参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/ysocean/p/7289529.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/fangjian0423/p/mybaits-dynamic-sql-analysis.html
mybatis 详解(五)------动态SQL
前面几篇博客我们通过实例讲解了用mybatis对一张表进行的CRUD操作,但是我们发现写的 SQL 语句都比较简单,如果有比较复杂的业务,我们需要写复杂的 SQL 语句,往往需要拼接,而拼接 SQL ,稍微不注意,由于引号,空格等缺失可能都会导致错误。
那么怎么去解决这个问题呢?这就是本篇所讲的使用 mybatis 动态SQL,通过 if, choose, when, otherwise, trim, where, set, foreach等标签,可组合成非常灵活的SQL语句,从而在提高 SQL 语句的准确性的同时,也大大提高了开发人员的效率。
我们以 User 表为例来说明:

1、动态SQL:if 语句
根据 username 和 sex 来查询数据。如果username为空,那么将只根据sex来查询;反之只根据username来查询
首先不使用 动态SQL 来书写
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> <!-- 这里和普通的sql 查询语句差不多,对于只有一个参数,后面的 #{id}表示占位符,里面不一定要写id, 写啥都可以,但是不要空着,如果有多个参数则必须写pojo类里面的属性 --> select * from user where username=#{username} and sex=#{sex}</select> |
上面的查询语句,我们可以发现,如果 #{username} 为空,那么查询结果也是空,如何解决这个问题呢?使用 if 来判断
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> select * from user where <if test="username != null"> username=#{username} </if> <if test="username != null"> and sex=#{sex} </if></select> |
这样写我们可以看到,如果 sex 等于 null,那么查询语句为 select * from user where username=#{username},但是如果usename 为空呢?那么查询语句为 select * from user where and sex=#{sex},这是错误的 SQL 语句,如何解决呢?请看下面的 where 语句
2、动态SQL:if+where 语句
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> select * from user <where> <if test="username != null"> username=#{username} </if> <if test="username != null"> and sex=#{sex} </if> </where></select> |
这个“where”标签会知道如果它包含的标签中有返回值的话,它就插入一个‘where’。此外,如果标签返回的内容是以AND 或OR 开头的,则它会剔除掉。
3、动态SQL:if+set 语句
同理,上面的对于查询 SQL 语句包含 where 关键字,如果在进行更新操作的时候,含有 set 关键词,我们怎么处理呢?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
<!-- 根据 id 更新 user 表的数据 --><update id="updateUserById" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> update user u <set> <if test="username != null and username != ''"> u.username = #{username}, </if> <if test="sex != null and sex != ''"> u.sex = #{sex} </if> </set> where id=#{id}</update> |
这样写,如果第一个条件 username 为空,那么 sql 语句为:update user u set u.sex=? where id=?
如果第一个条件不为空,那么 sql 语句为:update user u set u.username = ? ,u.sex = ? where id=?
4、动态SQL:choose(when,otherwise) 语句
有时候,我们不想用到所有的查询条件,只想选择其中的一个,查询条件有一个满足即可,使用 choose 标签可以解决此类问题,类似于 Java 的 switch 语句
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<select id="selectUserByChoose" resultType="com.ys.po.User" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> select * from user <where> <choose> <when test="id !='' and id != null"> id=#{id} </when> <when test="username !='' and username != null"> and username=#{username} </when> <otherwise> and sex=#{sex} </otherwise> </choose> </where> </select> |
也就是说,这里我们有三个条件,id,username,sex,只能选择一个作为查询条件
如果 id 不为空,那么查询语句为:select * from user where id=?
如果 id 为空,那么看username 是否为空,如果不为空,那么语句为 select * from user where username=?;
如果 username 为空,那么查询语句为 select * from user where sex=?
