目录·:
1、概述
2、设备号、设备节点
3、字符设备驱动框架
4、申请设备号
5、创建设备节点
6、实现文件IO接口--fops
7、应用程序控制驱动
8、驱动程序控制外设
1、概述:
linux中一切皆文件,设备也如此,并且以操作文件即文件IO的方式访问设备。
应用程序只能通过库函数中的系统调用来操作硬件,对于每个系统调用,驱动程序中都会有一个与之对应的函数,对于字符设备驱动,这些函数集中在file_operations结构体中。当应用程序使用系统调用read、write等函数访问设备时,最终会调用到file_opeartions中的成员,当然一开始fops中的只是一大堆函数指针的调用接口,具体的函数就需要我们在驱动中实现,实现对应操作函数后,与fops一对接,应用程序最终就能对硬件进行控制了。
那么问题来了,当应用程序使用系统调用访问设备时,linux系统怎么知道调用哪一个驱动的fops中的成员呢?
2、设备号、设备节点
设备号和驱动相关联
设备号是一个ID,设备节点就是驱动文件
字符设备和块设备是独立的,虽然设备号可能相同,但却是不同的设备
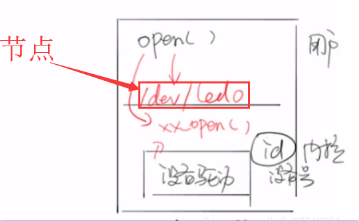
3、字符设备驱动框架
作为字符设备驱动要素: 1,必须有一个设备号,用在众多到设备驱动中进行区分 2,用户必须知道设备驱动对应到设备节点(设备文件) linux把所有到设备都看成文件 crw-r----- 1 root root 13, 64 Mar 28 20:14 event0 crw-r----- 1 root root 13, 65 Mar 28 20:14 event1 crw-r----- 1 root root 13, 66 Mar 28 20:14 event2 3,对设备操作其实就是对文件操作,应用空间操作open,read,write的时候 实际在驱动代码有对应到open, read,write
4、申请设备号
// 1、注册获取设备号 // 2、初始化设备 // 3、操作设备 file_operations – open release read write ioctl… // 4、两个宏定义 module_init module_exit // 5、注册设备号 register_chrdev_region // 6、cdev_init 初始化字符设备 // 7、cdev_add 添加字符设备到系统
1)向系统申请主设备号
int register_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char * name, const struct file_operations * fops) //参数: //1、major:主设备号 // 设备号(32bit–dev_t)==主设备号(高12bit) + 次设备号(低20bit) // 主设备号:表示一类设备—(如:camera) // 次设备号: 表示一类设备中某一个—(如:前置camera/后置camera) // 0 -->动态分配 ; 250 --> 给定整数,静态指定 //2、name: 描述设备信息,可自定义 // 在目录/proc/devices列举出了所有的已经注册的设备 //3、fops: 文件操作对象 // 提供open, read,write //返回值:成功-0,失败-负数
2)释放设备号
void unregister_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char * name)
3)例:主设备号的申请

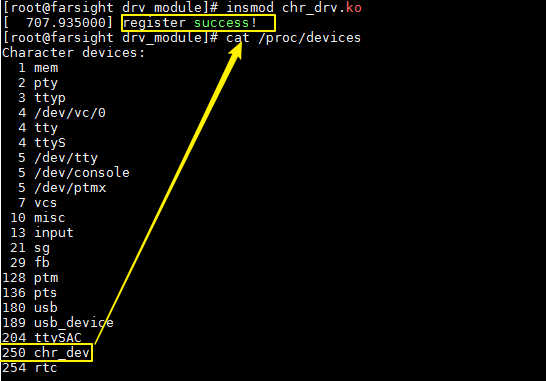
1 #include <linux/init.h> 2 #include <linux/module.h> 3 #include <linux/fs.h> 4 5 //静态指定 6 static int dev_major = 250; 7 8 const struct file_operations my_fops = {}; 9 10 static int __init chr_drv_init(void) 11 { 12 //申请设备号 13 int ret; 14 ret = register_chrdev(dev_major, "chr_dev", &my_fops); 15 if(ret == 0) 16 { 17 printk("register success! "); 18 } 19 else 20 { 21 printk("register failed! "); 22 return -EFAULT; 23 } 24 return 0; 25 } 26 27 static void __exit chr_drv_exit(void) 28 { 29 //释放设备号资源 30 unregister_chrdev(dev_major, "chr_dev"); 31 } 32 33 module_init(chr_drv_init); 34 module_exit(chr_drv_exit); 35 36 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
加载驱动前:
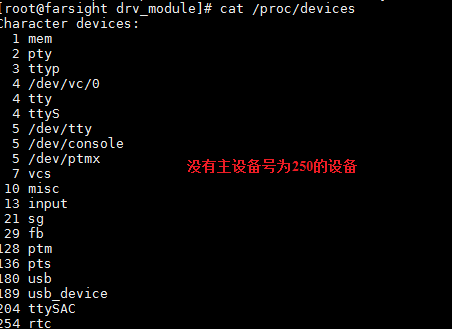
加载驱动后:
5、创建设备节点
1)手动创建
·· 缺点/dev/目录中文件都是在内存中,断电后/dev/文件就会消失
mknod /dev/设备名 类型 主设备号 次设备号 (主设备号要和驱动中申请的主设备号保持一致) 比如: mknod /dev/chr0 c 250 0
eg: [root@farsight drv_module]# ls /dev/chr0 -l crw-r--r-- 1 0 0 250, 0 Jan 1 00:33 /dev/chr0
2)自动创建
通过udev/mdev机制
