前言:
百度百科:
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集。MyBatis 可 以使用简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原生信息,将接口和 Java 的 POJOs(Plain Ordinary Java Object,普通的 Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录。
这篇文章讲解如何 使用mysql数据库,总结mybatis的一对一、一对多、多对多映射如何进行增删改查。
准备工作:
1.打开ecplise创建一个普通的java项目。项目结构如下图所示:
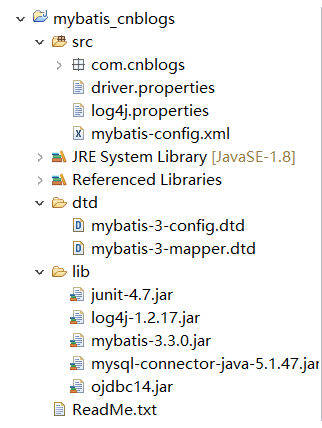
2.先看jar包,这次我们用到4个jar包,单元测试jar包junit-4.7.jar,日志包log4j-1.2.17.jar,mybatis所用的jar包以及连接mysql数据库用到的mysql-connector-java-5.1.47.jar
【ojdbc14.jar是连接oracle数据库用到的jar包】。
注:jar包记得build path
3.dtd约束文件:是对全局配置文件和sql映射文件的约束。在ecplise中点击 window --> preference ,在输入栏键入xml,然后选择 XML Catalog,点击Add。
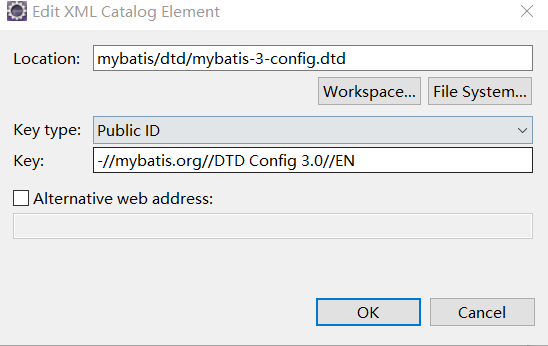
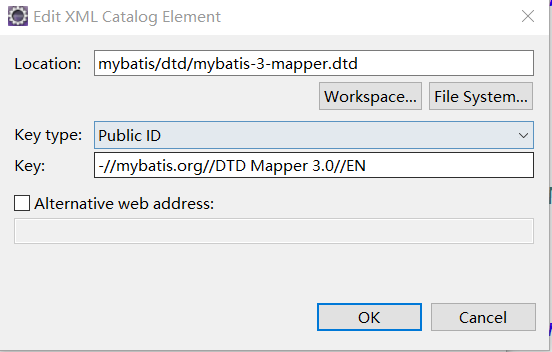
注:-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN 、-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN ,key值是规定的,location是点击workspace在项目中选择的约束文件。
4.driver.properties配置文件是连接数据库所用到的配置信息。在mybaits-config.xml中会用到。
#基于mysql数据库
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
#?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8为了支持中文数据的写入
url=jdbc:mysql://188.131.246.182:3306/cnblogs?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username=study
password=123456
#基于Oracle数据库
#driver=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
#url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:XE
#username=briup
#password=briup
5.log4j.properties是日志jar包要用到的配置文件。其中定义了输出日志级别、输出位置以及是否打印sql语句。
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d [%-5p] %c - %m%n
#show sql
log4j.logger.java.sql.ResultSet=INFO
log4j.logger.org.apache=INFO
log4j.logger.java.sql.Connection=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.Statement=DEBUG
log4j.logger.java.sql.PreparedStatement=DEBUG
6.全局配置文件:mybatis-config.xml。该文件的详细信息可网上找资料。我这里给一个简单能用的。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- dtd约束 -->
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd" >
<configuration>
<!-- properties必须是第一个子标签
定义变量,定义完成后,可以在后面的标签中使用
resource引入配置文件,优先级更高
-->
<properties resource="driver.properties">
<property name="driver" value=""/>
<property name="url" value=""/>
<property name="username" value=""/>
<property name="password" value=""/>
</properties>
<typeAliases>
<!-- 给包下的类定义别名 -->
<package name="com.cnblogs.bean"/>
</typeAliases>
<!-- 使用mysql数据库,如果要切换到Oracle数据库,default="oracle" -->
<environments default="mysql">
<!-- mysql -->
<environment id="mysql">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${url}" />
<property name="username" value="${username}" />
<property name="password" value="${password}" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
<!-- oracle -->
<environment id="oracle">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${url}" />
<property name="username" value="${username}" />
<property name="password" value="${password}" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/cnblogs/OneToMany/OneToMany.xml" />
</mappers>
</configuration>
准备工作完成以后就可以开始写sql语句了。
注:嵌套结果查询:一次查一张表,分多次查。
嵌套结果映射:一次查多张表,分别映射。
一对一映射
1.创建bean类:Student【学生】、FoodCard【饭卡】
Student.java

