背景:大家都在说Skywalking Agent实现的核心原理就是
Java Agent+字节码操作。但是这两者是如何起作用的,一直比较模糊,所以通过这篇博客来记录一下解疑答惑的过程。
通过这篇博客应该可以解答如下几个问题:
- Skywalking具体使用什么来操作字节码;
- Skywalking的插件是怎么开发的;
- Skywalking是怎么让插件生效的;
ByteBuddy入门
ByteBuddy封装了一系列API来轻松创建一个agent,下面通过AgentBuilder来创建一个简单的agent:假设我们定义了一个注解ToString,我们匹配所有标注@ToString的类,修改toString方法,让其返回"transformed"。
public class ToStringAgent {
public static void premain(String arguments, Instrumentation instrumentation) {
new AgentBuilder.Default()
.type(isAnnotatedWith(ToString.class))
.transform(new AgentBuilder.Transformer() {
@Override
public DynamicType.Builder transform(DynamicType.Builder builder,
TypeDescription typeDescription,
ClassLoader classloader) {
return builder.method(named("toString"))
.intercept(FixedValue.value("transformed"));
}
}).installOn(instrumentation);
}
}
- type 接受 一个ElementMatcher 匹配 ToString注解
- transform 接受AgentBuilder.Transformer 来描述修改逻辑,每有一个类加载时,触发transformer逻辑,对类进行匹配和修改。
- installOn ,将修改,应用到instrumentation中。
自定义Skywalking插件
1、引入依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itmuch.skywalking</groupId>
<artifactId>apm-string-replace-plugin</artifactId>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<skywalking.version>6.6.0</skywalking.version>
<shade.package>org.apache.skywalking.apm.dependencies</shade.package>
<shade.net.bytebuddy.source>net.bytebuddy</shade.net.bytebuddy.source>
<shade.net.bytebuddy.target>${shade.package}.${shade.net.bytebuddy.source}</shade.net.bytebuddy.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.skywalking</groupId>
<artifactId>apm-agent-core</artifactId>
<version>${skywalking.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.skywalking</groupId>
<artifactId>apm-util</artifactId>
<version>${skywalking.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.4</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<shadedArtifactAttached>false</shadedArtifactAttached>
<createDependencyReducedPom>true</createDependencyReducedPom>
<createSourcesJar>true</createSourcesJar>
<shadeSourcesContent>true</shadeSourcesContent>
<relocations>
<relocation>
<pattern>${shade.net.bytebuddy.source}</pattern>
<shadedPattern>${shade.net.bytebuddy.target}</shadedPattern>
</relocation>
</relocations>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>6</source>
<target>6</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
编写插件定义
public class ToStringInstrumentation extends ClassInstanceMethodsEnhancePluginDefine {
@Override
protected ClassMatch enhanceClass() {
// 指定想要监控的类
return NameMatch.byName("java.lang.String");
}
@Override
public ConstructorInterceptPoint[] getConstructorsInterceptPoints() {
return new ConstructorInterceptPoint[0];
}
@Override
public InstanceMethodsInterceptPoint[] getInstanceMethodsInterceptPoints() {
// 指定想要监控的实例方法,每个实例方法对应一个InstanceMethodsInterceptPoint
return new InstanceMethodsInterceptPoint[]{
@Override