5、动态SQL:trim 语句
trim标记是一个格式化的标记,可以完成set或者是where标记的功能
①、用 trim 改写上面第二点的 if+where 语句
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> select * from user <!-- <where> <if test="username != null"> username=#{username} </if> <if test="username != null"> and sex=#{sex} </if> </where> --> <trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and | or"> <if test="username != null"> and username=#{username} </if> <if test="sex != null"> and sex=#{sex} </if> </trim> </select> |
prefix:前缀
prefixoverride:去掉第一个and或者是or
②、用 trim 改写上面第三点的 if+set 语句
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
<!-- 根据 id 更新 user 表的数据 --> <update id="updateUserById" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> update user u <!-- <set> <if test="username != null and username != ''"> u.username = #{username}, </if> <if test="sex != null and sex != ''"> u.sex = #{sex} </if> </set> --> <trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=","> <if test="username != null and username != ''"> u.username = #{username}, </if> <if test="sex != null and sex != ''"> u.sex = #{sex}, </if> </trim> where id=#{id} </update> |
suffix:后缀
suffixoverride:去掉最后一个逗号(也可以是其他的标记,就像是上面前缀中的and一样)
6、动态SQL: SQL 片段
有时候可能某个 sql 语句我们用的特别多,为了增加代码的重用性,简化代码,我们需要将这些代码抽取出来,然后使用时直接调用。
比如:假如我们需要经常根据用户名和性别来进行联合查询,那么我们就把这个代码抽取出来,如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<!-- 定义 sql 片段 --><sql id="selectUserByUserNameAndSexSQL"> <if test="username != null and username != ''"> AND username = #{username} </if> <if test="sex != null and sex != ''"> AND sex = #{sex} </if></sql> |
引用 sql 片段
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"> select * from user <trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and | or"> <!-- 引用 sql 片段,如果refid 指定的不在本文件中,那么需要在前面加上 namespace --> <include refid="selectUserByUserNameAndSexSQL"></include> <!-- 在这里还可以引用其他的 sql 片段 --> </trim></select> |
注意:①、最好基于 单表来定义 sql 片段,提高片段的可重用性
②、在 sql 片段中最好不要包括 where
7、动态SQL: foreach 语句
需求:我们需要查询 user 表中 id 分别为1,2,3的用户
sql语句:select * from user where id=1 or id=2 or id=3
select * from user where id in (1,2,3)
①、建立一个 UserVo 类,里面封装一个 List<Integer> ids 的属性
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
package com.ys.vo;import java.util.List;public class UserVo { //封装多个用户的id private List<Integer> ids; public List<Integer> getIds() { return ids; } public void setIds(List<Integer> ids) { this.ids = ids; }} |
②、我们用 foreach 来改写 select * from user where id=1 or id=2 or id=3
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<select id="selectUserByListId" parameterType="com.ys.vo.UserVo" resultType="com.ys.po.User"> select * from user <where> <!-- collection:指定输入对象中的集合属性 item:每次遍历生成的对象 open:开始遍历时的拼接字符串 close:结束时拼接的字符串 separator:遍历对象之间需要拼接的字符串 select * from user where 1=1 and (id=1 or id=2 or id=3) --> <foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="and (" close=")" separator="or"> id=#{id} </foreach> </where></select> |
测试:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
//根据id集合查询user表数据@Testpublic void testSelectUserByListId(){ String statement = "com.ys.po.userMapper.selectUserByListId"; UserVo uv = new UserVo(); List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>(); ids.add(1); ids.add(2); ids.add(3); uv.setIds(ids); List<User> listUser = session.selectList(statement, uv); for(User u : listUser){ System.out.println(u); } session.close();} |
③、我们用 foreach 来改写 select * from user where id in (1,2,3)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<select id="selectUserByListId" parameterType="com.ys.vo.UserVo" resultType="com.ys.po.User"> select * from user <where> <!-- collection:指定输入对象中的集合属性 item:每次遍历生成的对象 open:开始遍历时的拼接字符串 close:结束时拼接的字符串 separator:遍历对象之间需要拼接的字符串 select * from user where 1=1 and id in (1,2,3) --> <foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="and id in (" close=") " separator=","> #{id} </foreach> </where> </select> |
8、总结
其实动态 sql 语句的编写往往就是一个拼接的问题,为了保证拼接准确,我们最好首先要写原生的 sql 语句出来,然后在通过 mybatis 动态sql 对照着改,防止出错。
Mybatis解析动态sql原理分析
前言
废话不多说,直接进入文章。
我们在使用mybatis的时候,会在xml中编写sql语句。
比如这段动态sql代码:
<update id="update" parameterType="org.format.dynamicproxy.mybatis.bean.User">
UPDATE users
<trim prefix="SET" prefixOverrides=",">
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="age != null and age != ''">
, age = #{age}
</if>
<if test="birthday != null and birthday != ''">
, birthday = #{birthday}
</if>
</trim>
where id = ${id}
</update>
mybatis底层是如何构造这段sql的?
