1.ecxcel导入导出的实现
1.创建Book类,并编写set方法和get方法

package com.bean; public class Book { private int id; private String name; private String type; // public int a; public String getType() { System.out.println("调用了类型方法"); return type; } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; } // public void test (String name,int a){ // System.out.println("调用了多参数的方法"); // } public String getName() { System.out.println("调用了名称方法"); return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getId() { System.out.println("调用了序号方法"); return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } }
2.创建ExcelBook类实现导入导出

package com.main; import java.io.File; import java.util.ArrayList; import com.bean.Book; import jxl.Cell; import jxl.Sheet; import jxl.Workbook; import jxl.write.Label; import jxl.write.WritableSheet; import jxl.write.WritableWorkbook; public class ExcelBook { public static void main(String[] args) { ExcelBook excelBook = new ExcelBook(); //创建集合 // ArrayList<Book> arrayList = new ArrayList<Book>(); // Book book = new Book(); // book.setId(1); // book.setName("Java语言"); // book.setType("面向对象"); // Book book1 = new Book(); // book1.setId(2); // book1.setName("西游记"); // book1.setType("故事"); // Book book2 = new Book(); // book2.setId(3); // book2.setName("高数"); // book2.setType("难"); // arrayList.add(book); // arrayList.add(book1); // arrayList.add(book2); // excelBook.excelOut(arrayList); ArrayList<Book> ar1 = excelBook.excelIn(); for(Book bo2 : ar1){ System.out.println(bo2.getId()+" "+bo2.getName()+" "+bo2.getType()); } } public void excelOut(ArrayList<Book>arrayList){ WritableWorkbook bookk = null;//Excle对象 try { //创建excel对象 bookk = Workbook.createWorkbook(new File("D:/Sourcecode/Java/fanshe/book.xls")); //通过excel对象创建一个选项卡 WritableSheet sheet = bookk.createSheet("sheet1", 0); //创建一个单元格对象参数为 列 行 值 for(int i = 0; i < arrayList.size();i++){ Book bo = arrayList.get(i); Label la1 = new Label(0, i,String.valueOf(bo.getId())); Label la2 = new Label(1, i,bo.getName()); Label la3 = new Label(2, i, bo.getType()); sheet.addCell(la1);//放入选项卡中 sheet.addCell(la2); sheet.addCell(la3); } //写入目标路径 bookk.write(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { bookk.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public ArrayList<Book> excelIn(){ ArrayList<Book> ar = new ArrayList<Book>();//返回集合 Workbook book = null; try { //获取到excle对象 book = Workbook.getWorkbook(new File("D:/Sourcecode/Java/fanshe/book.xls"));//文件路径 Sheet sheet = book.getSheet(0);//获取第一个选项卡对象(第零列) for(int i = 0; i < sheet.getRows();i++){//向文件中读入值,getRows()获取数据中有多少条数据 Book bo = new Book(); Cell cell = sheet.getCell(0,i);//cell对象为单元格对象,取出数据i行0列 bo.setId(Integer.valueOf(cell.getContents()));//getContents获取单元格对象的值 bo.setName(sheet.getCell(1,i).getContents()); bo.setType(sheet.getCell(2,0).getContents()); ar.add(bo); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ book.close(); } return ar; } }
运行结果:导出时,在指定路径出现下图内容
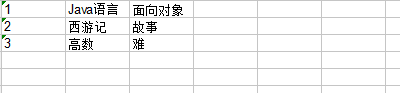
导出时结果如下:
调用了序号方法 调用了名称方法 调用了类型方法 1 Java语言 面向对象 调用了序号方法 调用了名称方法 调用了类型方法 2 西游记 面向对象 调用了序号方法 调用了名称方法 调用了类型方法 3 高数 面向对象
此方法虽然可以实现excel的导入导出,但因导入导出的数据信息比较少,但如果数据信息比较多,此方法实现起来非常麻烦,所以应该利用java反射机制实现。
2.利用反射实现通用的excel导入导出
如果一个项目中存在多种信息的导入导出,为了简化代码,就需要用反射实现通用的excel导入导出
实例代码如下:
1.创建一个 Book类,并编写set和get方法
1 package com.bean; 2 3 public class Book { 4 private int id; 5 private String name; 6 private String type; 7 // public int a; 8 9 public String getType() { 10 System.out.println("调用了类型方法"); 11 return type; 12 } 13 14 public void setType(String type) { 15 this.type = type; 16 } 17 // public void test (String name,int a){ 18 // System.out.println("调用了多参数的方法"); 19 // } 20 21 public String getName() { 22 System.out.println("调用了名称方法"); 23 return name; 24 } 25 26 public void setName(String name) { 27 this.name = name; 28 } 29 30 public int getId() { 31 System.out.println("调用了序号方法"); 32 return id; 33 } 34 35 public void setId(int id) { 36 this.id = id; 37 } 38 39 }
2.创建一个ExcelUtil类,实现导入导出