public ElementMatcher<MethodDescription> getMethodsMatcher() {
// 实例方法名称
return ElementMatchers.named("toString");
}
@Override
public String getMethodsInterceptor() {
// 该实例方法的监控拦截器类名全路径
return "com.itmuch.skywalking.plugin.tostring.ToStringInterceptor";
}
@Override
public boolean isOverrideArgs() {
return false;
}
};
}
@Override
public StaticMethodsInterceptPoint[] getStaticMethodsInterceptPoints() {
// 指定想要监控的静态方法,每一个方法对应一个StaticMethodsInterceptPoint
return new StaticMethodsInterceptPoint[0];
}
}
编写拦截器
public class ToStringInterceptor implements InstanceMethodsAroundInterceptor {
@Override
public void beforeMethod(Class aClass, Method method, Object[] argumentsTypes, Class<?>[] classes, MethodInterceptResult methodInterceptResult) {
System.out.print("在toString之前执行beforeMethod方法");
}
@Override
public Object afterMethod(Class aClass, Method method, Object[] objects, Class<?>[] classes, Object o) {
return o + "在toString之后执行afterMethod";
}
@Override
public void handleMethodException(Class aClass, Method method, Object[] objects, Class<?>[] classes, Throwable throwable) {
System.out.print(throwable.getMessage());
}
}
上面的操作步骤完全仿照Skywalking源码中的插件的定义。
使用的哪种字节码操作框架
首先找到入口类premain-class。
apm-sniffer/apm-agent/pom.xml:
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<!-- javaagent对应的premain方法 -->
<premain.class>org.apache.skywalking.apm.agent.SkyWalkingAgent</premain.class>
<can.redefine.classes>true</can.redefine.classes>
<can.retransform.classes>true</can.retransform.classes>
<shade.net.bytebuddy.source>net.bytebuddy</shade.net.bytebuddy.source>
<shade.net.bytebuddy.target>${shade.package}.${shade.net.bytebuddy.source}</shade.net.bytebuddy.target>
</properties>
找到了入口类SkyWalkingAgent,那来看看他的源码:
public static void premain(String agentArgs, Instrumentation instrumentation) throws PluginException {
final PluginFinder pluginFinder;
try {
//1、初始化一些核心配置
SnifferConfigInitializer.initializeCoreConfig(agentArgs);
} catch (Exception e) {
// try to resolve a new logger, and use the new logger to write the error log here
LogManager.getLogger(SkyWalkingAgent.class)
.error(e, "SkyWalking agent initialized failure. Shutting down.");
return;
} finally {
// refresh logger again after initialization finishes
LOGGER = LogManager.getLogger(SkyWalkingAgent.class);
}
try {
//2、加载插件
pluginFinder = new PluginFinder(new PluginBootstrap().loadPlugins());
} catch (AgentPackageNotFoundException ape) {
LOGGER.error(ape, "Locate agent.jar failure. Shutting down.");
return;
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error(e, "SkyWalking agent initialized failure. Shutting down.");
return;
}
//3、初始化字节码操作框架ByteBuddy
final ByteBuddy byteBuddy = new ByteBuddy().with(TypeValidation.of(Config.Agent.IS_OPEN_DEBUGGING_CLASS));
AgentBuilder agentBuilder = new AgentBuilder.Default(byteBuddy).ignore(
nameStartsWith("net.bytebuddy.")
.or(nameStartsWith("org.slf4j."))
.or(nameStartsWith("org.groovy."))