struct class *class_create(owner, name)//创建一个类 //参数: //1、owner:THIS_MODULE //2、name :字符串名字,自定义 //返回: // 返回一个class指针
创建一个设备文件:
//创建一个设备文件 struct device *device_create(struct class * class, struct device * parent, dev_t devt, void * drvdata, const char * fmt,...) //参数: //1、class结构体,class_create调用之后的返回值 //2、表示父亲,一般直接填NULL //3、设备号类型 dev_t //4、私有数据,一般直接填NULL //5/6、表示可变参数,字符串,表示设备节点名字 设备号类型:dev_t devt #define MAJOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) >> MINORBITS)) //获取主设备号 #define MINOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) & MINORMASK)) //获取次设备号 #define MKDEV(ma,mi) (((ma) << MINORBITS) | (mi)) //生成设备号
销毁设备文件:
void device_destroy(devcls, MKDEV(dev_major, 0)); //参数: //1、class结构体,class_create调用之后到返回值 //2、设备号类型 dev_t void class_destroy(devcls); //参数:class结构体,class_create调用之后到返回值
3)示例:

1 #include <linux/init.h> 2 #include <linux/module.h> 3 #include <linux/fs.h> 4 #include <linux/device.h> 5 6 /* 7 设备号给定方式有两种: 8 1,动态--参数1直接填0 9 2,静态--指定一个整数,250 10 */ 11 static unsigned int dev_major = 250; 12 static unsigned int dev_minor = 0; 13 static struct class *devcls; 14 static struct device *dev; 15 16 const struct file_operations my_fops = { 17 18 }; 19 20 static int __init chr_dev_init(void) 21 { 22 //装载一般都是申请设备号资源 23 //申请设备号 24 int ret; 25 26 ret = register_chrdev(dev_major, "chr_dev_test", &my_fops); 27 if(ret == 0){ 28 printk("register ok "); 29 } 30 else{ 31 printk("register failed "); 32 return -EINVAL; 33 } 34 35 //自动创建设备节点 36 devcls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "chr_cls"); 37 dev = device_create(devcls,NULL,MKDEV(dev_major,dev_minor),NULL,"chr2"); 38 39 return 0; 40 } 41 42 static void __exit chr_dev_exit(void) 43 { 44 //卸载一般都是释放资源 45 46 //销毁节点和类 47 device_destroy(devcls,MKDEV(dev_major,dev_minor)); 48 class_destroy(devcls); 49 //释放设备号 50 unregister_chrdev(dev_major, "chr_dev_test"); 51 } 52 53 module_init 54 (chr_dev_init); 55 module_exit(chr_dev_exit); 56 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
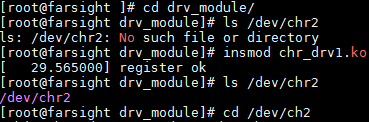
7、实现文件IO接口--fops
1)驱动中实现文件io操作接口:struct file_operations
1 struct file_operations { 2 struct module *owner; 3 loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int); 4 ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); 5 ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); 6 ssize_t (*aio_read) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t); 7 ssize_t (*aio_write) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t); 8 int (*iterate) (struct file *, struct dir_context *); 9 unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *); 10 long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); 11 long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); 12 int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *); 13 int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *); 14 .... 