栈
定义:
栈(Stack),是运算受限的线性表,插入和取出操作都只能在表头进行,也称之为后进先出(LIFO)线性表;
案例:
有名为stk的栈,按顺序插入:1,2,3三个元素,插入完成后取出全部,顺序为:3,2,1;
栈的实现:
既然是线性表,则可以通过顺序结构和链接结构来实现,通过顺序结构实现的栈称为顺序栈,通过链接结构实现的栈称为链栈;
常用操作:
- 初始化
- 入栈
- 出栈
- 取栈顶元素
- 空栈判断
使用场景:
程序中函数(方法)的执行通常都是借助栈来完成的,当要执行一个函数时,会将函数代码压入栈中,执行完毕则出栈,执行过程中若调用了其他函数,则被调函数同样会入栈,所以程序中的函数嵌套调用时,也是遵循后进先出;
顺序实现
顺序栈数据结构:
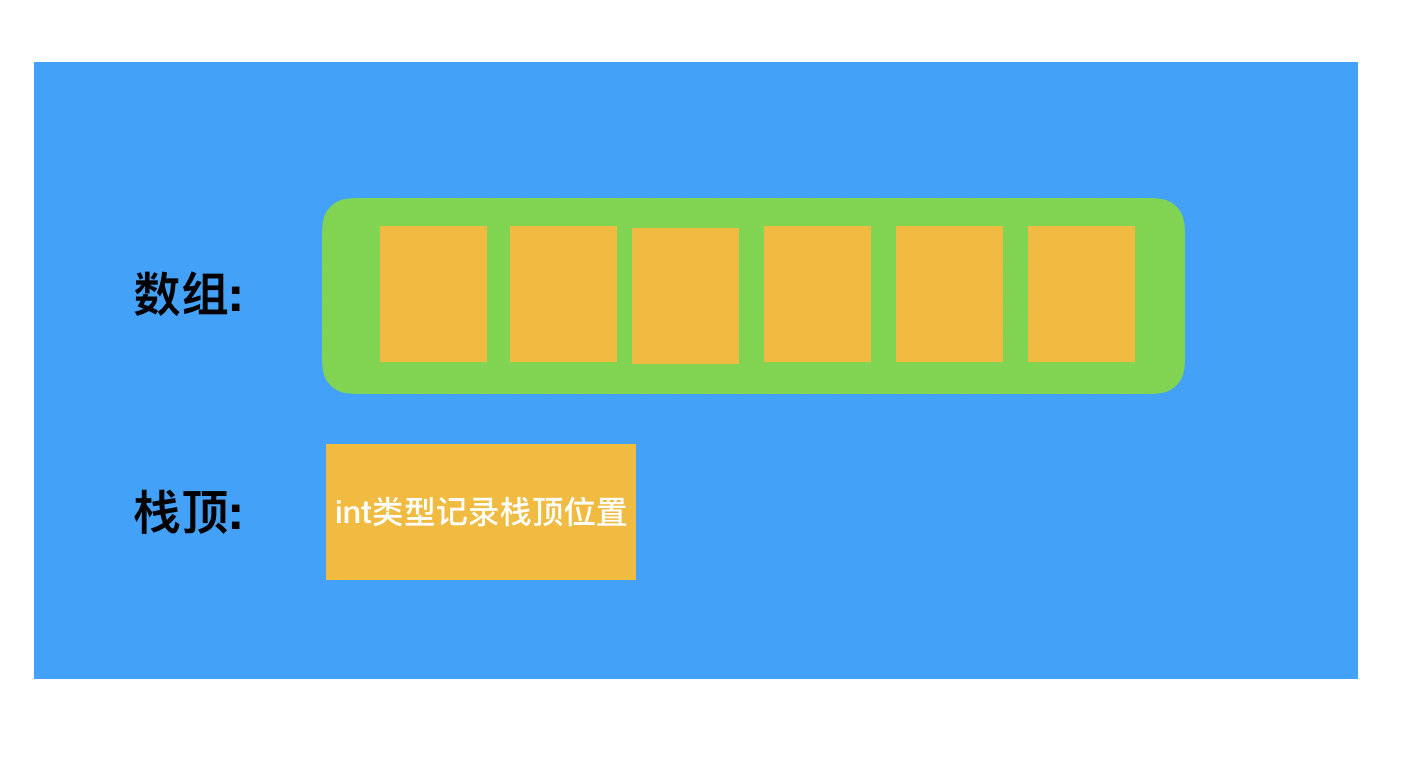
c语言实现:
#include <stdio.h>
//栈的顺序实现
//定义数据结构
const int SIZE = 5;
typedef struct{
int data[SIZE];
int top;
}seqStk,*SEQStack;
SEQStack initalStack(){
SEQStack stack = malloc(sizeof(seqStk));
stack->top = -1;
return stack;
}
int isEmpty(SEQStack stack){
if(stack->top == -1){
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int getTop(SEQStack stack){
if (isEmpty(stack)) {
printf("err:stack is empty!