这方面的知识网上资料不多,于是就写了这么一篇文章。
下面带着这个疑问,我们一步一步分析。
介绍MyBatis中一些关于动态SQL的接口和类
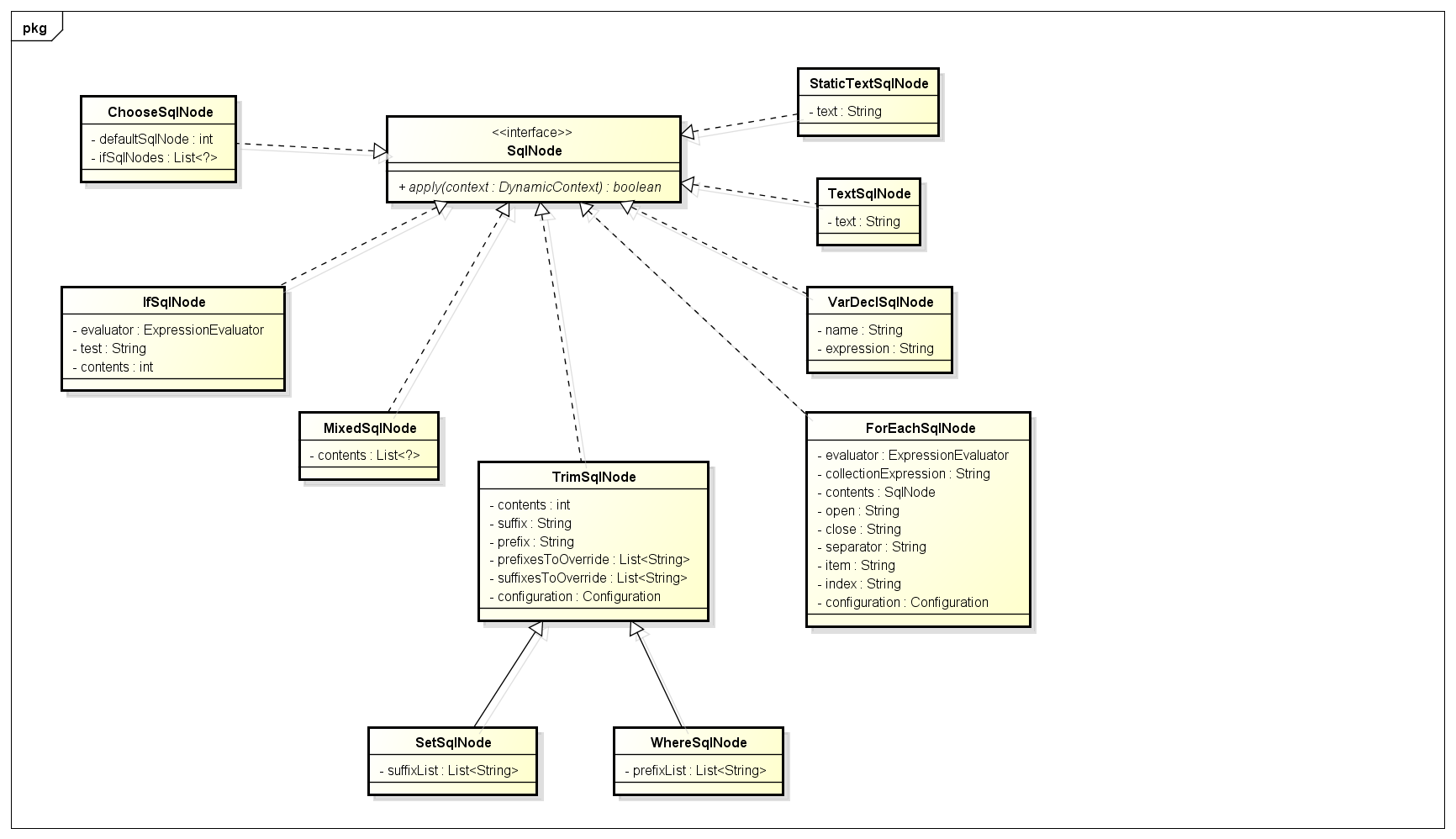
SqlNode接口,简单理解就是xml中的每个标签,比如上述sql的update,trim,if标签:
public interface SqlNode {
boolean apply(DynamicContext context);
}
SqlSource Sql源接口,代表从xml文件或注解映射的sql内容,主要就是用于创建BoundSql,有实现类DynamicSqlSource(动态Sql源),StaticSqlSource(静态Sql源)等:
public interface SqlSource {
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
}
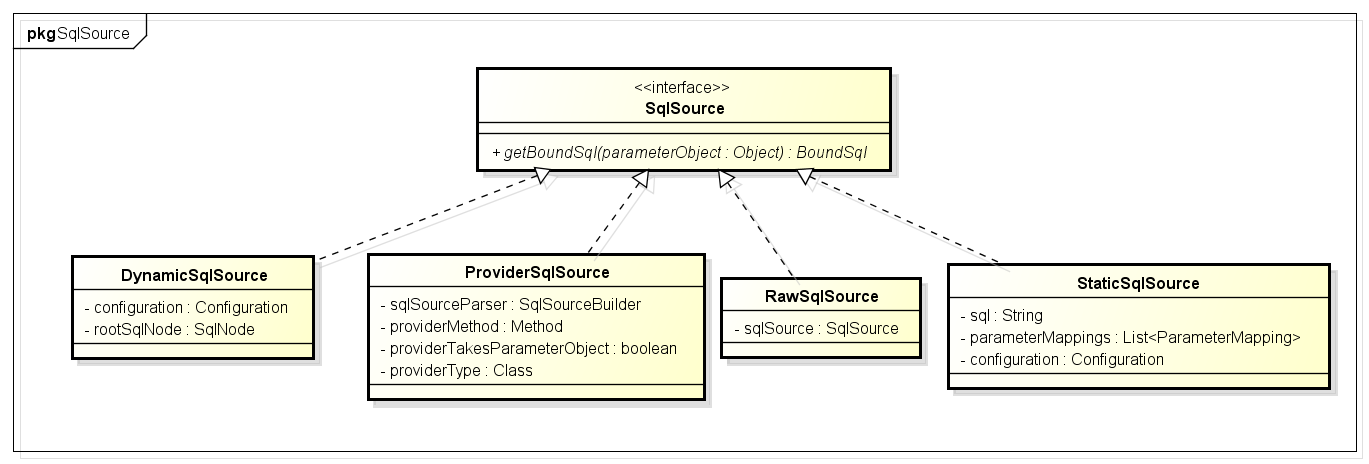
BoundSql类,封装mybatis最终产生sql的类,包括sql语句,参数,参数源数据等参数:

XNode,一个Dom API中的Node接口的扩展类。

BaseBuilder接口及其实现类(属性,方法省略了,大家有兴趣的自己看),这些Builder的作用就是用于构造sql:

下面我们简单分析下其中4个Builder:
1 XMLConfigBuilder
解析mybatis中configLocation属性中的全局xml文件,内部会使用XMLMapperBuilder解析各个xml文件。