1 package com.util; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.lang.reflect.Field; 5 import java.util.ArrayList; 6 7 import com.bean.Book; 8 9 import jxl.Sheet; 10 import jxl.Workbook; 11 import jxl.write.Label; 12 import jxl.write.WritableSheet; 13 import jxl.write.WritableWorkbook; 14 15 public class ExcelUtil { 16 //第一个参数为要导出的数据的实体类的对象,实例类不确定,第二个参数为导入路径 17 public static void excleOut(ArrayList ar,String str){ 18 WritableWorkbook book = null;//编写WritableWorkbook对象,该对象代表了excel对象 19 try { 20 book = Workbook.createWorkbook(new File(str));//创建文件路径str 21 WritableSheet sheet = book.createSheet("sheet",0);//获取sheet对象 22 //对集合进行遍历 23 for(int i = 0; i < ar.size();i++){ 24 Object ob = ar.get(i);//集合中的对象不确定,用Object代替 25 //利用反射机制 26 Class cl = ob.getClass();//运行时获得传递过来的对象 27 Field[] fi = cl.getDeclaredFields();//获取所有属性的对象,用来获取属性 28 for(int j = 0; j <fi.length;j++){//将获得的对象遍历出来 29 fi[j].setAccessible(true);//启用访问权限 30 //获取值 列(j),行(i),值fi[j]为字符串方式 31 Label la = new Label(j, i, String.valueOf(fi[j].get(ob))); 32 sheet.addCell(la);//将数据写入sheet对象中 33 } 34 } 35 book.write(); 36 } catch (Exception e) { 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 }finally{ 39 try { 40 book.close(); 41 } catch (Exception e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 //第一个参数为要导入的数据的实体类的对象,第二个参数为导入路径 47 public static ArrayList excleIn(Class cl,String str){ 48 ArrayList ar =new ArrayList();//创建空的集合用于存储数据 49 Workbook book = null;//声明一个workbook对象 50 try { 51 book =Workbook.getWorkbook(new File(str));//获取到类对象 52 Sheet sheet = book.getSheet(0);//获取sheet对象 53 Field []fi = cl.getDeclaredFields();//获取类属性信息 54 for(int i = 0;i < sheet.getRows();i++){//对读取进来的excle数据进行遍历 55 Object ob = cl.newInstance();//创建实例化对象,创建新的存储数据的对象,用Object对象代替 56 //将所有的属性封装到对象中 57 for(int j = 0;j <fi.length;j++){//将属性进行循环 58 fi[i].setAccessible(true);//启用属性访问权限 59 String con = sheet.getCell(j,i).getContents();//从excel中读取数据 60 //判断属性的类型 61 if(fi[j].getType().toString().equals("Class java.lang.String")){ 62 //将读入的数据(在con中)封装到对象(ob)的属性(fi[i])中 63 fi[j].set(ob,con);//ob.id=con正常方法 64 }else if(fi[j].getType().toString().equals("int")){ 65 fi[j].setInt(ob,Integer.valueOf(con));//将信息封装到对象中 66 }else if(fi[j].getType().toString().equals("Integer")){ 67 fi[j].setInt(ob,Integer.valueOf(con));//将信息封装到对象中 68 } 69 70 ar.add(ob); 71 } 72 } 73 } catch (Exception e) { 74 e.printStackTrace(); 75 }finally{ 76 book.close(); 77 } 78 return ar; 79 80 } 81 82 public static void main(String[] args) { 83 // ArrayList<Book> arrayList = new ArrayList<Book>(); 84 // Book book = new Book(); 85 // book.setId(1); 86 // book.setName("Java语言"); 87 // book.setType("面向对象"); 88 // Book book1 = new Book(); 89 // book1.setId(2); 90 // book1.setName("西游记"); 91 // book1.setType("故事"); 92 // Book book2 = new Book(); 93 // book2.setId(3); 94 // book2.setName("高数"); 95 // book2.setType("难"); 96 // arrayList.add(book); 97 // arrayList.add(book1); 98 // arrayList.add(book2); 99 // ExcelUtil.excleOut(arrayList,"D:/Sourcecode/Java/fanshe/book1.xls"); 100 //导入的数据位Book类型 101 ArrayList<Book> ar = ExcelUtil.excleIn(Book.class,"D:/Sourcecode/Java/fanshe/book1.xls"); 102 for(Book bo:ar){ 103 System.out.println(bo.getId()+" "+bo.getName()+" "+bo.getType()); 104 } 105 } 106 107 }
运行结果:导出时在指定路径出现excel表格,上面显示导出的数据,如下图所示:

导入时,在控制台输出表格中的信息