package com.cnblogs.bean; /** * 和饭卡一一对应 * CREATE TABLE `student` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(255) NOT NULL, `gender` varchar(255) NOT NULL, `age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) * */ public class Student { private Integer id; private String name; private String gender; private int age; public Student() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Student(String name, String gender, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.gender = gender; this.age = age; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(String gender) { this.gender = gender; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", gender=" + gender + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
FoodCard.java

package com.cnblogs.bean; /** * 饭卡,和学生一对一映射 * CREATE TABLE `food_card` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `number` varchar(255) NOT NULL, `balance` double DEFAULT NULL, `stu_id` int(11) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `stu_id` (`stu_id`), CONSTRAINT `stu_id` FOREIGN KEY (`stu_id`) REFERENCES `student` (`id`) ) * */ public class FoodCard { private Integer id; // 卡号 private String number; //余额 private Double balance; // 对应的学生 private Student stu; public FoodCard() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public FoodCard(String number, Double balance) { super(); this.number = number; this.balance = balance; } public FoodCard(String number, Double balance, Student stu) { super(); this.number = number; this.balance = balance; this.stu = stu; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(String number) { this.number = number; } public Double getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(Double balance) { this.balance = balance; } public Student getStu() { return stu; } public void setStu(Student stu) { this.stu = stu; } @Override public String toString() { return "FoodCard [id=" + id + ", number=" + number + ", balance=" + balance + ", stu=" + stu + "]"; } }
3.编写sql映射文件。首先告诉mybatis那个xml文件是你的映射文件。在mybatis的<Mappers>标签中添加一条
" <mapper resource="com/cnblogs/oneToOne/OneToOne.xml"/> " 按住Ctrl+鼠标左键点击跳转到xml映射文件代表配置成功。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- com.cnblogs.oneToOne.OneToOne是我们定义接口的全限定名字 这样就可以使用接口调用映射的SQL语句了 这个
名字一定要和接口对应上-->
<mapper namespace="com.cnblogs.oneToOne.OneToOne">
<!-- 插入一条学生信息 -->
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="Student" useGeneratedKeys="true"
keyProperty="id">
insert into student(name,gender,age)
values(#{name},#{gender},#{age})
</insert>
<!-- 插入一条饭卡信息 自动生成主键
#{number}代表调用getNumber()方法
-->
<insert id="insertFoodCard" parameterType="FoodCard" useGeneratedKeys="true"
keyProperty="id">
insert into food_card(number,balance,stu_id)
values(#{number},#{balance},#{stu.id})
</insert>
<!-- 删除一条饭卡信息-->
<delete id="deleteFoodCardById" parameterType="int">
delete from food_card where id=#{id}
</delete>
<!-- 根据学生id删除一条饭卡信息 -->
<delete id="deleteFoodCardByStuId" parameterType="int">
delete from food_card where stu_id=#{id}
</delete>
<!-- 删除一条学生信息 由于主键被饭卡表引用,需要级联删除,先调用deleteFoodCardByStuId -->
<delete id="deleteStudentById" parameterType="int">
delete from student where id=#{id}
</delete>
<!-- 模拟一个业务需求:假设一批学生毕业了,需要删除关于这批学生的所有饭卡信息 -->
<delete id="deleteFoodCardByStuIds" parameterType="java.util.List">
delete from food_card where stu_id in(
<foreach collection="list" item="stu" separator="," >
#{stu.id}
</foreach>
)
</delete>
<!-- 如果方法要传入两个参数,#{param1}代表第一个参数,#{param2}代表第二个参数 -->
<!-- 根据名字和年龄更改一条学生记录 -->
<update id="updateStudentByNameAndAge">
update student set age=21
where name=#{param1} and age=#{param2}
</update>
<!-- 一对一映射
查询两张表food_card和student,如何将student查到的记录映射到
FoodCard对象中?