2 XMLMapperBuilder
遍历mybatis中mapperLocations属性中的xml文件中每个节点的Builder,比如user.xml,内部会使用XMLStatementBuilder处理xml中的每个节点。
3 XMLStatementBuilder
解析xml文件中各个节点,比如select,insert,update,delete节点,内部会使用XMLScriptBuilder处理节点的sql部分,遍历产生的数据会丢到Configuration的mappedStatements中。
4 XMLScriptBuilder
解析xml中各个节点sql部分的Builder。
LanguageDriver接口及其实现类(属性,方法省略了,大家有兴趣的自己看),该接口主要的作用就是构造sql:
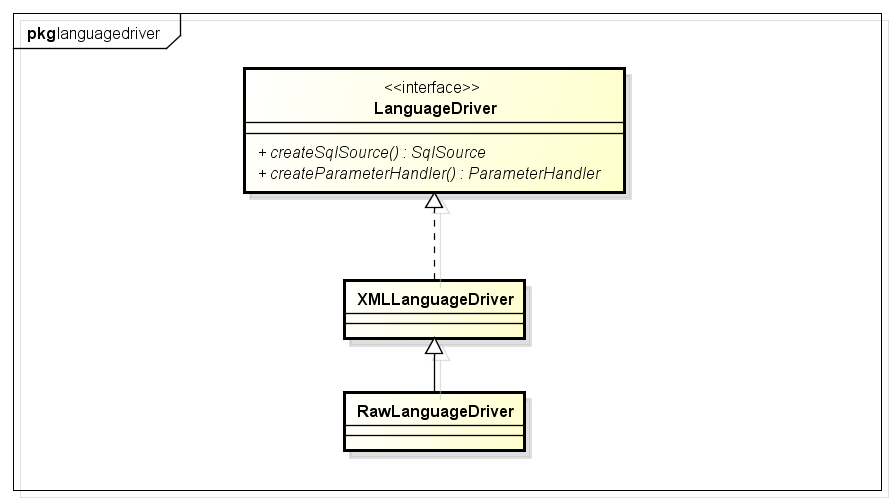
简单分析下XMLLanguageDriver(处理xml中的sql,RawLanguageDriver处理静态sql):
XMLLanguageDriver内部会使用XMLScriptBuilder解析xml中的sql部分。
ok, 大部分比较重要的类我们都已经介绍了,下面源码分析走起。
源码分析走起
Spring与Mybatis整合的时候需要配置SqlSessionFactoryBean,该配置会加入数据源和mybatis xml配置文件路径等信息:
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatisConfig.xml"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath*:org/format/dao/*.xml"/>