16 long (*fallocate)(struct file *file, int mode, loff_t offset, loff_t len); 17 int (*show_fdinfo)(struct seq_file *m, struct file *f); 18 }; //函数指针的集合,其实就是接口,我们写驱动到时候需要去实现 19 20 const struct file_operations my_fops = { 21 .open = chr_drv_open, 22 .read = chr_drv_read, 23 .write = chr_drv_write, 24 .release = chr_drv_close, 25 };
示例:

1 #include <linux/init.h> 2 #include <linux/module.h> 3 #include <linux/fs.h> 4 #include <linux/device.h> 5 6 /* 7 设备号给定方式有两种: 8 1,动态--参数1直接填0 9 2,静态--指定一个整数,250 10 */ 11 static unsigned int dev_major = 250; 12 static unsigned int dev_minor = 0; 13 static struct class *devcls; 14 static struct device *dev; 15 16 ssize_t chr_drv_write (struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *fpos) 17 { 18 printk("---------write %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 19 20 return 0; 21 } 22 23 ssize_t chr_drv_read (struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *fops) 24 { 25 printk("---------read %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 26 27 return 0; 28 } 29 30 int chr_drv_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) 31 { 32 printk("---------open %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 33 34 return 0; 35 } 36 37 int chr_drv_close (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) 38 { 39 printk("---------close %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 40 41 return 0; 42 } 43 44 45 46 const struct file_operations my_fops = { 47 .open = chr_drv_open, 48 .read = chr_drv_read, 49 .write = chr_drv_write, 50 .release = chr_drv_close 51 }; 52 53 static int __init chr_dev_init(void) 54 { 55 //装载一般都是申请设备号资源 56 //申请设备号 57 int ret; 58 59 ret = register_chrdev(dev_major, "chr_dev_test", &my_fops); 60 if(ret == 0){ 61 printk("register ok "); 62 } 63 else{ 64 printk("register failed "); 65 return -EINVAL; 66 } 67 68 //自动创建设备节点 69 devcls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "chr_cls"); 70 dev = device_create(devcls,NULL,MKDEV(dev_major,dev_minor),NULL,"chr2"); 71 72 return 0; 73 } 74 75 static void __exit chr_dev_exit(void) 76 { 77 //卸载一般都是释放资源 78 79 //销毁节点和类 80 device_destroy(devcls,MKDEV(dev_major,dev_minor)); 81 class_destroy(devcls); 82 //释放设备号 83 unregister_chrdev(dev_major, "chr_dev_test"); 84 } 85 86 module_init 87 (chr_dev_init); 88 module_exit(chr_dev_exit); 89 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
实现了底层的fops成员函数,再实现应用程序的调用
2)应用程序调用文件IO控制驱动 :open、read...