-->
<resultMap type="Student" id="StudentMap">
<id column="id" property="id" />
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<result column="age" property="age"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- 嵌套结果映射 -->
<resultMap type="FoodCard" id="FoodCardMap">
<id column="id" property="id" />
<result column="number" property="number"/>
<result column="balance" property="balance"/>
<!-- 一对一映射,将很多列映射到stu属性上 -->
<association property="stu" resultMap="StudentMap" />
</resultMap>
<select id="selectFoodCardWithStudent" parameterType="int" resultMap="FoodCardMap">
select * from student stu,food_card fc
where fc.id=#{id} and fc.stu_id=stu.id
</select>
<!-- 嵌套结果查询 -->
<select id="selectStudentById" resultType="Student">
select * from student where id=#{id}
</select>
<resultMap type="FoodCard" id="FoodCardMap2">
<id column="id" property="id" />
<result column="number" property="number"/>
<result column="balance" property="balance"/>
<!-- 一对一 嵌套结果查询-->
<association property="stu" select="selectStudentById" column="stu_id"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectFoodCardWithStudent2" parameterType="int" resultMap="FoodCardMap2">
select * from food_card fc where fc.id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
*嵌套结果映射:
<!-- 嵌套结果映射 -->
<resultMap type="FoodCard" id="FoodCardMap">
<id column="id" property="id" />
<result column="number" property="number"/>
<result column="balance" property="balance"/>
<!-- 一对一映射,将很多列映射到stu属性上 -->
<association property="stu" resultMap="StudentMap" />
</resultMap>
<select id="selectFoodCardWithStudent" parameterType="int" resultMap="FoodCardMap">
select * from student stu,food_card fc where fc.id=#{id} and fc.stu_id=stu.id
</select>
resultMap标签,type属性表示和那种类型对应,id值起唯一标识作用,主键用id标签,表的其它列用result标签,column代表和数据库表对应的列,property
表示type值对应的属性【property指getXXX和setXXX】,column和property组合起来表示把查到的记录对应的列映射到对应的属性上。
嵌套结果查询的SQL语句,返回值不能再用resultType指定了,用resultMap指定。
注:嵌套结果映射中,如果两个表有同名的列,自然链接的时候只会保留一个列,上述中如果直接 'select * ' 会导致饭卡id和学生id一致。
必须显式的指定返回的列, ' select fc.id,fc.number,fc.balance,fc.stu_id,stu.id,stu.name,stu.age,stu.gender
from student stu,food_card fc where fc.id=#{id} and fc.stu_id=stu.id'。嵌套结果查询不需要显式指定。
*嵌套结果查询
<!-- 嵌套结果查询 -->
<select id="selectStudentById" resultType="Student">
select * from student where id=#{id}
</select>
<resultMap type="FoodCard" id="FoodCardMap2">
<id column="id" property="id" />
<result column="number" property="number"/>
<result column="balance" property="balance"/>
<!-- 一对一 嵌套结果查询-->
<association property="stu" select="selectStudentById" column="stu_id"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectFoodCardWithStudent2" parameterType="int" resultMap="FoodCardMap2">
select * from food_card fc where fc.id=#{id}
</select>
一次查一张表,多次查。<association property="stu" select="selectStudentById" column="stu_id"/>
property代表映射到那个属性,select代表调用那个方法,column指定当前查表返回的那个列作为方法的参数。如果
还需要再查一张表,按照规则再加一条<association>
所有的sql语句对应的接口中必须有该方法。

package com.cnblogs.oneToOne; import java.util.List; import com.cnblogs.bean.FoodCard; import com.cnblogs.bean.Student; public interface OneToOne { /** * 插入一条饭卡信息 */ public abstract void insertFoodCard(FoodCard foodCard); /** * 插入一条学生信息 */ public abstract void insertStudent(Student stu); /** * 删除一条饭卡记录 */ public abstract void deleteFoodCardById(Integer id); /** * 根据学生id删除一条饭卡记录 */ public abstract void deleteFoodCardByStuId(Integer id); /** * 删除一条学生记录根据id * 调用该方(法应该先调用deleteFoodCardByStuId(Integer) */ public abstract void deleteStudentById(Integer id); /** * 提供一批学生信息,删除对应的饭卡 */ public abstract void deleteFoodCardByStuIds(List<Student> stus); /** * 根据年龄和姓名更改一条学生记录 */ public abstract void updateStudentByNameAndAge(String name,Integer age); /** * 根据id查找饭卡的详细信息[包括学生属性] * 使用嵌套结果映射 */ public abstract FoodCard selectFoodCardWithStudent(Integer id); /** * 根据id查找学生记录 */ public abstract Student selectStudentById(Integer id); /** * 根据id查找饭卡的详细信息[包括学生属性] * 使用嵌套结果查询 */ public abstract FoodCard selectFoodCardWithStudent2(Integer id); }
单元测试类:

package com.cnblogs.jtest; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.ArrayList; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import org.junit.Test; import com.cnblogs.bean.FoodCard; import com.cnblogs.bean.Student; import com.cnblogs.oneToOne.OneToOne; import com.cnblogs.utils.MySqlSessionFactory; public class OneToOneTest { @Test public void insertStudent() { Student student1 = new Student("jack","男",20); Student student2 = new Student("Tina", "女", 16); InputStream inputStream; try{ // 读取配置文件 inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); // 手动提交事务 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(false); OneToOne mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OneToOne.class); mapper.insertStudent(student1); mapper.insertStudent(student2); // 