.or(nameContains("javassist"))
.or(nameContains(".asm."))
.or(nameContains(".reflectasm."))
.or(nameStartsWith("sun.reflect"))
.or(allSkyWalkingAgentExcludeToolkit())
.or(ElementMatchers.isSynthetic()));
JDK9ModuleExporter.EdgeClasses edgeClasses = new JDK9ModuleExporter.EdgeClasses();
try {
agentBuilder = BootstrapInstrumentBoost.inject(pluginFinder, instrumentation, agentBuilder, edgeClasses);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error(e, "SkyWalking agent inject bootstrap instrumentation failure. Shutting down.");
return;
}
try {
agentBuilder = JDK9ModuleExporter.openReadEdge(instrumentation, agentBuilder, edgeClasses);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error(e, "SkyWalking agent open read edge in JDK 9+ failure. Shutting down.");
return;
}
if (Config.Agent.IS_CACHE_ENHANCED_CLASS) {
try {
agentBuilder = agentBuilder.with(new CacheableTransformerDecorator(Config.Agent.CLASS_CACHE_MODE));
LOGGER.info("SkyWalking agent class cache [{}] activated.", Config.Agent.CLASS_CACHE_MODE);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error(e, "SkyWalking agent can't active class cache.");
}
}
agentBuilder.type(pluginFinder.buildMatch())
//4、重点:描述如何修改字节码
.transform(new Transformer(pluginFinder))
.with(AgentBuilder.RedefinitionStrategy.RETRANSFORMATION)
.with(new RedefinitionListener())
.with(new Listener())
.installOn(instrumentation);
try {
ServiceManager.INSTANCE.boot();
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error(e, "Skywalking agent boot failure.");
}
Runtime.getRuntime()
.addShutdownHook(new Thread(ServiceManager.INSTANCE::shutdown, "skywalking service shutdown thread"));
}
通过上面编号3处的代码可以看到使用的是ByteBuddy字节码操作框架。
如何修改字节码
我们都知道通过Javaagent来修改字节码离不开ClassFileTransformer,同样的ByteBuddy也根据transform来描述如何修改字节码,如上面的编号4处的代码。
private static class Transformer implements AgentBuilder.Transformer {
private PluginFinder pluginFinder;
Transformer(PluginFinder pluginFinder) {
this.pluginFinder = pluginFinder;
}
/**
* 转换方法
* @param builder
* @param typeDescription 要被修改的Class类型
* @param classLoader
* @param module
* @return
*/
@Override
public DynamicType.Builder<?> transform(final DynamicType.Builder<?> builder,
final TypeDescription typeDescription,
final ClassLoader classLoader,
final JavaModule module) {
//1、找到typeDescription要被哪些插件增强
List<AbstractClassEnhancePluginDefine> pluginDefines = pluginFinder.find(typeDescription);
if (pluginDefines.size() > 0) {
DynamicType.Builder<?> newBuilder = builder;
EnhanceContext context = new EnhanceContext();
for (AbstractClassEnhancePluginDefine define : pluginDefines) {
//2、使用插件增强
DynamicType.Builder<?> possibleNewBuilder = define.define(
typeDescription, newBuilder, classLoader, context);
if (possibleNewBuilder != null) {
newBuilder = possibleNewBuilder;
}
}
if (context.isEnhanced()) {
LOGGER.debug("Finish the prepare stage for {}.", typeDescription.getName());
