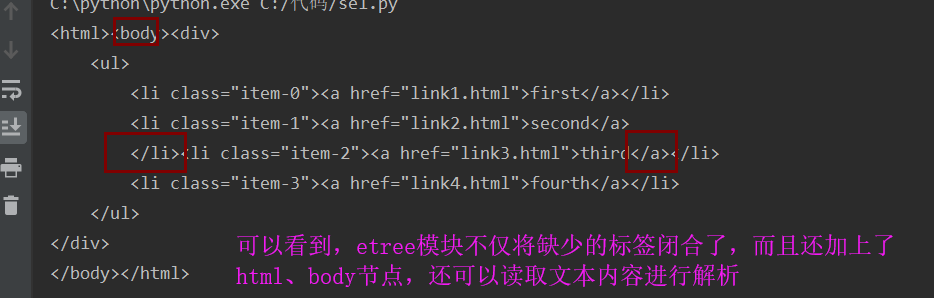
注意查看代码中的html片段,第二个li没有闭合,第三个li的a标签没有闭合
查看结果:
新建 hello.html
<div>
<ul>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link1.html">first</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second</a></li>
<li class="item-2"><a href="link3.html">third</a></li>
<li class="item-3"><a href="link4.html">fourth</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
.py文件
from lxml import etree
html = etree.parse('./test.html', etree.HTMLParser())
result = etree.tostring(html)
print(result.decode('utf-8'))
结果:
<html><body>
<div>
<ul>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link1.html">first</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second</a></li>
<li class="item-2"><a href="link3.html">third</a></li>
<li class="item-3"><a href="link4.html">fourth</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body></html>
获取节点
获取所有节点
//*表示匹配所有节点
html = etree.parse('./hello.html', etree.HTMLParser())
result = html.xpath('//*')
print(result)
结果:
[<Element html at 0x252593df0c8>, <Element head at 0x252596a7c88>, <Element meta at 0x252596a7cc8>, <Element title at 0x252596a7d48>, <Element body at 0x252596a7f48>, <Element div at 0x252596b40c8>, <Element ul at 0x252596b4148>, <Element li at 0x252596b4188>, <Element a at 0x252596b41c8>, <Element li at 0x252596b4088>, <Element a at 0x252596b4208>, <Element li at 0x252596b4248>, <Element a at 0x252596b4288>, <Element li at 0x252596b42c8>, <Element a at 0x252596b4308>]
匹配指定节点,如获取所有li节点
from lxml import etree
html = etree.parse('./test.html', etree.HTMLParser())
result = html.xpath('//li')
print(result) # 所有li节点
print(result[0]) # 第一个li节点
结果:
[<Element li at 0x29d8c7f7bc8>, <Element li at 0x29d8c7f7c08>, <Element li at 0x29d8c7f7c88>, <Element li at 0x29d8c7f7f88>]
<Element li at 0x29d8c7f7bc8>
获取子节点
/表示匹配子节点
获取li节点的直接子节点
from lxml import etree
html = etree.parse('./test.html', etree.HTMLParser())
result = html.xpath('//li/a') # 获取所有li节点的直接子节点a
print(result)
结果:
[<Element a at 0x2305cda7c88>, <Element a at 0x2305cda7cc8>, <Element a at 0x2305cda7d48>, <Element a at 0x2305cda7f48>]
改成 // 可以这么写:
from lxml import etree
html = etree.parse('./test.html', etree.HTMLParser())
result = html.xpath('//div//a') # 获取div的所有后代a节点
print(result)
获取父节点
..表示匹配父节点
from lxml import etree
html = etree.parse('./test.html', etree.HTMLParser())
# 获取href属性为link2.html的a标签的父节点的class名
result = html.xpath('//a[@href="link2.html"]/../@class')
print(result)
# ['item-1'] #结果
属性匹配
@表示匹配属性
根据属性值匹配节点
from lxml import etree
html = etree.parse('./test.html', etree.HTMLParser())
# 获取属性class值为item-0的li
result = html.xpath('//li[@class="item-0"]')