提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void insertFoodCard() { Student stu1 = new Student(); stu1.setId(15); Student stu2 = new Student(); stu2.setId(16); FoodCard foodCard1 = new FoodCard("123456",100.0,stu1); FoodCard foodCard2 = new FoodCard("123457",312.4,stu2); InputStream inputStream; try{ // 读取配置文件 inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); OneToOne mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OneToOne.class); mapper.insertFoodCard(foodCard1); mapper.insertFoodCard(foodCard2); // 提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void deleteFoodCardById() { InputStream inputStream; try{ // 读取配置文件 inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); OneToOne mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OneToOne.class); mapper.deleteFoodCardById(5); // 提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void deleteStudentById() { InputStream inputStream; try{ // 读取配置文件 inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); OneToOne mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OneToOne.class); mapper.deleteFoodCardByStuId(6); mapper.deleteStudentById(6); // 提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void deleteFoodCardByStuIds() { InputStream inputStream; try{ // 读取配置文件 inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); OneToOne mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OneToOne.class); Student stu1 = new Student(); stu1.setId(5); Student stu2 = new Student(); stu2.setId(7); Student stu3 = new Student(); stu3.setId(10); ArrayList<Student> stus = new ArrayList<Student>(); stus.add(stu1); stus.add(stu2); stus.add(stu3); mapper.deleteFoodCardByStuIds(stus); // 提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @SuppressWarnings("unused") @Test public void updateStudentByNameAndAge() { SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { // 手动提交事务 sqlSession = MySqlSessionFactory.opensession(); OneToOne mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OneToOne.class); mapper.updateStudentByNameAndAge("jack", 20); sqlSession.commit(); } catch (IOException e) { if(sqlSession != null) sqlSession.rollback(); e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void selectFoodCardWithStudent() { SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { sqlSession = MySqlSessionFactory.opensession(); OneToOne mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OneToOne.class); FoodCard foodCard = mapper.selectFoodCardWithStudent(12); System.out.println(foodCard); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void selectFoodCardWithStudent2() { SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { sqlSession = MySqlSessionFactory.opensession(); OneToOne mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OneToOne.class); FoodCard foodCard = mapper.selectFoodCardWithStudent2(12); System.out.println(foodCard); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
获得SqlSesion对象的步骤重多,我们可以进行封装成一个工厂类。
package com.cnblogs.utils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
public class MySqlSessionFactory {
public static SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException{
// 读取配置文件
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
if(inputStream == null)
throw new IOException("配置文件路径不对或者配置文件内容出错");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
return sqlSessionFactory;
}
/**
*
* @param flag true 自动提交事务,false 手动提交事务
* @return
*/
public static SqlSession opensession(boolean flag) throws IOException{
return getSqlSessionFactory().openSession(flag);
}
/**
* 默认手动提交事务
* @return
*/
public static SqlSession opensession() throws IOException{
return opensession(false);
}
}
一对多映射
简单模拟一下映射关系,一个人只能有一个户籍所在地,而一个户籍所在地可以对应许多人。把外键放在一的那边。
1)pojo类:
Human.java

package com.cnblogs.bean; import java.util.Date; /** * create table human( * id int, * name varchar, * gender varchar, * age int, * dob datetime, * address_id int reference address(id) * ) * */ public class Human { private Integer id; private String name; private String gender; private Integer age; private Date dob; // 人对应的地址 private Address address; public Human() { super(); } public Human(String name, String gender, Integer age, Date dob) { super(); this.name = name; this.gender = gender; this.age = age; this.dob = dob; } public Human(String name, String gender, Integer age, Date dob, Address address) { super(); this.name = name; this.gender = gender; this.age = age; this.dob = dob; this.address = address; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(String gender) { this.gender = gender; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Date getDob() { return dob; } public void setDob(Date dob) { this.dob = dob; } public Address getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(Address address) { this.address = address; } @Override public String toString() { return "Human [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", gender=" + gender + ", age=" + age + ", dob=" + dob + ", address=" + address + "]"; } }