1 #include <linux/init.h> 2 #include <linux/module.h> 3 #include <linux/fs.h> 4 #include <linux/device.h> 5 6 /* 7 设备号给定方式有两种: 8 1,动态--参数1直接填0 9 2,静态--指定一个整数,250 10 */ 11 static unsigned int dev_major = 250; 12 static unsigned int dev_minor = 0; 13 static struct class *devcls; 14 static struct device *dev; 15 16 ssize_t chr_drv_write (struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *fpos) 17 { 18 printk("---------write %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 19 20 return 0; 21 } 22 23 ssize_t chr_drv_read (struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *fops) 24 { 25 printk("---------read %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 26 27 return 0; 28 } 29 30 int chr_drv_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) 31 { 32 printk("---------open %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 33 34 return 0; 35 } 36 37 int chr_drv_close (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) 38 { 39 printk("---------close %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 40 41 return 0; 42 } 43 44 45 46 const struct file_operations my_fops = { 47 .open = chr_drv_open, 48 .read = chr_drv_read, 49 .write = chr_drv_write, 50 .release = chr_drv_close 51 }; 52 53 static int __init chr_dev_init(void) 54 { 55 //装载一般都是申请设备号资源 56 //申请设备号 57 int ret; 58 59 ret = register_chrdev(dev_major, "chr_dev_test", &my_fops); 60 if(ret == 0){ 61 printk("register ok "); 62 } 63 else{ 64 printk("register failed "); 65 return -EINVAL; 66 } 67 68 //自动创建设备节点 69 devcls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "chr_cls"); 70 dev = device_create(devcls,NULL,MKDEV(dev_major,dev_minor),NULL,"chr2"); 71 72 return 0; 73 } 74 75 static void __exit chr_dev_exit(void) 76 { 77 //卸载一般都是释放资源 78 79 //销毁节点和类 80 device_destroy(devcls,MKDEV(dev_major,dev_minor)); 81 class_destroy(devcls); 82 //释放设备号 83 unregister_chrdev(dev_major, "chr_dev_test"); 84 } 85 86 module_init 87 (chr_dev_init); 88 module_exit(chr_dev_exit); 89 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <sys/types.h> 6 #include <sys/stat.h> 7 #include <fcntl.h> 8 9 int main(int argc, char * argv [ ]) 10 { 11 //调用驱动 12 int fd; 13 int value = 0; //buf 14 15 fd = open("/dev/chr2", O_RDWR); 16 if(fd < 0) 17 { 18 perror("open"); 19 exit(1); 20 } 21 22 read(fd, &value, 4); 23 24 write(fd, &value, 4); 25 26 close(fd); 27 28 return 0; 29 }