</bean>
我们就分析这一段配置背后的细节:
SqlSessionFactoryBean实现了Spring的InitializingBean接口,InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet方法中会调用buildSqlSessionFactory方法
buildSqlSessionFactory方法内部会使用XMLConfigBuilder解析属性configLocation中配置的路径,还会使用XMLMapperBuilder属性解析mapperLocations属性中的各个xml文件。
部分源码如下:
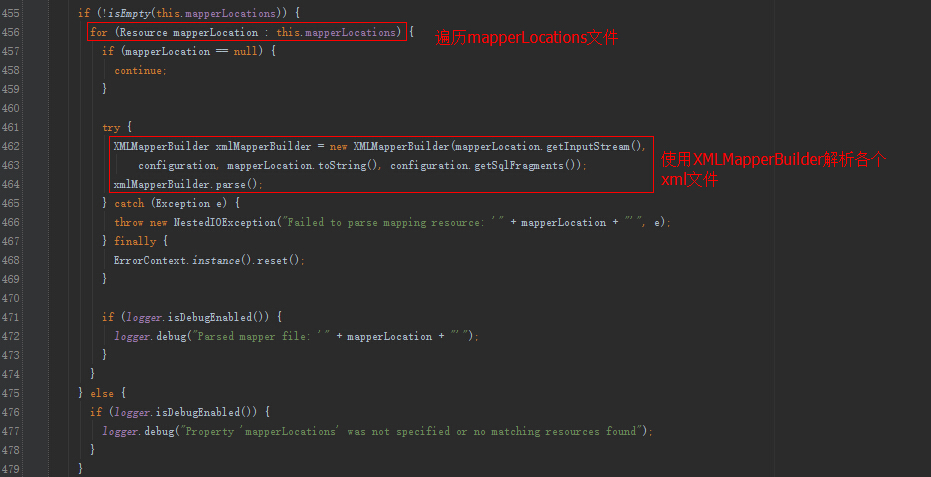
由于XMLConfigBuilder内部也是使用XMLMapperBuilder,我们就看看XMLMapperBuilder的解析细节。
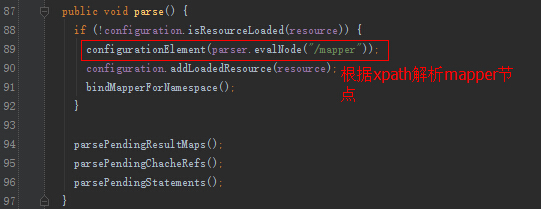
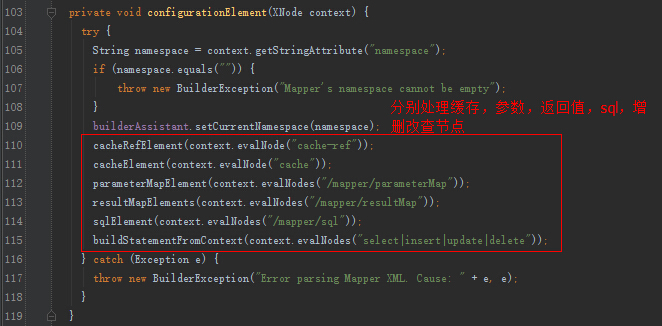
我们关注一下,增删改查节点的解析。
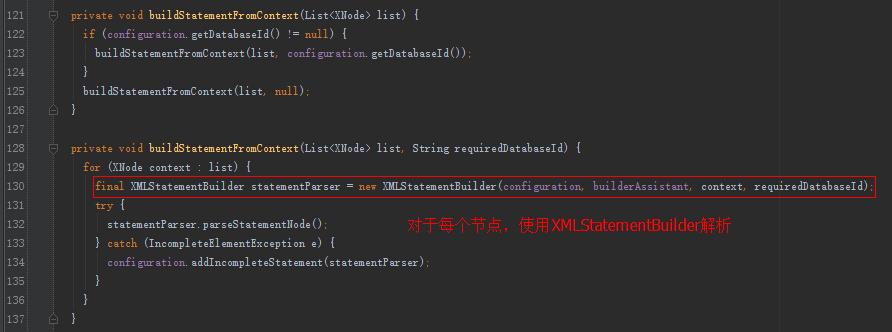
XMLStatementBuilder的解析:

默认会使用XMLLanguageDriver创建SqlSource(Configuration构造函数中设置)。
XMLLanguageDriver创建SqlSource:

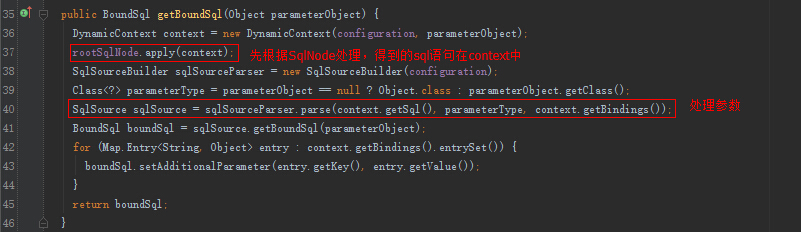
XMLScriptBuilder解析sql:

得到SqlSource之后,会放到Configuration中,有了SqlSource,就能拿BoundSql了,BoundSql可以得到最终的sql。
实例分析
我以以下xml的解析大概说下parseDynamicTags的解析过程:
<update id="update" parameterType="org.format.dynamicproxy.mybatis.bean.User">
UPDATE users
<trim prefix="SET" prefixOverrides=",">
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="age != null and age != ''">
, age = #{age}
</if>
<if test="birthday != null and birthday != ''">
, birthday = #{birthday}
</if>
</trim>
where id = ${id}
</update>
在看这段解析之前,请先了解dom相关的知识,xml dom知识, dom博文
parseDynamicTags方法的返回值是一个List,也就是一个Sql节点集合。SqlNode本文一开始已经介绍,分析完解析过程之后会说一下各个SqlNode类型的作用。
1 首先根据update节点(Node)得到所有的子节点,分别是3个子节点
(1)文本节点 UPDATE users
(2)trim子节点 ...