Address.java

package com.cnblogs.bean; import java.util.List; /** * table * address( * id int key, * province varchar, * city varchar, * street varchar * ) * */ public class Address { private Integer id; private String province; private String city; private String street; // 地址对应的人 private List<Human> humans; public Address() { super(); } public Address(String province, String city, String street) { super(); this.province = province; this.city = city; this.street = street; } public Address(String province, String city, String street, List<Human> humans) { super(); this.province = province; this.city = city; this.street = street; this.humans = humans; } public Address(Integer id, String province, String city, String street) { super(); this.id = id; this.province = province; this.city = city; this.street = street; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getProvince() { return province; } public void setProvince(String province) { this.province = province; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getStreet() { return street; } public void setStreet(String street) { this.street = street; } public List<Human> getHumans() { return humans; } public void setHumans(List<Human> humans) { this.humans = humans; } @Override public String toString() { return "Address [id=" + id + ", province=" + province + ", city=" + city + ", street=" + street + "]"; } }
2)在mybatis<Mappers>下加一条:<mapper resource="com/cnblogs/oneToMany/OneToMany.xml" />
3)编写OneToMany.xml和OneTomany.java接口
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- com.cnblogs.OneToMany.OneToMany是我们定义接口的全限定名字 这样就可以使用接口调用映射的SQL语句了 这个
名字一定要和接口对应上-->
<mapper namespace="com.cnblogs.oneToMany.OneToMany">
<!-- 插入一条地址信息 -->
<insert id="insertAddress" parameterType="Address"
useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into address(province,city,street)
values(#{province},#{city},#{street})
</insert>
<!-- 插入一条人类信息 -->
<insert id="insertHuman" parameterType="Human"
useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into human(name,gender,age,dob,address_id)
values(#{name},#{gender},#{age},#{dob},#{address.id})
</insert>
<!-- 删改类似,省略.... -->
<!-- 结果集映射
基础结果集,说明了如何从数据库加载对象
-->
<resultMap type="Address" id="addressBaseMap">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="province" column="province"/>
<result property="city" column="city"/>
<result property="street" column="street"/>
</resultMap>
<resultMap type="Human" id="humanBaseMap">
<id property="id" column="id" />
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="gender" column="gender"/>
<result property="age" column="age"/>
<result property="dob" column="dob"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- 结果集映射
一个人对应一个户籍,所以这里还是一对一映射
继承基础结果集
-->
<!-- 嵌套结果映射
继承:namespace + id 完全限定名
-->
<resultMap type="Human" id="humanMap"
extends="com.cnblogs.oneToMany.OneToMany.humanBaseMap">
<!-- 避免human的id和address的id起冲突,sql语句会给列起别名,相应的这里也需要更改 -->
<id property="id" column="hid" />
<association property="address" resultMap="addressBaseMap"></association>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectHumanWithAddressById" parameterType="int" resultMap="humanMap">
select h.id hid,h.name,h.gender,h.age,h.dob,a.*
from human h,address a
where h.id=#{id} and h.address_id = a.id
</select>
<!-- 一对多
一个户籍地对应多个人
-->
<!-- 嵌套结果映射 -->
<resultMap type="Address" id="AddressMap"
extends="com.cnblogs.oneToMany.OneToMany.addressBaseMap">
<!-- 避免human的id和address的id起冲突,sql语句会给列起别名,相应的这里也需要更改 -->
<id property="id" column="aid"/>
<!-- 一对多使用collection集合 -->
<collection property="humans" resultMap="humanBaseMap" />
</resultMap>
<!-- 嵌套结果映射sql语句 -->
<select id="selectAddressWithHumanById" parameterType="int" resultMap="AddressMap">
select a.id aid,a.province,a.city,a.street,h.*
from address a,human h
where a.id=#{id} and a.id=h.address_id
</select>
<!-- 嵌套结果查询 -->
<!-- 嵌套结果查询中被用到的另一条sql语句 -->
<select id="selectHumanByAddressId" parameterType="int" resultMap="humanBaseMap">
select * from human
where address_id=#{id}
</select>
<!-- 结果集 -->
<resultMap type="Address" id="AddressMap2"
extends="com.cnblogs.oneToMany.OneToMany.addressBaseMap">
<!-- 把id传过去 -->
<collection property="humans" select="selectHumanByAddressId" column="id" />
</resultMap>
<!-- 嵌套结果查询sql语句 -->
<select id="selectAddressWithHumanById2" parameterType="int" resultMap="AddressMap2">
select * from address
where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
OneTOMany.java

