一:time模块
时间的表示形式:
在python中对于时间的表示形式有:时间戳,元组(struct_time),格式化的时间字符串
import time #1,时间戳 print(time.time()) #打印当时的时间戳 """1493195132.1191132""" #2,时间元组 print(time.localtime()) #打印当时的时间元组 """time.struct_time(tm_year=2017, tm_mon=4, tm_mday=26, tm_hour=16, tm_min=26, tm_sec=18, tm_wday=2, tm_yday=116, tm_isdst=0) 年,月,日,时,分,秒,星期几,一年中第几天等,是否是夏令时""" #3,时间字符串 print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X")) #打印当时的时间字符串 """2017-04-26 16:30:02"""
小结:时间戳是计算机能够识别的时间;时间字符串是人能够看懂的时间;元组则是用来操作时间的
几种时间形式的转换:
(1)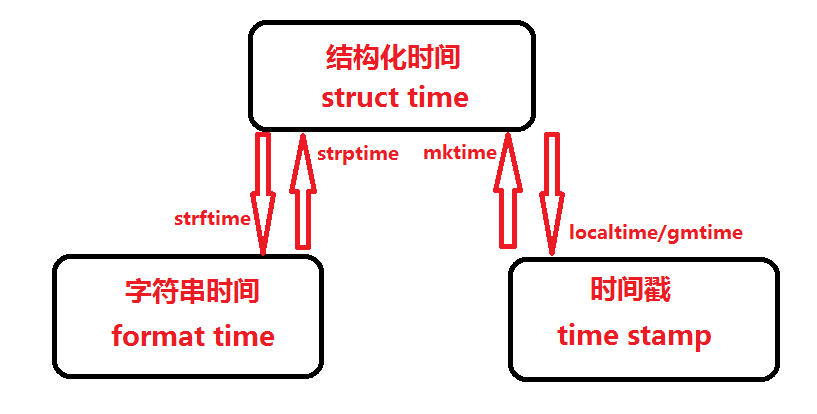
#一 时间戳<---->结构化时间: localtime/gmtime mktime >>> time.localtime(3600*24) >>> time.gmtime(3600*24) >>> time.mktime(time.localtime()) #字符串时间<---->结构化时间: strftime/strptime >>> time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.localtime()) >>> time.strptime("2017-03-16","%Y-%m-%d")
(2)
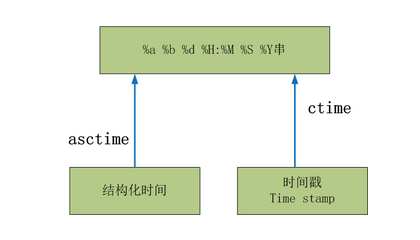
>>> time.asctime(time.localtime(312343423)) 'Sun Nov 25 10:03:43 1979' >>> time.ctime(312343423) 'Sun Nov 25 10:03:43 1979'
1 #--------------------------其他方法 2 # sleep(secs) 3 # 线程推迟指定的时间运行,单位为秒。
二:random模块
import random print(random.random()) # 大于0且小于1之间的小数 print(random.randint(1,15)) # 大于等于1且小于等于15之间的整数 print(random.randrange(1,5)) # 大于等于1且小于5之间的整数 print(random.choice([1,"2",[4,5]])) #1或2或[4,5] print(random.sample(range(1,33),6)) #1到33中任意6个数的组合 print(random.uniform(1,3)) #大于1小于3的小数
import random """生成验证码""" def v_code(): code = '' for i in range(5): num=random.randint(0,9) alf=chr(random.randint(65,90)) add=random.choice([num,alf]) code="".join([code,str(add)]) return code print(v_code())
三:sys模块
sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径 sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0) sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息 sys.maxint 最大的Int值 sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值 sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称
四:os模块
os模块是与操作系统交互的一个接口
''' os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径 os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cd os.curdir 返回当前目录: ('.') os.pardir 获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:('..') os.makedirs('dirname1/dirname2') 可生成多层递归目录 os.removedirs('dirname1') 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推 os.mkdir('dirname') 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirname os.rmdir('dirname') 删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirname os.listdir('dirname') 列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印 os.remove() 删除一个文件 os.rename("oldname","newname") 重命名文件/目录 os.stat('path/filename') 获取文件/目录信息 os.sep 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\",Linux下为"/" os.linesep 输出当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为" ",Linux下为" " os.pathsep 输出用于分割文件路径的字符串 win下为;,Linux下为: os.name 输出字符串指示当前使用平台。win->'nt'; Linux->'posix' os.system("bash command") 运行shell命令,直接显示 os.environ 获取系统环境变量 os.path.abspath(path) 返回path规范化的绝对路径 os.path.split(path) 将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回 os.path.dirname(path) 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素 os.path.basename(path) 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素 os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回False os.path.isabs(path) 如果path是绝对路径,返回True os.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回False os.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回False os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略 os.path.getatime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间 os.path.getmtime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间 os.path.getsize(path) 返回path的大小 '''
五:摘要算法
用于加密相关的操作,代替了md5模块和sha模块,主要提供 SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512 ,MD5 算法
什么是摘要算法呢?摘要算法又称哈希算法、散列算法。它通过一个函数,把任意长度的数据转换为一个长度固定的数据串(通常用16进制的字符串表示)。
import hashlib # ######## md5 ######## hash = hashlib.md5() hash.update('admin'.encode("utf8")) print(hash.hexdigest()) # ######## sha1 ######## hash = hashlib.sha1() hash.update('admin'.encode("utf8")) print(hash.hexdigest()) # ######## sha256 ######## hash = hashlib.sha256() hash.update('admin'.encode("utf8")) print(hash.hexdigest()) # ######## sha384 ######## hash = hashlib.sha384() hash.update('admin'.encode("utf8")) print(hash.hexdigest()) # ######## sha512 ######## hash = hashlib.sha512() hash.update('admin'.encode("utf8")) print(hash.hexdigest())