}
return newBuilder;
}
LOGGER.debug("Matched class {}, but ignore by finding mechanism.", typeDescription.getTypeName());
return builder;
}
}
重点看看编号2处的代码如何用插件增强目标类。
public DynamicType.Builder<?> define(TypeDescription typeDescription, DynamicType.Builder<?> builder,
ClassLoader classLoader, EnhanceContext context) throws PluginException {
//1、插件的全路径名
String interceptorDefineClassName = this.getClass().getName();
//2、要被增强类的全路径名
String transformClassName = typeDescription.getTypeName();
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(transformClassName)) {
LOGGER.warn("classname of being intercepted is not defined by {}.", interceptorDefineClassName);
return null;
}
LOGGER.debug("prepare to enhance class {} by {}.", transformClassName, interceptorDefineClassName);
WitnessFinder finder = WitnessFinder.INSTANCE;
/**
* find witness classes for enhance class
*/
//3、一些插件需要依赖一些外部的类,他会找是否有对应依赖的类,如果没有就直接 return null,不再去修改字节码了
String[] witnessClasses = witnessClasses();
if (witnessClasses != null) {
for (String witnessClass : witnessClasses) {
if (!finder.exist(witnessClass, classLoader)) {
LOGGER.warn("enhance class {} by plugin {} is not working. Because witness class {} is not existed.", transformClassName, interceptorDefineClassName, witnessClass);
return null;
}
}
}
//4、一些插件需要依赖一些外部的方法,他会找是否有对应依赖的方法,如果没有就直接 return null,不再去修改字节码了
List<WitnessMethod> witnessMethods = witnessMethods();
if (!CollectionUtil.isEmpty(witnessMethods)) {
for (WitnessMethod witnessMethod : witnessMethods) {
if (!finder.exist(witnessMethod, classLoader)) {
LOGGER.warn("enhance class {} by plugin {} is not working. Because witness method {} is not existed.", transformClassName, interceptorDefineClassName, witnessMethod);
return null;
}
}
}
/**
* find origin class source code for interceptor
*/
//5、真正的增强
DynamicType.Builder<?> newClassBuilder = this.enhance(typeDescription, builder, classLoader, context);
context.initializationStageCompleted();
LOGGER.debug("enhance class {} by {} completely.", transformClassName, interceptorDefineClassName);
return newClassBuilder;
}
上面编号5处的方法才是真正的增强逻辑,继续跟进去看看。
protected DynamicType.Builder<?> enhance(TypeDescription typeDescription, DynamicType.Builder<?> newClassBuilder,
ClassLoader classLoader, EnhanceContext context) throws PluginException {
//1、增强静态方法
newClassBuilder = this.enhanceClass(typeDescription, newClassBuilder, classLoader);
//2、增强实例方法
newClassBuilder = this.enhanceInstance(typeDescription, newClassBuilder, classLoader, context);
return newClassBuilder;
}
这里分两个步骤,增强静态方法和增强实例方法,这里以编号2处的举例,继续跟进去。
private DynamicType.Builder<?> enhanceInstance(TypeDescription typeDescription,
DynamicType.Builder<?> newClassBuilder, ClassLoader classLoader,
EnhanceContext context) throws PluginException {
//1、构造器拦截点,在执行构造器之前也有可能会执行其他逻辑来增强构造方法
ConstructorInterceptPoint[] constructorInterceptPoints = getConstructorsInterceptPoints();