package com.cnblogs.oneToMany; import java.util.List; import com.cnblogs.bean.Address; import com.cnblogs.bean.Human; public interface OneToMany { /** * 插入一条地址信息 * @param address */ public abstract void insertAddress(Address address); /** * 插入一条人类信息 * @param humam */ public abstract void insertHuman(Human humam); /** * 根据id查询一条人类信息[包括户籍的详细信息] * @param id */ public abstract Human selectHumanWithAddressById(Integer id); /** * 嵌套结果映射 * 根据id查询一条户籍信息[包括户籍所在地人的信息] * @param id * @return */ public abstract Address selectAddressWithHumanById(Integer id); /** * 根据户籍地id查找人 * @param id * @return */ public abstract List<Human> selectHumanByAddressId(Integer id); /** * 嵌套结果查询 * 根据id查询一条户籍信息[包括户籍所在地人的信息] * @param id * @return */ public abstract Address selectAddressWithHumanById2(Integer id); }
4)测试类

package com.cnblogs.jtest; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Date; import java.util.List; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.junit.Test; import com.cnblogs.bean.Address; import com.cnblogs.bean.Human; import com.cnblogs.oneToMany.OneToMany; import com.cnblogs.utils.MySqlSessionFactory; public class OnetoManyTest { @Test public void insertHumanAndAddress() { try{ SqlSession sqlSession = MySqlSessionFactory.opensession(); OneToMany mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OneToMany.class); // 准备数据 Address address1 = new Address("湖南", "张家界", "步行街"); Address address2 = new Address("湖南", "长沙", "步行街"); mapper.insertAddress(address1); mapper.insertAddress(address2); //提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @SuppressWarnings("unused") @Test public void insertHuman() { SqlSession session = null; try { session = MySqlSessionFactory.opensession(); OneToMany mapper = session.getMapper(OneToMany.class); // 准备数据 Address address1 = new Address(); address1.setId(3); Address address2 = new Address(); address2.setId(4); Human human1 = new Human("jack","男",22,new Date(),address1); Human human2 = new Human("tom","男",20,new Date(),address2); Human human3 = new Human("tina","女",22,new Date(),address1); Human human4 = new Human("alias","女",18,new Date(),address1); // 插入数据 mapper.insertHuman(human1); mapper.insertHuman(human2); mapper.insertHuman(human3); mapper.insertHuman(human4); // 提交事务 session.commit(); } catch (IOException e) { if(session != null) session.close(); e.printStackTrace(); } } @SuppressWarnings("unused") @Test public void selectHumanWithAddressById() { SqlSession session = null; try { session = MySqlSessionFactory.opensession(); OneToMany mapper = session.getMapper(OneToMany.class); Human human1 = mapper.selectHumanWithAddressById(1); Human human2 = mapper.selectHumanWithAddressById(3); System.out.println("human: " + human1); System.out.println("human: " + human2); } catch (IOException e) { if(session != null) session.close(); e.printStackTrace(); } } @SuppressWarnings("unused") @Test public void selectAddressWithHumanById() { SqlSession session = null; try { session = MySqlSessionFactory.opensession(); OneToMany mapper = session.getMapper(OneToMany.class); Address address1 = mapper.selectAddressWithHumanById(3); Address address2 = mapper.selectAddressWithHumanById(4); System.out.println("address: " + address1); List<Human> humans1 = address1.getHumans(); System.out.println("humans : "); for(Human h : humans1) System.out.println(h); System.out.println("============================"); System.out.println("address: " + address2); List<Human> humans2 = address2.getHumans(); System.out.println("humans : "); for(Human h : humans2) System.out.println(h); } catch (IOException e) { if(session != null) session.close(); e.printStackTrace(); } } @SuppressWarnings("unused") @Test public void selectAddressWithHumanById2() { SqlSession session = null; try { session = MySqlSessionFactory.opensession(); OneToMany mapper = session.getMapper(OneToMany.class); Address address1 = mapper.selectAddressWithHumanById2(3); Address address2 = mapper.selectAddressWithHumanById2(4); System.out.println("address: " + address1); List<Human> humans1 = address1.getHumans(); System.out.println("humans : "); for(Human h : humans1) System.out.println(h); System.out.println("============================"); System.out.println("address: " + address2); List<Human> humans2 = address2.getHumans(); System.out.println("humans : "); for(Human h : humans2) System.out.println(h); } catch (IOException e) { if(session != null) session.close(); e.printStackTrace(); } } }
多对多
描述:一个老师可以讲多门课,一门课可以有多个老师教。
1)pojo类
Teacher.java

