题目描述
Zero has an old printer that doesn't work well sometimes. As it is antique, he still like to use it to print articles. But it is too old to work for a long time and it will certainly wear and tear, so Zero use a cost to evaluate this degree.
One day Zero want to print an article which has N words, and each word i has a cost Ci to be printed. Also, Zero know that print k words in one line will cost
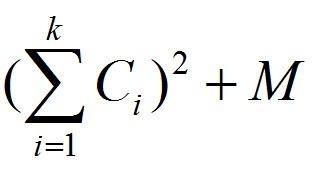
M is a const number.
Now Zero want to know the minimum cost in order to arrange the article perfectly.
输入输出格式
输入格式
There are many test cases. For each test case, There are two numbers N and M in the first line (0 ≤ (N) ≤ 500000, 0 ≤ (M) ≤ 1000). Then, there are (N) numbers in the next 2 to (N+1) lines. Input are terminated by EOF.
输出格式
A single number, meaning the mininum cost to print the article.
题意
有(N)个数,将序列分为若干段,代价为每一段的和的平方加常数(M),求最小代价。
思路
这是一道比较基础的斜率优化DP的题
首先,我们可以推出最基础的DP状态转移
我们定义(dp_i)为前i个数的最小代价,则
(dp_i=min(dp_j+(sum_i-sum_j)^2+M)) ((sum_i)表示序列前(i)个数的前缀和)
显然,这个状态转移方程的复杂度为(O(n^2))
但这个题里(n≤500000)显然是会超时的,那么我们可以使用斜率优化DP降低复杂度
我们假设在求解(dp_i)时,有两个决策点(k<j<i),且(j)更优。
那么,
(dp_j+( sum_i-sum_j )^2 < dp_k+( sum_i-sum_k )^2)
(Longrightarrow) (dp_j+sum_i^2-2sum_i*sum_j+sum_j^2 < dp_k+sum_i^2-2sum_i*sum_k+sum_k^2)
(Longrightarrow) (( dp_j+sum_j^2 )-( dp_k+sum_k^2 ) < 2sum_i*( sum_j-sum_k ))
(Longrightarrow) (frac{( dp_j+sum_j^2 )-( dp_k+sum_k^2 )}{2( sum_j-sum_k )} < sum_i)
记(dp_j+sum_j^2)为(y_j),(dp_k+sum_k^2)为(y_k),(sum_j)为(x_j),(sum_k)为(x_k)
即 (frac{y_j-y_k}{2*( x_j-x_k )}<sum_i)
令(g_{kj}=frac{y_j-y_k}{x_j-x_k}),我们可以看出以下两点:
1、如果不等式成立,那就说明(j)比(k)优,而且随着(i)的增大不等式一定是成立的,也就是说之后对(i)算DP时(j)都比(k)优,所以(k)可以淘汰。
2、如果(k<j<i),而且(g_{kj}>g_{ji})那么(j)就可以淘汰。假设(g_{ji}<sum_i)就是(i)比(j)优,即(j)可淘汰。反之如果(g_{ji}>sum_i)那么同样有g_{kj}>sum_i,那么(k)比(j)优,(j)也可淘汰
所以我们相当于在维护一个下凸的图形,斜率不断变大,我们就可以通过一个队列进行维护。
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn=5e5+5;
int dp[maxn],sum[maxn],q[maxn],n,m,a[maxn];
int calc_up(int j,int k) {
return dp[j]+sum[j]*sum[j]-(dp[k]+sum[k]*sum[k]);//分子
}
int calc_down(int j,int k) {
return 2*(sum[j]-sum[k]);//分母
}
signed main() {
while(cin>>n>>m) {
sum[0]=dp[0]=0;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
cin>>a[i];
sum[i]=sum[i-1]+a[i];//前缀和
}
int l=1,r=0;//初始化
q[++r]=0;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
while(l+1<=r && calc_up(q[l+1],q[l])<=sum[i]*calc_down(q[l+1],q[l])) l++;
int j=q[l];//最优的决策点
dp[i]=dp[j]+m+(sum[i]-sum[j])*(sum[i]-sum[j]);
while(l+1<=r && calc_up(i,q[r])*calc_down(q[r],q[r-1])<=calc_up(q[r],q[r-1])*calc_down(i,q[r])) r--;
q[++r]=i;
}
cout<<dp[n]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}