1 ROOTFS_DIR = /home/linux/source/rootfs#根文件系统路径 2 3 APP_NAME = chr_test 4 5 CROSS_COMPILE = /home/linux/toolchains/gcc-4.6.4/bin/arm-none-linux-gnueabi- 6 CC = $(CROSS_COMPILE)gcc 7 8 ifeq ($(KERNELRELEASE),) 9 10 KERNEL_DIR = /home/linux/kernel/linux-3.14-fs4412 #编译过的内核源码的路径 11 CUR_DIR = $(shell pwd) #当前路径 12 13 all: 14 make -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(CUR_DIR) modules #把当前路径编成modules 15 $CC $(APP_NAME).c -o $(APP_NAME) 16 @#make -C 进入到内核路径 17 @#M 指定当前路径(模块位置) 18 19 clean: 20 make -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(CUR_DIR) clean 21 22 install: 23 sudo cp -raf *.ko $(APP_NAME) $(ROOTFS_DIR)/drv_module #把当前的所有.ko文件考到根文件系统的drv_module目录 24 25 else 26 27 obj-m += chr_drv1.o #指定内核要把哪个文件编译成ko 28 29 endif
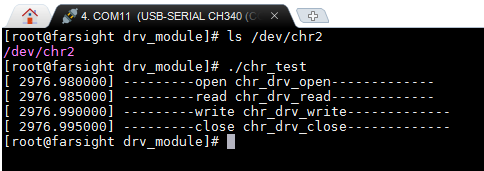
测试结果;
7、应用程序控制驱动
应用程序要控制驱动,就涉及用户空间与内核空间的数据交互,如何实现?通过以下函数:
1)copy_to_user
1 //将数据从内核空间拷贝到用户空间,一般是在驱动中chr_drv_read()用 2 int copy_to_user(void __user * to, const void * from, unsigned long n) 3 //参数: 4 //1:应用驱动中的一个buffer 5 //2:内核空间到一个buffer 6 //3:个数 7 //返回值:大于0,表示出错,剩下多少个没有拷贝成功等于0,表示正确
2)copy_from_user
1 //将数据从用户空间拷贝到内核空间,一般是在驱动中chr_drv_write()用 2 int copy_from_user(void * to, const void __user * from, unsigned long n) 3 //参数: 4 //1:内核驱动中的一个buffer 5 //2:应用空间到一个buffer 6 //3:个数
示例:

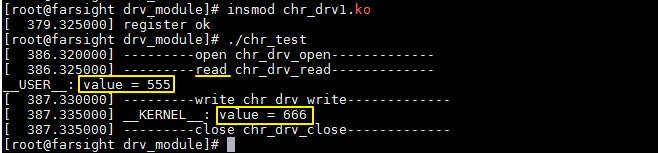
1 #include <linux/init.h> 2 #include <linux/module.h> 3 #include <linux/fs.h> 4 #include <linux/device.h> 5 #include <asm/uaccess.h> 6 7 8 /* 9 设备号给定方式有两种: 10 1,动态--参数1直接填0 11 2,静态--指定一个整数,250 12 */ 13 static unsigned int dev_major = 250; 14 static unsigned int dev_minor = 0; 15 static struct class *devcls; 16 static struct device *dev; 17 18 static int kernal_val = 555; 19 20 // 用户空间向内核空间传数据 21 ssize_t chr_drv_write (struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *fpos) 22 { 23 printk("---------write %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 24 25 int ret; 26 int value; //从用户空间获取到的数据存在value中 27 ret = copy_from_user(&value, buf, count); 28 if(ret > 0) 29 { 30 printk("copy_from_user"); 31 return -EFAULT; 32 } 33 34 printk("__KERNEL__: value = %d ", value); 35 36 return 0; 37 } 38 39 // read(fd, buf, size) 用户空间获取内核空间的数据 40 ssize_t chr_drv_read (struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *fops) 41 { 42 printk("---------read %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 43 44 int ret; 45 ret = copy_to_user(buf, &kernal_val, count); 46 if(ret > 0) 47 { 48 printk("copy_to_user"); 49 return -EFAULT; 50 } 51 52 return 0; 53 } 54 55 int chr_drv_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) 56 { 57 printk("---------open %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 58 59 return 0; 60 } 61 62 int chr_drv_close (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) 63 { 64 printk("---------close %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 65 66 return 0; 67 } 68 69 70 71 const struct file_operations my_fops = { 72 .open = chr_drv_open, 73 .read = chr_drv_read, 74 .write = chr_drv_write, 75 .release = chr_drv_close 76 }; 77 78 static int __init chr_dev_init(void) 