spring中的事件驱动模型Event(也叫发布订阅模式),是观察者模式的一个典型的应用
好处:业务解耦,在不影响原来业务逻辑的情况下,加入其它业务
场景:
app上线后已实现用户注册功能,现需要在用户注册成功后给用户发送短信提示。
因为怕发送短信的代码逻辑发送异常会影响以前的用户注册功能,所以将发送短信功能设置成监听事件,在用户注册成功后发布一个事件,在事件监听器中监听到该事件后处理发送短信逻辑。如果发送短信发生异常,不会影响用户注册功能。
代码实现:
新建maven项目,引入依赖:
<!--父依赖包--> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.3.2.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>
项目其他结构:
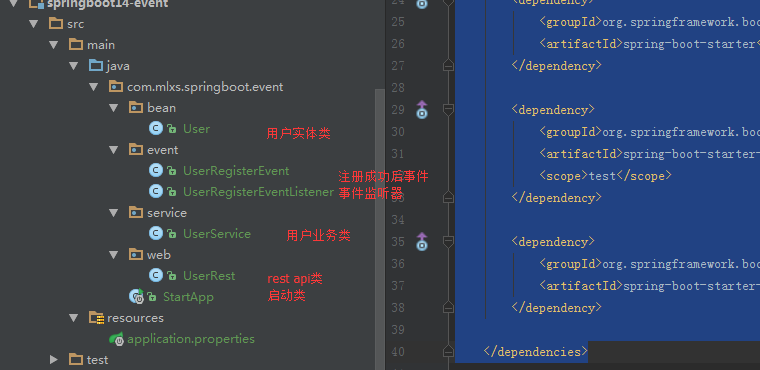
User
public class User { private int id; private String name; public User() { } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
UserService
import com.mlxs.springboot.event.bean.User; import com.mlxs.springboot.event.event.UserRegisterEvent; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * UserService类描述: * * @author yangzhenlong * @since 2018/1/12 */ @Service public class UserService { @Autowired private ApplicationContext applicationContext; private List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>(); public User register(User user) { userList.add(user); //发布事件 applicationContext.publishEvent(new UserRegisterEvent(this, user)); return user; } public List<User> getAll(){ return userList; } }
UserRest
@RestController public class UserRest { @Autowired private UserService userService; @RequestMapping("/user/all") List<User> getAll(){ return userService.getAll(); } @RequestMapping("/user/register") User register(@RequestBody User user){ return userService.register(user); } }
StartApp
@SpringBootApplication public class StartApp { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(StartApp.class, args); } }
UserRegisterEvent 用户注册事件
public class UserRegisterEvent extends ApplicationEvent { private Object source; private User user; public UserRegisterEvent(Object source, User user) { super(source); this.user = user; } @Override public Object getSource() { return source; } public void setSource(Object source) { this.source = source; } public User getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(User user) { this.user = user; } }
UserRegisterEventListener 用户事件监听
@Component public class UserRegisterEventListener { @EventListener public void register(UserRegisterEvent event){ User user = event.getUser(); System.out.println("-----------监听到用户注册事件------,给用户【" + user.getName() + "】发送短信..."); } }
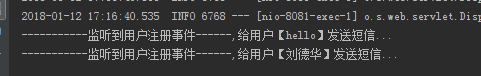
启动项目,调用 register接口,注册2个用户:
{ "id":1, "name":"hello" } ------------------------------ { "id":2, "name":"刘德华" }
查看控制台