//2、实例方法拦截点,对实例方法的增强
InstanceMethodsInterceptPoint[] instanceMethodsInterceptPoints = getInstanceMethodsInterceptPoints();
String enhanceOriginClassName = typeDescription.getTypeName();
boolean existedConstructorInterceptPoint = false;
if (constructorInterceptPoints != null && constructorInterceptPoints.length > 0) {
existedConstructorInterceptPoint = true;
}
boolean existedMethodsInterceptPoints = false;
if (instanceMethodsInterceptPoints != null && instanceMethodsInterceptPoints.length > 0) {
existedMethodsInterceptPoints = true;
}
/**
* nothing need to be enhanced in class instance, maybe need enhance static methods.
*/
if (!existedConstructorInterceptPoint && !existedMethodsInterceptPoints) {
return newClassBuilder;
}
/**
* Manipulate class source code.<br/>
*
* new class need:<br/>
* 1.Add field, name {@link #CONTEXT_ATTR_NAME}.
* 2.Add a field accessor for this field.
*
* And make sure the source codes manipulation only occurs once.
*
*/
if (!typeDescription.isAssignableTo(EnhancedInstance.class)) {
if (!context.isObjectExtended()) {
newClassBuilder = newClassBuilder.defineField(
CONTEXT_ATTR_NAME, Object.class, ACC_PRIVATE | ACC_VOLATILE)
.implement(EnhancedInstance.class)
.intercept(FieldAccessor.ofField(CONTEXT_ATTR_NAME));
context.extendObjectCompleted();
}
}
/**
* 3、enhance constructors 增强构造方法
*/
if (existedConstructorInterceptPoint) {
for (ConstructorInterceptPoint constructorInterceptPoint : constructorInterceptPoints) {
if (isBootstrapInstrumentation()) {
newClassBuilder = newClassBuilder.constructor(constructorInterceptPoint.getConstructorMatcher())
.intercept(SuperMethodCall.INSTANCE.andThen(MethodDelegation.withDefaultConfiguration()
.to(BootstrapInstrumentBoost
.forInternalDelegateClass(constructorInterceptPoint
.getConstructorInterceptor()))));
} else {
newClassBuilder = newClassBuilder.constructor(constructorInterceptPoint.getConstructorMatcher())
.intercept(SuperMethodCall.INSTANCE.andThen(MethodDelegation.withDefaultConfiguration()
.to(new ConstructorInter(constructorInterceptPoint
.getConstructorInterceptor(), classLoader))));
}
}
}
/**
* 4、enhance instance methods 增强实例方法
*/
if (existedMethodsInterceptPoints) {
for (InstanceMethodsInterceptPoint instanceMethodsInterceptPoint : instanceMethodsInterceptPoints) {
String interceptor = instanceMethodsInterceptPoint.getMethodsInterceptor();
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(interceptor)) {
throw new EnhanceException("no InstanceMethodsAroundInterceptor define to enhance class " + enhanceOriginClassName);
}
ElementMatcher.Junction<MethodDescription> junction = not(isStatic()).and(instanceMethodsInterceptPoint.getMethodsMatcher());
if (instanceMethodsInterceptPoint instanceof DeclaredInstanceMethodsInterceptPoint) {
junction = junction.and(ElementMatchers.<MethodDescription>isDeclaredBy(typeDescription));
}
if (instanceMethodsInterceptPoint.isOverrideArgs()) {
