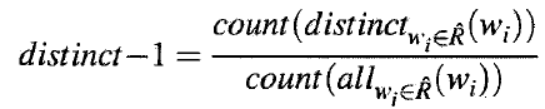1. Perplexity (PPL)
假设长度为 $n$ 的句子 $s=(w_1,w_2,...,w_n)$,它的 perplexity 定义为:
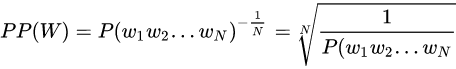
先取对数再取指数,则变换为下式:
![]()
由公式可知,句子概率越大,语言模型越好,迷惑度越小。
下面是一些 ngram 的概率计算:
![]()
![]()
![]()
2. BLEU
在自然语言处理中的机器翻译任务中, BLEU非常常见, 它是用于评估模型生成的句子(candidate)和实际句子(reference)的差异的指标.
它的取值范围在0.0到1.0之间, 如果两个句子完美匹配(perfect match), 那么BLEU是1.0, 反之, 如果两个句子完美不匹配(perfect mismatch), 那么BLEU为0.0.
首先给出两个句子计算 n-gram 精确度的公式:
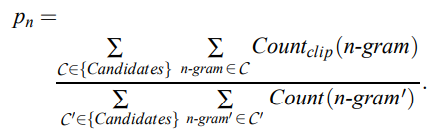
神经网络生成的句子是 candidate,给定的标准译文是 reference。
对于分子:
1)第一个求和符号统计的是所有的 candidate,因为计算时可能有多个句子,
2)第二个求和符号统计的是一条 candidate 中所有的 n−gram,而 表示某一个 n−gram 在 reference 中的个数。
所以整个分子就是在给定的 candidate 中有多少个 n-gram 词语出现在 reference 中。
对于分母:
前两个求和符号和分子中的含义一样,Count(n-gram') 表示 n−gram′在 candidate 中的个数,综上可知,分母是获得所有的 candidate 中 n-gram 的个数。
累积 N-Gram 得分指的是为各个 gram 对应的权重加权, 来计算得到一个加权几何平均(weighted geometric mean). 默认情况下, sentence_bleu()和corpus_bleu()
都是计算累积的 4-gram BLEU 分数的, 也称之为BLEU-4.

- BLEU 需要计算译文 1-gram,2-gram,...,N-gram 的精确率,一般 N 设置为 4 即可,公式中的 Pn 指 n-gram 的精确率。
- Wn 指 n-gram 的权重,一般设为均匀权重,即对于任意 n 都有 Wn = 1/N。
- BP 是惩罚因子,如果译文的长度小于最短的参考译文,则 BP 小于 1。
- BLEU 的 1-gram 精确率表示译文忠于原文的程度,而其他 n-gram 表示翻译的流畅程度。
一个 nltk 的参考代码:
from nltk.translate.bleu_score import sentence_bleu reference = [['this', 'is', 'small', 'test']] candidate = ['this', 'is', 'a', 'test'] score = sentence_bleu(reference, candidate) print(score) score = sentence_bleu(reference, candidate, weights=(0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25)) print(score)
3. distinct
在某些生成场景中(对话,广告文案)等,还需要追求文本的多样性。李纪为的《A diversity-promoting objective function for neural conversation models》
提出了Distinct指标,后续也被许多人采用。