");
return NULL;
}else{
return stack->data[stack->top];
}
}
int pop(SEQStack stack){
//先进后出,出栈是判断是否空
if (isEmpty(stack)) {
printf("err:stack is empty!
");
return NULL;
}else{
int temp = getTop(stack);
stack->top--;
return temp;
}
}
void push(SEQStack stack,int data){
if (stack->top == SIZE-1) {
printf("err:stack already full!
");
}else{
stack->top++;
stack->data[stack->top] = data;
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
SEQStack stack = initalStack();
push(stack,100);
push(stack,200);
push(stack,300);
push(stack,400);
push(stack,500);
push(stack,600);
printf("geted:%d
",pop(stack));
printf("geted:%d
",getTop(stack));
printf("geted:%d
",pop(stack));
printf("geted:%d
",pop(stack));
printf("geted:%d
",pop(stack));
printf("geted:%d
",pop(stack));
printf("Hello, World!
");
return 0;
}
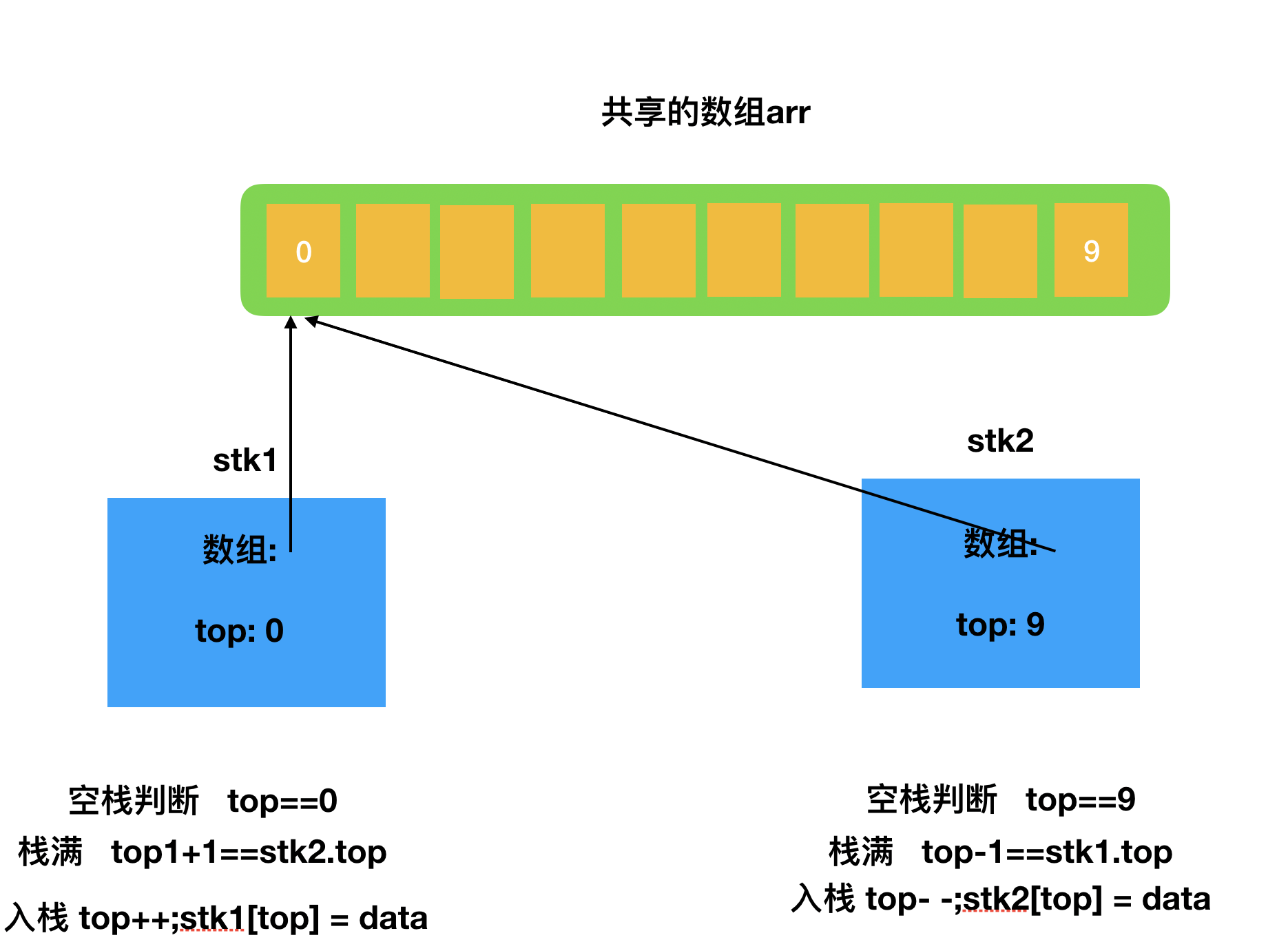
双栈
顺序实现的弊端就在于,无法预估数据长度,会造成空间浪费,为了避免这个问题,我们可以让两个栈共享同一个顺序存储空间,起始地址和结束地址分别作为两个栈的栈底;
- 数据结构及相关操作:
链接实现
数据结构:

c语言实现:
#include <stdio.h>
//结构定义
typedef struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
}Node,*LinkStk;
LinkStk initialStack(){
LinkStk stack = malloc(sizeof(Node));
stack->next = NULL;
return stack;
}
int isEmpty(LinkStk stack){