79 { 80 //装载一般都是申请设备号资源 81 //申请设备号 82 int ret; 83 84 ret = register_chrdev(dev_major, "chr_dev_test", &my_fops); 85 if(ret == 0){ 86 printk("register ok "); 87 } 88 else{ 89 printk("register failed "); 90 return -EINVAL; 91 } 92 93 //自动创建设备节点 94 devcls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "chr_cls"); 95 dev = device_create(devcls,NULL,MKDEV(dev_major,dev_minor),NULL,"chr2"); 96 97 return 0; 98 } 99 100 static void __exit chr_dev_exit(void) 101 { 102 //卸载一般都是释放资源 103 104 //销毁节点和类 105 device_destroy(devcls,MKDEV(dev_major,dev_minor)); 106 class_destroy(devcls); 107 //释放设备号 108 unregister_chrdev(dev_major, "chr_dev_test"); 109 } 110 111 module_init 112 (chr_dev_init); 113 module_exit(chr_dev_exit); 114 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <sys/types.h> 6 #include <sys/stat.h> 7 #include <fcntl.h> 8 9 10 int main(int argc, char * argv [ ]) 11 { 12 //调用驱动 13 int fd; 14 int value = 0; //buf 15 16 fd = open("/dev/chr2", O_RDWR); 17 if(fd < 0) 18 { 19 perror("open"); 20 exit(1); 21 } 22 23 read(fd, &value, 4); //应用程序从内核获取4字节数据存放在value中 24 printf("__USER__: value = %d ", value); //打印获取的值 25 sleep(1); //sleep1秒,防止串口打印信息不完整 26 27 //重新给value赋值,传给内核 28 value = 666; 29 write(fd, &value, 4); 30 31 32 close(fd); 33 34 return 0; 35 }
测试:
8、驱动程序控制外设
之前我们了解了应用程序如何与内核空间进行数据交互,那么内核驱动与外设间的控制是怎么样的?
写过裸机程序的都知道,可以通过修改外设对应的控制寄存器来控制外设,即向寄存器的地址写入数据,这个地址就是物理地址,且物理地址是已知的,有硬件设计决定。
在内核中,同样也是操作地址控制外设,但是内核中的地址,是经过MMU映射后的虚拟地址,而且CPU通常并没有为这些已知的外设I/O内存资源的物理地址预定义虚拟地址范围,驱动程序并不能直接通过物理地址访问I/O内存资源,而必须将它们映射到核心虚地址空间内,然后才能根据映射所得到的核心虚地址范围,通过访内指令访问这些I/O内存资源。Linux在io.h头文件中声明了函数ioremap(),用来将I/O内存资源的物理地址映射到核心虚地址空间中

ioremap的函数如下:
1 //映射虚拟地址 2 void *ioremap(cookie, size) 3 //参数: 4 //1、cookie:物理地址 5 //2、size:长度(连续映射一定长度的地址空间) 6 //返回值:虚拟地址
解除映射:
1 //去映射--解除映射 2 void iounmap(void __iomem *addr) 3 //参数:映射后的虚拟地址
实例:通过驱动控制LED灯
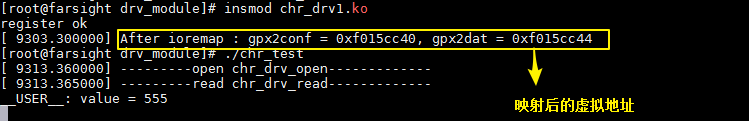
LED —— GPX2_7 —— GPX2CON —— 0x11000C40
GPX2DAT—— 0x11000C44
将0x11000c40映射为虚拟地址

1 #include <linux/init.h> 2 #include <linux/module.h> 3 #include <linux/fs.h> 4 #include <linux/device.h> 5 #include <asm/uaccess.h> 6 #include <asm/io.h> 7 8 //物理地址 9 #define GPX2CON 0x11000C40 10 #define GPX2_SIZE 8 11 12 //存放虚拟地址的指针 13 volatile unsigned long *gpx2conf; 14 volatile unsigned long *gpx2dat; 15 16 static unsigned int dev_major = 250; 17 static unsigned int dev_minor = 0; 18 static struct class *devcls; 19 static struct device *dev; 20 21 static int kernal_val = 555; 22 23 // 用户空间向内核空间传数据 24 ssize_t chr_drv_write (struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *fpos) 25 { 26 27 int ret; 28 int value; //从用户空间获取到的数据存在value中 29 ret = copy_from_user(&value, buf, count); 30 if(ret > 0) 31 { 32 printk("copy_from_user"); 33 return -EFAULT; 34 } 