(3)文本节点 where id = #{id}
2 遍历各个子节点
(1) 如果节点类型是文本或者CDATA,构造一个TextSqlNode或StaticTextSqlNode
(2) 如果节点类型是元素,说明该update节点是个动态sql,然后会使用NodeHandler处理各个类型的子节点。这里的NodeHandler是XMLScriptBuilder的一个内部接口,其实现类包括TrimHandler、WhereHandler、SetHandler、IfHandler、ChooseHandler等。看类名也就明白了这个Handler的作用,比如我们分析的trim节点,对应的是TrimHandler;if节点,对应的是IfHandler...
这里子节点trim被TrimHandler处理,TrimHandler内部也使用parseDynamicTags方法解析节点
3 遇到子节点是元素的话,重复以上步骤
trim子节点内部有7个子节点,分别是文本节点、if节点、是文本节点、if节点、是文本节点、if节点、文本节点。文本节点跟之前一样处理,if节点使用IfHandler处理
遍历步骤如上所示,下面我们看下几个Handler的实现细节。
IfHandler处理方法也是使用parseDynamicTags方法,然后加上if标签必要的属性。
private class IfHandler implements NodeHandler {
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
List<SqlNode> contents = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = new MixedSqlNode(contents);
String test = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("test");
IfSqlNode ifSqlNode = new IfSqlNode(mixedSqlNode, test);
targetContents.add(ifSqlNode);
}
}
TrimHandler处理方法也是使用parseDynamicTags方法,然后加上trim标签必要的属性。
private class TrimHandler implements NodeHandler {
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
List<SqlNode> contents = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = new MixedSqlNode(contents);
String prefix = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("prefix");
String prefixOverrides = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("prefixOverrides");
String suffix = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("suffix");
String suffixOverrides = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("suffixOverrides");
TrimSqlNode trim = new TrimSqlNode(configuration, mixedSqlNode, prefix, prefixOverrides, suffix, suffixOverrides);
targetContents.add(trim);
}
}
以上update方法最终通过parseDynamicTags方法得到的SqlNode集合如下:
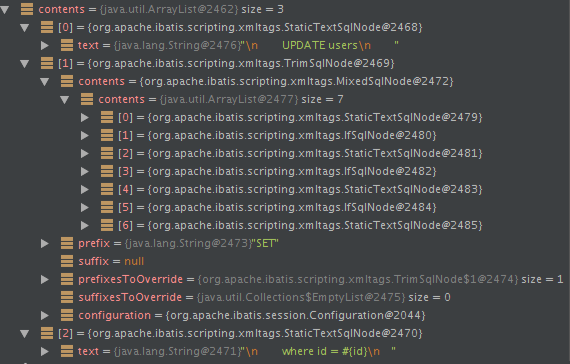
trim节点:
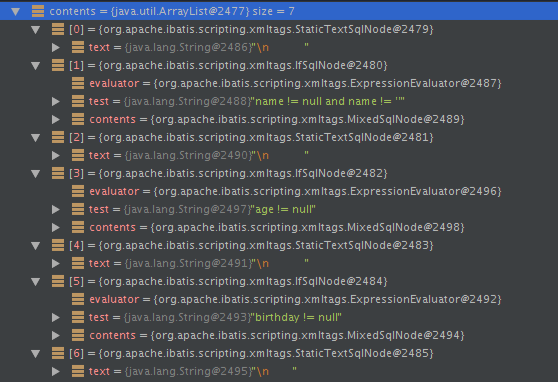
由于这个update方法是个动态节点,因此构造出了DynamicSqlSource。
DynamicSqlSource内部就可以构造sql了:
DynamicSqlSource内部的SqlNode属性是一个MixedSqlNode。
然后我们看看各个SqlNode实现类的apply方法
下面分析一下两个SqlNode实现类的apply方法实现:
MixedSqlNode:
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
for (SqlNode sqlNode : contents) {
sqlNode.apply(context);
}
return true;
}
MixedSqlNode会遍历调用内部各个sqlNode的apply方法。
StaticTextSqlNode:
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
context.appendSql(text);
return true;
}
直接append sql文本。
IfSqlNode:
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
if (evaluator.evaluateBoolean(test, context.getBindings())) {
contents.apply(context);
return true;
}
return false;
}
这里的evaluator是一个ExpressionEvaluator类型的实例,内部使用了OGNL处理表达式逻辑。
TrimSqlNode:
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
FilteredDynamicContext filteredDynamicContext = new FilteredDynamicContext(context);
boolean result = contents.apply(filteredDynamicContext);
filteredDynamicContext.applyAll();
return result;
}
public void applyAll() {
sqlBuffer = new StringBuilder(sqlBuffer.toString().trim());
String trimmedUppercaseSql = sqlBuffer.toString().toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if (trimmedUppercaseSql.length() > 0) {
applyPrefix(sqlBuffer, trimmedUppercaseSql);
applySuffix(sqlBuffer, trimmedUppercaseSql);
}
delegate.appendSql(sqlBuffer.toString());
}
private void applyPrefix(StringBuilder sql, String trimmedUppercaseSql) {
if (!prefixApplied) {
prefixApplied = true;
if (prefixesToOverride != null) {
for (String toRemove : prefixesToOverride) {
if (trimmedUppercaseSql.startsWith(toRemove)) {
sql.delete(0, toRemove.trim().length());
break;
}
}
}
if (prefix != null) {
sql.insert(0, " ");
sql.insert(0, prefix);
}
}
}
TrimSqlNode的apply方法也是调用属性contents(一般都是MixedSqlNode)的apply方法,按照实例也就是7个SqlNode,都是StaticTextSqlNode和IfSqlNode。 最后会使用FilteredDynamicContext过滤掉prefix和suffix。
总结
大致讲解了一下mybatis对动态sql语句的解析过程,其实回过头来看看不算复杂,还算蛮简单的。 之前接触mybaits的时候遇到刚才分析的那一段动态sql的时候总是很费解。
<update id="update" parameterType="org.format.dynamicproxy.mybatis.bean.User">
UPDATE users
<trim prefix="SET" prefixOverrides=",">
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="age != null and age != ''">
, age = #{age}
</if>
<if test="birthday != null and birthday != ''">
, birthday = #{birthday}
</if>
</trim>
where id = ${id}
</update>
想搞明白这个trim节点的prefixOverrides到底是什么意思(从字面上理解就是前缀覆盖),而且官方文档上也没这方面知识的说明。我将这段xml改成如下:
<update id="update" parameterType="org.format.dynamicproxy.mybatis.bean.User">
UPDATE users
<trim prefix="SET" prefixOverrides=",">
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
, name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="age != null and age != ''">
, age = #{age}
</if>
<if test="birthday != null and birthday != ''">
, birthday = #{birthday}
</if>
</trim>
where id = ${id}
</update>
(第二段第一个if节点多了个逗号) 结果我发现这2段xml解析的结果是一样的,非常迫切地想知道这到底是为什么,然后这也促使了我去看源码的决心。最终还是看下来了。