if (stack->next == NULL) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void push(LinkStk stack,int data){
Node *p = malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->next = stack->next;
p->data = data;
stack->next = p;
}
Node *getTop(LinkStk stack){
return stack->next;
}
void *pop(LinkStk stack){
if (isEmpty(stack)) {
printf("error:stack is empty!
");
return NULL;
}
Node *temp = stack->next;
stack->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
LinkStk stack = initialStack();
push(stack, 100);
push(stack, 200);
push(stack, 300);
pop(stack);
pop(stack);
pop(stack);
Node *a = getTop(stack);
if (a != NULL){
printf("%d
",a->data);
}
push(stack, 900);
Node *w = getTop(stack);
printf("%d
",w->data);
printf("Hello, World!
");
return 0;
}
案例中所有操作算法时间复杂度均为O(1);
队列
定义:
队列(Queue),同栈相同,也是运算受限的线性表,其插入只能在表未进行,而删除只能在表头进行,称之为先进先出(FIFO)线性表;
案例:
有名为stk的栈,按顺序插入:1,2,3三个元素,插入完成后取出全部,顺序为:1,2,3;
队列的实现:
既然是线性表,同样也可以通过顺序结构和链接结构来实现;
常用操作:
- 初始化
- 入队列
- 出队列
- 取队列首元素
- 空队列判断
使用场景:
队列的核心就在于,先来先得,先进队列的一定先出,这非常适合用在需要保证处理顺序的业务上,例如秒杀活动;
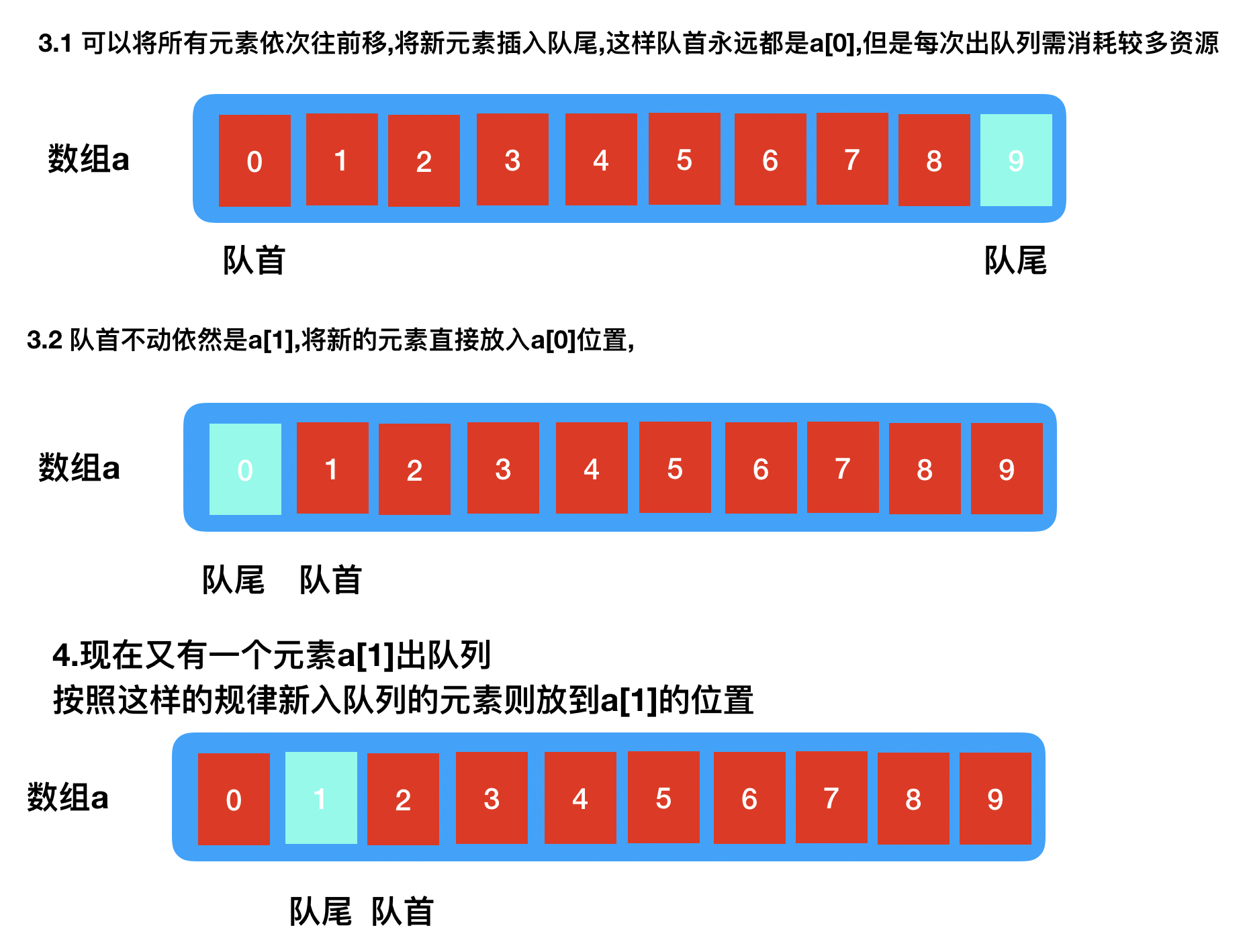
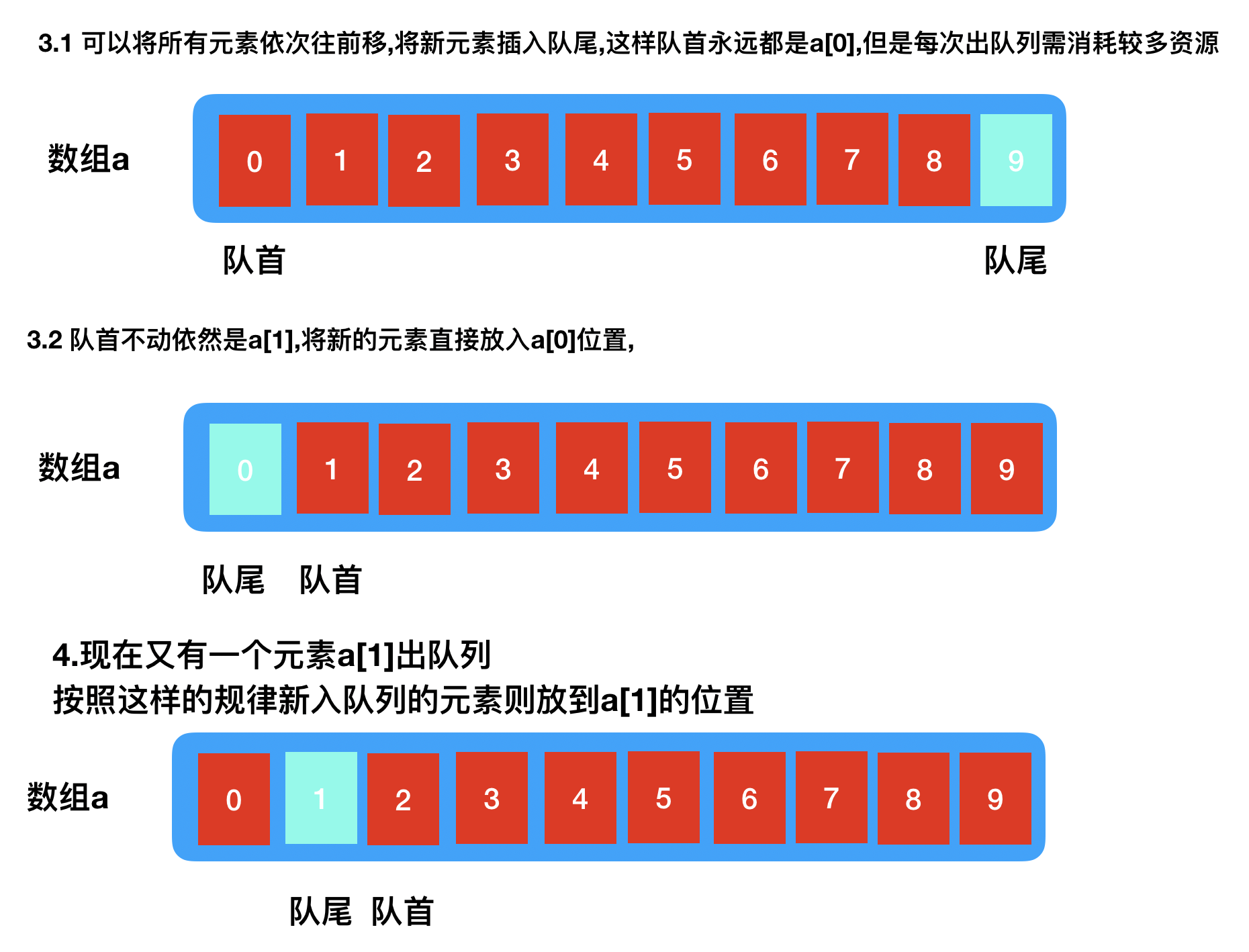
顺序实现
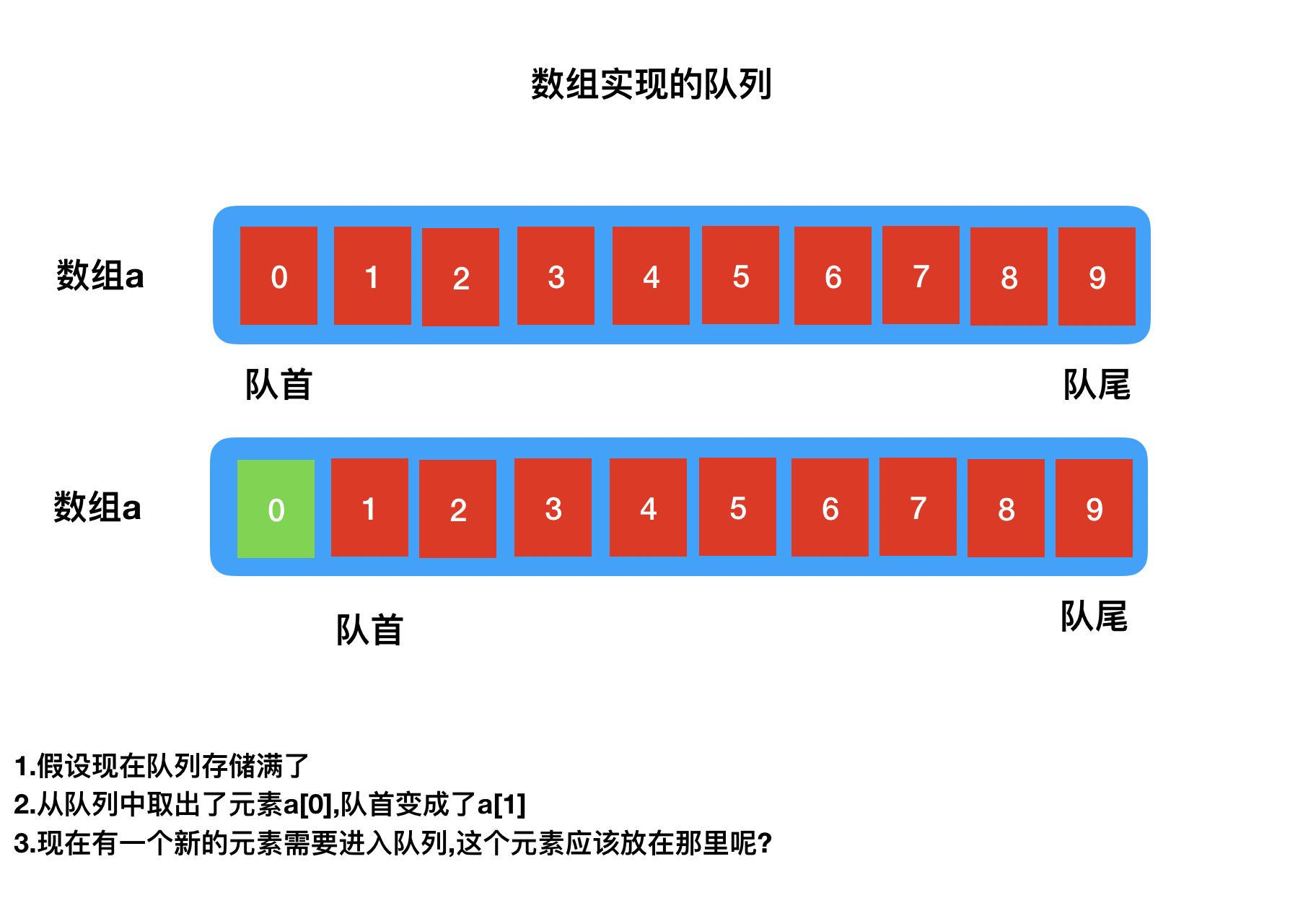
队列中的元素是具有顺序的所以可通过顺序结构实现,常见的方式就是通过数组,但是数组的问题是无法准确预估元素大小