if (isBootstrapInstrumentation()) {
newClassBuilder = newClassBuilder.method(junction)
.intercept(MethodDelegation.withDefaultConfiguration()
.withBinders(Morph.Binder.install(OverrideCallable.class))
.to(BootstrapInstrumentBoost.forInternalDelegateClass(interceptor)));
} else {
newClassBuilder = newClassBuilder.method(junction)
.intercept(MethodDelegation.withDefaultConfiguration()
.withBinders(Morph.Binder.install(OverrideCallable.class))
.to(new InstMethodsInterWithOverrideArgs(interceptor, classLoader)));
}
} else {
if (isBootstrapInstrumentation()) {
newClassBuilder = newClassBuilder.method(junction)
.intercept(MethodDelegation.withDefaultConfiguration()
.to(BootstrapInstrumentBoost.forInternalDelegateClass(interceptor)));
} else {
//5、一般情况下会走到这里
newClassBuilder = newClassBuilder.method(junction)
.intercept(MethodDelegation.withDefaultConfiguration()
.to(new InstMethodsInter(interceptor, classLoader)));
}
}
}
}
return newClassBuilder;
}
看到上述编号5的时候是不是就觉得熟悉了,这不就是ByteBuddy创建agent的代码吗,按照这个逻辑InstMethodsInter这个类就是委托类,他里面的intercept方法才是真正增强/代理的核心。
@RuntimeType
public Object intercept(@This Object obj, @AllArguments Object[] allArguments, @SuperCall Callable<?> zuper,
@Origin Method method) throws Throwable {
//1、要增强的对象
EnhancedInstance targetObject = (EnhancedInstance) obj;
MethodInterceptResult result = new MethodInterceptResult();
try {
//2、在真正方法调用之前进行增强
interceptor.beforeMethod(targetObject, method, allArguments, method.getParameterTypes(), result);
} catch (Throwable t) {
LOGGER.error(t, "class[{}] before method[{}] intercept failure", obj.getClass(), method.getName());
}
Object ret = null;
try {
if (!result.isContinue()) {
ret = result._ret();
} else {
//3、真正的方法调用
ret = zuper.call();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
try {
//4、真正的方法调用之后处理异常
interceptor.handleMethodException(targetObject, method, allArguments, method.getParameterTypes(), t);
} catch (Throwable t2) {
LOGGER.error(t2, "class[{}] handle method[{}] exception failure", obj.getClass(), method.getName());
}
throw t;
} finally {
try {
//5、真正的方法调用之后进行增强
ret = interceptor.afterMethod(targetObject, method, allArguments, method.getParameterTypes(), ret);
} catch (Throwable t) {
LOGGER.error(t, "class[{}] after method[{}] intercept failure", obj.getClass(), method.getName());
}
}
return ret;
}
那这里会问这个interceptor到底是什么呢,往回跟踪代码
InstanceMethodsInterceptPoint[] instanceMethodsInterceptPoints = getInstanceMethodsInterceptPoints();
for (InstanceMethodsInterceptPoint instanceMethodsInterceptPoint : instanceMethodsInterceptPoints) {
String interceptor = instanceMethodsInterceptPoint.getMethodsInterceptor();
看到这个getInstanceMethodsInterceptPoints是不是又很熟悉呢,这其实就是我们上面自定义插件的时候实现的ClassInstanceMethodsEnhancePluginDefine里面的方法。
那现在问题清楚了,总的来说可以用下面的图描述:
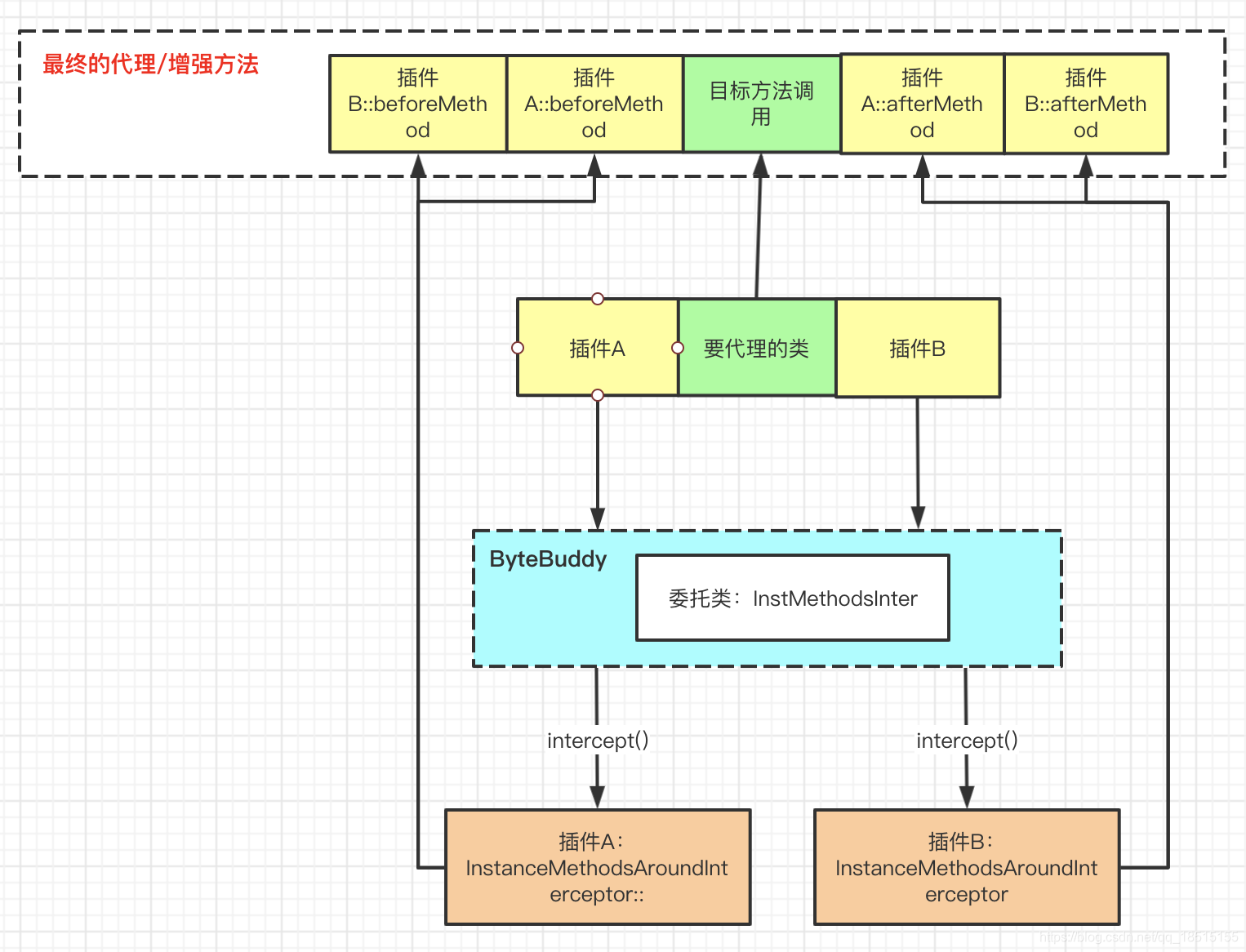
总结
其实Skywalking只是通过ByteBuddy修改字节码,在目标方法前后执行增强代码,但是具体增强的逻辑还是在各自的插件里面定义。只能感叹插件机制真强大。