print(result)
# [<Element li at 0x2aa50947cc8>]
属性多值匹配
使用contains函数匹配

可以看出 contains函数表示意思是,第一个参数字符串包含第二个参数时,返回true
实际用起来可能会有点差异(由于结合了路径表达式和属性)
from lxml import etree
text = '''
<li class="li li-first"><a href="link.html">first item</a></li>
'''
html = etree.HTML(text)
result = html.xpath('//li[@class="li"]/a/text()')
print(result)
# []
result = html.xpath('//li[contains(@class, "li")]/a/text()')
##选取class属性包含字符串"li"的节点
print(result)
# ['first item']
多属性匹配
需要匹配满足多个属性的节点,使用 and 运算符
from lxml import etree
text = '''
<li class="li li-first" name="item"><a href="link.html">first item</a></li>
'''
html = etree.HTML(text)
# 通过class和name两个属性进行匹配
result = html.xpath('//li[contains(@class, "li") and @name="item"]/a/text()')
print(result)
# ['first item']
文本获取
from lxml import etree
html = etree.parse('./test.html', etree.HTMLParser())
# 获取属性class值为item-0的li的子节点a的文本内容
result = html.xpath('//li[@class="item-0"]/a/text()')
print(result)
# ['first']
如果想要获取后代节点内部的所有文本,使用 //text()
from lxml import etree
html = etree.parse('./test.html', etree.HTMLParser())
# 获取所有li的后代节点中的文本
result = html.xpath('//li//text()')
print(result)
# ['first', 'second', 'third', 'fourth']
按序选择
根据节点所在的顺序进行提取
from lxml import etree
html = etree.parse('./test.html', etree.HTMLParser())
# 按索引排序
result = html.xpath('//li[1]/a/text()')
print(result)
# ['first']
# last 最后一个
result = html.xpath('//li[last()]/a/text()')
print(result)
# ['fourth']
# position 位置查找
result = html.xpath('//li[position()<3]/a/text()')
print(result)
# ['first', 'second']
# - 运算符
result = html.xpath('//li[last()-2]/a/text()')
print(result)
# ['second']
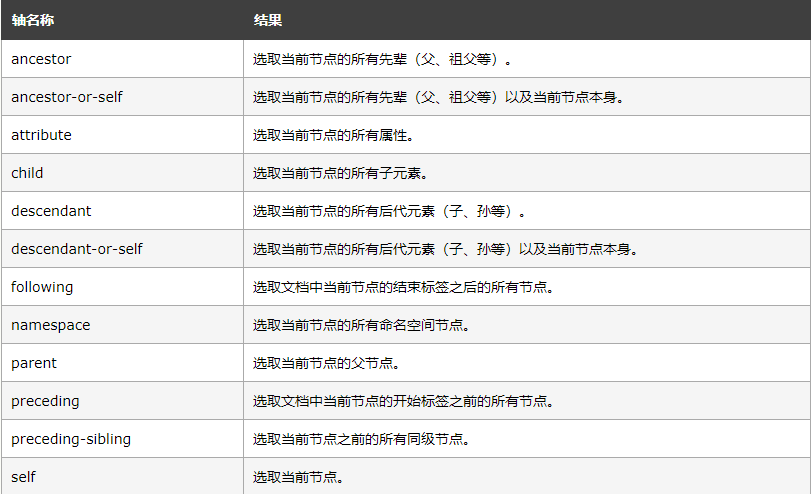
节点轴选择
from lxml import etree
html = etree.parse('./test.html', etree.HTMLParser())
# 所有祖先节点
result = html.xpath('//li[1]/ancestor::*')
print(result)
# [<Element html at 0x106e4be88>, <Element body at 0x106e4bf88>, <Element div at 0x106e4bfc8>, <Element ul at 0x106e6f048>]
# 祖先节点中的div
result = html.xpath('//li[1]/ancestor::div')
print(result)
# [<Element div at 0x106ce4fc8>]
# 第一个节点的所有属性
result = html.xpath('//li[1]/attribute::*')
print(result)
# ['item-0']
# 子节点
result = html.xpath('//li[1]/child::a[@href="link1.html"]')
print(result)
# [<Element a at 0x107941fc8>]
# 后代节点中的a
result = html.xpath('//li[1]/descendant::a')
print(result)
# [<Element a at 0x10eeb7fc8>]
# 该节点后面所有节点中的第2个 从1开始计数
result = html.xpath('//li[1]/following::*[2]')
print(result)
# [<Element a at 0x10f188f88>]
# 该节点后面的所有兄弟节点
result = html.xpath('//li[1]/following-sibling::*')
print(result)
# [<Element li at 0x104b7f048>, <Element li at 0x104b7f088>, <Element li at 0x104b7f0c8>]
补充
xpath的运算符介绍

xpath轴