package com.cnblogs.bean; import java.util.List; /** * 教师类 * 和课程对多多 */ public class Teacher { // 教师id private Long id; // 教师名称 private String name; // 教师职称 讲师 高级讲师 教授 private String title; // 教师讲授的课程 private List<Course> courses; public Teacher() { super(); } public Teacher(String name, String title) { super(); this.name = name; this.title = title; } public Teacher(String name, String title, List<Course> courses) { super(); this.name = name; this.title = title; this.courses = courses; } public Teacher(Long id, String name, String title, List<Course> courses) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.title = title; this.courses = courses; } public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getTitle() { return title; } public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; } public List<Course> getCourses() { return courses; } public void setCourses(List<Course> courses) { this.courses = courses; } @Override public String toString() { return "Teacher [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", title=" + title + ", courses=" + courses + "]"; } }
Course.java

package com.cnblogs.bean; import java.util.List; /** * 课程类 * 和教师多对多 * */ public class Course { // 课程id private Long id; // 课程名称 private String name; // 课程描述 private String description; // 课程对应的老师 private List<Teacher> teachers; public Course() { super(); } public Course(String name, String description) { super(); this.name = name; this.description = description; } public Course(String name, String description, List<Teacher> teachers) { super(); this.name = name; this.description = description; this.teachers = teachers; } public Course(Long id, String name, String description, List<Teacher> teachers) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.description = description; this.teachers = teachers; } public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getDescription() { return description; } public void setDescription(String description) { this.description = description; } public List<Teacher> getTeachers() { return teachers; } public void setTeachers(List<Teacher> teachers) { this.teachers = teachers; } @Override public String toString() { return "Course [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", description=" + description + "]"; } }
桥表类:TeacherCourse.java

package com.cnblogs.bean; import java.util.Date; /** * 桥表类 * 连接教师类和课程类 * */ public class TeacherCourse { // id private Long id; // 授课开始时间 private Date begin; // 授课结束时间 private Date end; // 教师 private Teacher teacher; // 课程 private Course course; public TeacherCourse() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public TeacherCourse(Date begin, Date end) { super(); this.begin = begin; this.end = end; } public TeacherCourse(Date begin, Date end, Teacher teacher, Course course) { super(); this.begin = begin; this.end = end; this.teacher = teacher; this.course = course; } public TeacherCourse(Long id, Date begin, Date end, Teacher teacher, Course course) { super(); this.id = id; this.begin = begin; this.end = end; this.teacher = teacher; this.course = course; } public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public Date getBegin() { return begin; } public void setBegin(Date begin) { this.begin = begin; } public Date getEnd() { return end; } public void setEnd(Date end) { this.end = end; } public Teacher getTeacher() { return teacher; } public void setTeacher(Teacher teacher) { this.teacher = teacher; } public Course getCourse() { return course; } public void setCourse(Course course) { this.course = course; } @Override public String toString() { return "TeacherCourse [id=" + id + ", begin=" + begin + ", end=" + end + ", teacher=" + teacher + ", course=" + course + "]"; } }
2)在mybatis-config.xml的<Mappers>下加一条:<mapper resource="com/cnblogs/oneToMany/OneToMany.xml" />
3)sql映射文件
xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.cnblogs.manyTOMany.ManyToMany">
<!-- 结果集映射关系 -->
<resultMap type="Teacher" id="TeacherBaseMap">
<id property="id" column="t_id"/>
<result property="name" column="t_name"/>
<result property="title" column="t_title"/>
</resultMap>
<resultMap type="Course" id="CourseBaseMap">
<id property="id" column="c_id"/>
<result property="name" column="c_name"/>
<result property="description" column="c_des"/>
</resultMap>
<resultMap type="TeacherCourse" id="TeacherCourseBaseMap">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="begin" column="begin"/>
<result property="end" column="end"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- 插入 -->
<insert id="insertTeacher" parameterType="Teacher"
useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into teacher(t_name,t_title)
values(#{name},#{title})
</insert>
<insert id="insertCourse" parameterType="Course"
useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into course(c_name,c_des)
values(#{name},#{description})
</insert>
<insert id="insertTeacherCourse" parameterType="TeacherCourse"
useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into teacher_course(begin,end,t_id,c_id)
values(#{begin},#{end},#{teacher.id},#{course.id})
</insert>
<!-- 嵌套结果映射
其实就是一对多查询,因为桥表的存在
-->
<resultMap type="Teacher" id="TeacherMap1"
extends="com.cnblogs.manyTOMany.ManyToMany.TeacherBaseMap">
<collection property="courses" resultMap="CourseBaseMap" column="c_id" />
</resultMap>
<!-- sql语句 -->