此外,当有元素从队列中出去时,队列则可以存如储新的元素,但是心存储的元素应该放在那里却成了一个问题,
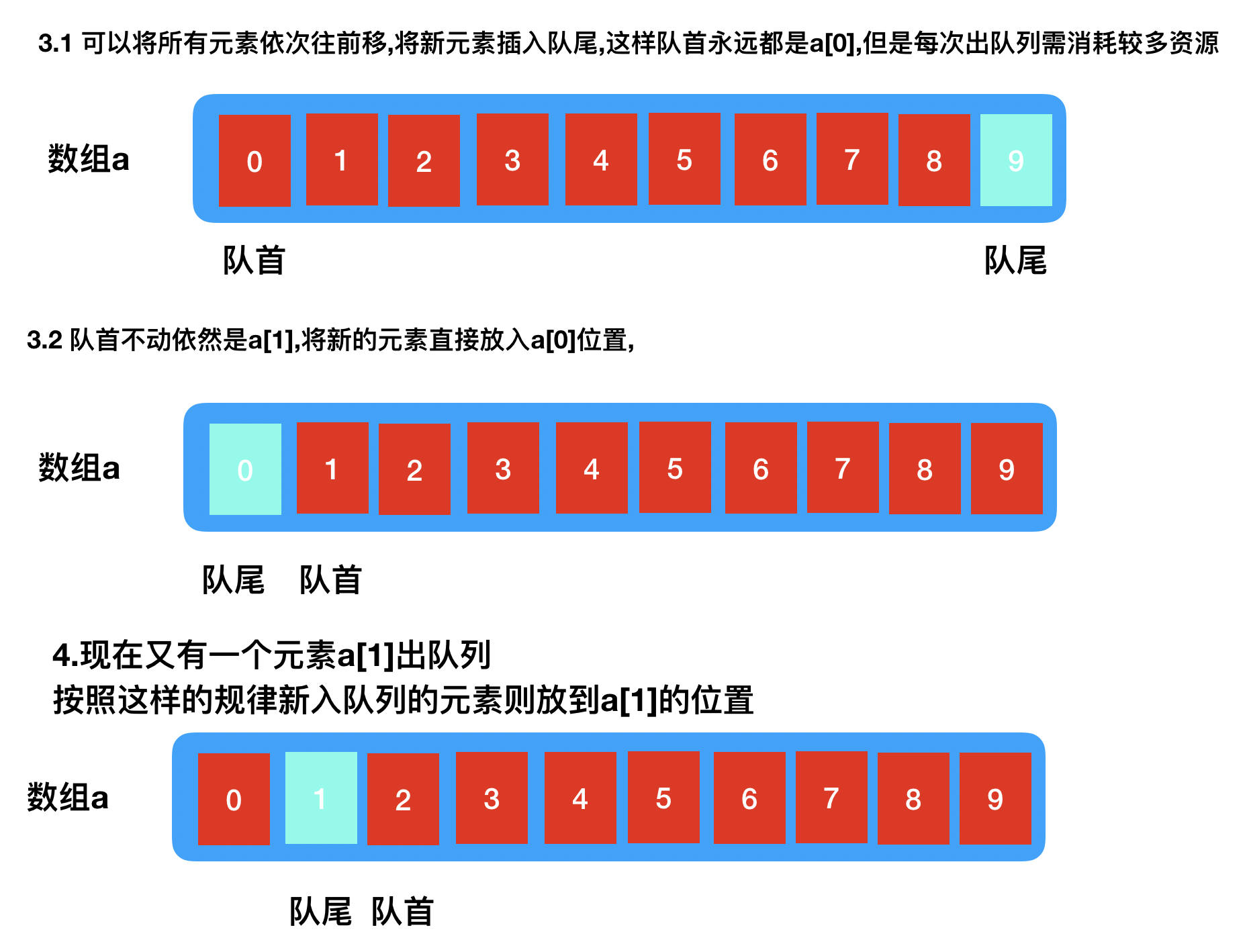
实现原理简述:

c语言实现:
#include <stdio.h>
const int max_size = 5;
//数据结构定义
typedef struct LQueue{
int data[max_size];
int front;
int rear;
}LQueue,*Queue;
//初始化
LQueue *initial(){
LQueue *queue = malloc(sizeof(LQueue));
queue->front = 0;
queue->rear = 0;
return queue;
}
//入队列
void put(LQueue *queue,int data){
if ((queue->rear+1)%max_size == queue->front){
printf("error:队列已满
");
exit(-1);
} else{
queue->rear = (queue->rear+1)%max_size;
queue->data[queue->rear] = data;
}
}
//判空
int isEmpty(LQueue *queue){
return queue->rear == queue->front;
}
//出队列
int get(LQueue *queue){
if (isEmpty(queue)){
printf("error:队列为空");
exit(-1);
}else{
queue->front = (queue->front+1)%max_size;
return queue->data[queue->front];
}
}
//测试
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
Queue queue = initial();
put(queue,1);
put(queue,2);
put(queue,3);
put(queue,4);
printf("%d
",get(queue));
printf("%d
",get(queue));
put(queue,5);
put(queue,6);
printf("%d
",get(queue));
printf("%d
",get(queue));
printf("%d
",get(queue));
printf("%d
",get(queue));
put(queue,7);
printf("%d
",get(queue));
printf("Hello, World!
");
return 0;
}
```