给定一个根为 root 的二叉树,每个节点的深度是 该节点到根的最短距离 。
如果一个节点在 整个树 的任意节点之间具有最大的深度,则该节点是 最深的 。
一个节点的 子树 是该节点加上它的所有后代的集合。
返回能满足 以该节点为根的子树中包含所有最深的节点 这一条件的具有最大深度的节点。
注意:本题与力扣 1123 重复:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-deepest-leaves/
示例 1:
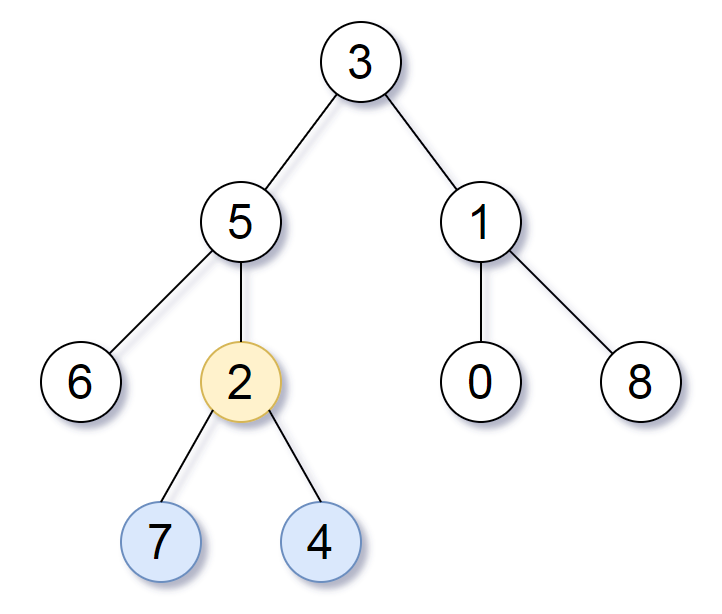
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
输出:[2,7,4]
解释:
我们返回值为 2 的节点,在图中用黄色标记。
在图中用蓝色标记的是树的最深的节点。
注意,节点 5、3 和 2 包含树中最深的节点,但节点 2 的子树最小,因此我们返回它。
示例 2:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]
解释:根节点是树中最深的节点。
示例 3:
输入:root = [0,1,3,null,2]
输出:[2]
解释:树中最深的节点为 2 ,有效子树为节点 2、1 和 0 的子树,但节点 2 的子树最小。
提示:
树中节点的数量介于 1 和 500 之间。
0 <= Node.val <= 500
每个节点的值都是独一无二的。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。

/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { Map<TreeNode,Integer>depth; int max_depth; public TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode root) { depth=new HashMap(); depth.put(null,-1); dfs(root,null); max_depth=-1; for(Integer d:depth.values()){ max_depth=Math.max(max_depth,d); } return ans(root); } public void dfs(TreeNode node,TreeNode parent){ if(node!=null){ depth.put(node,depth.get(parent)+1); dfs(node.left,node); dfs(node.right,node); } } public TreeNode ans(TreeNode node){ if(node==null||depth.get(node)==max_depth)return node; TreeNode L=ans(node.left); TreeNode R=ans(node.right); if(L!=null&&R!=null)return node; if(L!=null)return L; if(R!=null)return R; return null; } }