<select id="selectTeacherWithCourseById" parameterType="long" resultMap="TeacherMap1">
select * from teacher t,course c,teacher_course tc
where t.t_id=#{id} and t.t_id=tc.t_id and tc.c_id=c.c_id
</select>
<!-- 嵌套结果查询 -->
<select id="selectCourseById" parameterType="long" resultMap="CourseBaseMap">
select * from course
where c_id=#{id}
</select>
<resultMap type="Teacher" id="TeacherMap2"
extends="com.cnblogs.manyTOMany.ManyToMany.TeacherBaseMap">
<collection property="courses" select="selectCourseById" column="c_id" />
</resultMap>
<select id="selectTeacherWithCourseById2" parameterType="long"
resultMap="TeacherMap2">
select * from teacher t,teacher_course tc
where t.t_id=#{id} and t.t_id=tc.t_id
</select>
</mapper>
接口:

package com.cnblogs.manyTOMany; import com.cnblogs.bean.Course; import com.cnblogs.bean.Teacher; import com.cnblogs.bean.TeacherCourse; public interface ManyToMany { /** * 插入一条教师数据 * @param teacher */ public abstract void insertTeacher(Teacher teacher); /** * 插入一条课程数据 * @param course */ public abstract void insertCourse(Course course); /** * 插入一条桥表数据 * @param tc */ public abstract void insertTeacherCourse(TeacherCourse tc); /** * 嵌套结果映射 * 教师的详细信息 * @param id * @return */ public abstract Teacher selectTeacherWithCourseById(Long id); /** * 嵌套结果查询 * @param id * @return */ public abstract Teacher selectTeacherWithCourseById2(Long id); }
4)测试类

package com.cnblogs.jtest; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Date; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.junit.Test; import com.cnblogs.bean.Course; import com.cnblogs.bean.Teacher; import com.cnblogs.bean.TeacherCourse; import com.cnblogs.manyTOMany.ManyToMany; import com.cnblogs.utils.MySqlSessionFactory; public class ManyToManyTest { @Test public void insertTeacher() { SqlSession session = null; try { session = MySqlSessionFactory.opensession(); ManyToMany mapper = session.getMapper(ManyToMany.class); // 准备数据 Teacher teacher1 = new Teacher("li","讲师"); Teacher teacher2 = new Teacher("zj","高级讲师"); Teacher teacher3 = new Teacher("kb","教授"); mapper.insertTeacher(teacher1); mapper.insertTeacher(teacher2); mapper.insertTeacher(teacher3); // 提交事务 session.commit(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void insertCourse() { SqlSession session = null; try { session = MySqlSessionFactory.opensession(); ManyToMany mapper = session.getMapper(ManyToMany.class); // 准备数据 Course course1 = new Course("core java","核心java基础"); Course course2 = new Course("c语言","ccc"); Course course3 = new Course("c++","c++++"); mapper.insertCourse(course1); mapper.insertCourse(course2); mapper.insertCourse(course3); // 提交事务 session.commit(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void insertTeacherCourse() { SqlSession session = null; try { session = MySqlSessionFactory.opensession(); ManyToMany mapper = session.getMapper(ManyToMany.class); // 准备数据 Course course1 = new Course(); course1.setId(1L); Course course2 = new Course(); course2.setId(2L); Course course3 = new Course(); course3.setId(3L); Teacher teacher1 = new Teacher(); teacher1.setId(4L); Teacher teacher2 = new Teacher(); teacher2.setId(5L); Teacher teacher3 = new Teacher(); teacher3.setId(6L); TeacherCourse tc1 = new TeacherCourse(new Date(),new Date(),teacher1,course1); TeacherCourse tc2 = new TeacherCourse(new Date(),new Date(),teacher2,course2); TeacherCourse tc3 = new TeacherCourse(new Date(),new Date(),teacher3,course3); mapper.insertTeacherCourse(tc1); mapper.insertTeacherCourse(tc2); mapper.insertTeacherCourse(tc3); // 提交事务 session.commit(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void selectTeacherWithCourseById() { SqlSession session = null; try { session = MySqlSessionFactory.opensession(); ManyToMany mapper = session.getMapper(ManyToMany.class); // 准备数据 Teacher t1 = mapper.selectTeacherWithCourseById(4L); Teacher t2 = mapper.selectTeacherWithCourseById(6L); System.out.println("Teacher: " + t1); System.out.println("Teacher: " + t2); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void selectTeacherWithCourseById2() { SqlSession session = null; try { session = MySqlSessionFactory.opensession(); ManyToMany mapper = session.getMapper(ManyToMany.class); // 准备数据 Teacher t1 = mapper.selectTeacherWithCourseById2(4L); Teacher t2 = mapper.selectTeacherWithCourseById2(6L); System.out.println("Teacher: " + t1); System.out.println("Teacher: " + t2); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
总结:
使用mybatis操作数据库,把配置文件配置好以后,就非常简单了,就像在sql命令行直接输入sql语句一样。
要分清嵌套结果映射和嵌套结果查询的区别。
* resultMap – 是最复杂也是最强大的元素,用来描述如何从数据库结果集中来加载对象。
* 一对一:重点掌握<association>标签在嵌套结果映射和嵌套结果查询中的使用
* 一对多:重点掌握<collection>标签在嵌套结果映射和嵌套结果查询中的使用
* 多对多:其实和一对多一样使用,不过多了一个桥接表。
mybatis还有更强大的功能:动态sql,将会在下篇使用。同时还会介绍mybatis generator软件【一款根据数据库的表自动生成pojo类和sql映射文件】
如何想了解更多mybatis,可以去看文档。中文文档网址:http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3。