35 36 if(value) //根据用户传递的值决定灯的亮灭 37 { 38 *gpx2dat |= (0x1<<7); 39 }else 40 { 41 *gpx2dat &= ~(0x1<<7); 42 } 43 44 return 0; 45 } 46 47 // read(fd, buf, size) 用户空间获取内核空间的数据 48 ssize_t chr_drv_read (struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *fops) 49 { 50 printk("---------read %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 51 52 int ret; 53 ret = copy_to_user(buf, &kernal_val, count); 54 if(ret > 0) 55 { 56 printk("copy_to_user"); 57 return -EFAULT; 58 } 59 60 return 0; 61 } 62 63 int chr_drv_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) 64 { 65 printk("---------open %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 66 67 return 0; 68 } 69 70 int chr_drv_close (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) 71 { 72 printk("---------close %s------------- ",__FUNCTION__); 73 74 return 0; 75 } 76 77 78 79 const struct file_operations my_fops = { 80 .open = chr_drv_open, 81 .read = chr_drv_read, 82 .write = chr_drv_write, 83 .release = chr_drv_close, 84 }; 85 86 static int __init chr_dev_init(void) 87 { 88 //装载一般都是申请设备号资源 89 //申请设备号 90 int ret; 91 92 ret = register_chrdev(dev_major, "chr_dev_test", &my_fops); 93 if(ret == 0){ 94 printk("register ok "); 95 } 96 else{ 97 printk("register failed "); 98 return -EINVAL; 99 } 100 101 //自动创建设备节点 102 devcls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "chr_cls"); 103 dev = device_create(devcls,NULL,MKDEV(dev_major,dev_minor),NULL,"chr2"); 104 105 //对地址进行映射 106 gpx2conf = ioremap(GPX2CON, GPX2_SIZE); //映射两个寄存器 107 gpx2dat = gpx2conf + 1; 108 109 printk("After ioremap : gpx2conf = 0x%p, gpx2dat = 0x%p ",gpx2conf,gpx2dat); 110 111 //配置GPIO为输出功能 112 *gpx2conf &= ~(0xf << 28); 113 *gpx2conf |= (0x1 << 28); 114 115 return 0; 116 } 117 118 static void __exit chr_dev_exit(void) 119 { 120 //卸载一般都是释放资源 121 iounmap(gpx2conf); 122 123 //销毁节点和类 124 device_destroy(devcls,MKDEV(dev_major,dev_minor)); 125 class_destroy(devcls); 126 //释放设备号 127 unregister_chrdev(dev_major, "chr_dev_test"); 128 } 129 130 module_init 131 (chr_dev_init); 132 module_exit(chr_dev_exit); 133 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <sys/types.h> 6 #include <sys/stat.h> 7 #include <fcntl.h> 8 9 10 int main(int argc, char * argv [ ]) 11 { 12 //调用驱动 13 int fd; 14 int value = 0; //buf 15 16 fd = open("/dev/chr2", O_RDWR); 17 if(fd < 0) 18 { 19 perror("open"); 20 exit(1); 21 } 22 23 read(fd, &value, 4); //应用程序从内核获取4字节数据存放在value中 24 printf("__USER__: value = %d ", value); //打印获取的值 25 sleep(1); //sleep1秒,防止串口打印信息不完整 26 27 //应用程序控制灯 28 while(1) 29 { 30 value = 0; 31 write(fd, &value, 4); 32 sleep(1); 33 34 value = 1; 35 write(fd, &value, 4); 36 sleep(1); 37 } 38 39 40 close(fd); 41 42 return 0; 43 }
测试:
执行app后,可以看到LED等以一秒的间隔亮灭
