6。1编写一个函数,它在一个字符串中进行搜索,查找所有在一个给定字符集中出现的字符,返回第一个找到的字符位置指针,未找到返回NULL
#include <stdio.h>
char * find_char(char const *source, char const *chars)
{
char const *sptr = source;
char const *cptr = chars;
if (sptr == NULL || cptr == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
while (*sptr != '�') {
cptr = chars;
while (*cptr != '�') {
if (*cptr == *sptr) {
//找到打印source地址
printf("chars:0x%p
", chars);
//返回类型为 char *,此处类型转换一下把char const *转换回来
return (char *)cptr;
}
cptr++;
}
sptr++;
}
return NULL;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include "function.h"
int main()
{
char *source = "ABCDEF";
char *str1 = "XYZ";
char *str2 = "XRCQEF";
char *chars = str1;
char *ptr = NULL;
//没有对应的字符
ptr = find_char(source, chars);
printf("0x%p
", ptr);
//对应的字符C,第三个
chars = str2;
ptr = find_char(source, chars);
printf("0x%p
", ptr);
while (1)
;
return 0;
}
执行结果:

6.2删除字符串中子串部分,将剩下部分前移。
int del_substr(char *str, char const *substr)
{
if (str == NULL || substr == NULL) {
return 0;
}
//将数组首位赋值给指针数组
char *source = str;
char *sub = substr;
char *tmp = NULL;
while (*source != '�') {
//将指针重置指向子串首
sub = substr;
//使用临时变量进行对比,保持source位置信息不变
tmp = source;
//当遇到相同的字符,开始比较之后是否相同
while (*tmp++ == *sub++) {
//循环中已经sub++了,到达末尾,证明找到子串,开始前移
if (*sub == '�') {
//未到达字符串末尾,继续前移
while (*(tmp + 1) != '�') {
*source = *tmp;
}
return 1;
}
}
source++;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
char *source = "ABCDEF";
char *str1 = "CGE";
char *str2 = "CDE";
int isDel;
//无子串
isDel = del_substr(source, str1);
printf("del_substr: %d
", isDel);
//有子串
isDel = del_substr(source, str2);
printf("del_substr: %d
", isDel);
while (1)
;
return 0;
}
执行结果:

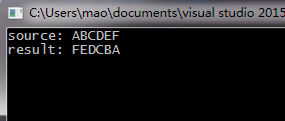
6.3 编写函数reverse_string,翻转字符串。
void reverse_string(char *string)
{
//先定义两个指针,一个指向首一个指向末尾
char *head = string;
//string本身指向第一位,加上字符串长度后是指向�后的,所以需要前移,指向最后一个字符
char *tail = string + strlen(string) - 1;
char tmp;
//同一数组内可以进行指针位置对比
while (head < tail) {
tmp = *head;
*head = *tail;
*tail = tmp;
head++;
tail--;
}
}
int main()
{
char source[] = "ABCDEF";
printf("source: %s
", source);
reverse_string(source);
printf("result: %s
", source);
return 0;
}
执行结果:
6.4 Eratosthenes法找质数,第一步写下2至某个上线之间的所有的数,第二步开始剔除不是质数的整数,找到列表第一个不被剔除的数(就是2)然后将表后面所有逢双的数都剔除,因为都可以被2整除,所以不是质数,然后回到表头,此时表头尚未被剔除的是三,然后每逢三位剔除,反复进行最后都是质数。
void find_primer(int *numbers, int length)
{
//0 1 不为质数
numbers[0] = FALSE;
numbers[1] = FALSE;
int tmp;
int loc;
int index = 2;
while (index < length) {
tmp = index;
//当前头部找到的质数,和后面的数相乘的结果对应的位置全部不是质数。
while ( (tmp += index) < length) {
*(numbers + tmp) = FALSE;
}
index++;
}
}
int main()
{
int numbers[10000];
for (int index = 0; index < 10000; index++) {
numbers[index] = TRUE;
}
find_primer(numbers, 10000);
for (int index = 0; index < 10000; index++) {
if (numbers[index]) {
printf("%-08d", index);
}
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:

6.5利用第五章的位数组求质数
位数组:
//字符偏移
unsigned int char_offset(unsigned bit_number)
{
return bit_number / CHAR_BIT;
}
//bit位偏移
unsigned int bit_offset(unsigned bit_number)
{
return bit_number % CHAR_BIT;
}
void set_bit(char bit_array[], unsigned bit_number)
{
bit_array[char_offset(bit_number)] |= 1 << bit_offset(bit_number);
}
void clear_bit(char bit_array[], unsigned bit_number)
{
bit_array[char_offset(bit_number)] &= ~(1 << bit_offset(bit_number));
}
void assign_bit(char bit_array[], unsigned bit_number, int value)
{
if (value != 0) {
set_bit(bit_array, bit_number);
}
else {
clear_bit(bit_array, bit_number);
}
}
int test_bit(char bit_array[], unsigned bit_number)
{
//对该bit位进行与操作,如果是1则结果还是 1<< (bit_number % CHAR_BIT)
return (bit_array[char_offset(bit_number)] & (1 << bit_offset(bit_number))) != 0;
}
位数组求质数:
void find_primer_bit(char bit_array[], unsigned long int length)
{
clear_bit(bit_array, 0);
clear_bit(bit_array, 1);
unsigned int tmp;
unsigned int loc;
unsigned int index = 2;
while (index < length) {
tmp = index;
//没逢index位置0
while ( (tmp += index) < length) {
clear_bit(bit_array, tmp);
}
index++;
}
}
#define MAX_LEN 1000000
#define MAX_ARR_SIZE (MAX_LEN / 8)
int main()
{
char bit_array[MAX_ARR_SIZE];
unsigned int count = 0;
unsigned int index = 0;
unsigned int total = 0;
while (index < MAX_ARR_SIZE) {
bit_array[index++] = 0xff;
}
find_primer_bit(bit_array, MAX_LEN);
index = 1;
while (index < MAX_LEN) {
if (test_bit(bit_array, index)) {
total++;
printf("%-8d", index);
}
index++;
}
printf("
共计: %d 个质数
", total);
return 0;
}
执行结果
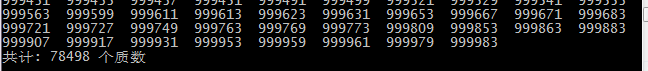
检测一下是否正确:
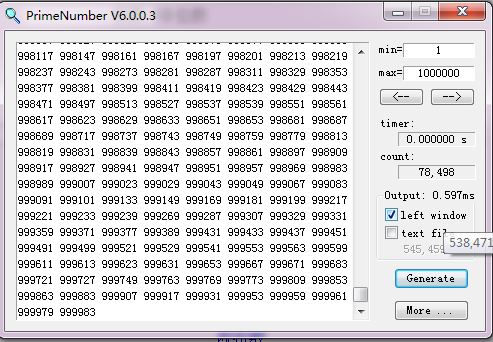
1000000万内有78498个质数
6.6计算每隔1000位质数个数:
统计一下每隔100000的质数
#define MAX_LEN 1000000
#define MAX_ARR_SIZE (MAX_LEN / 8)
int main()
{
char bit_array[MAX_ARR_SIZE];
unsigned int count = 0;
unsigned int index = 0;
unsigned int total = 0;
unsigned int limit = 100000;
while (index < MAX_ARR_SIZE) {
bit_array[index++] = 0xff;
}
find_primer_bit(bit_array, MAX_LEN);
index = 0;
while (index < MAX_LEN) {
if (index == limit) {
printf("%-6d %-6d avg: %5.2f
", index - 100000, index, (float)count / 100);
count = 0;
limit += 100000;
}
if (test_bit(bit_array, index)) {
count++;
total++;
}
index++;
}
printf("
共计: %d 个质数
", total);
while (1)
;
return 0;
}
