Java 7
1. 以前泛型初始化比较麻烦,现在对于Map<String, List<Trade>> trades = new TreeMap<String, List<Trade>> ();这种初始化,可以直接推测Map<String, List<Trade>> trades = new TreeMap <> ();
2. 引入switch
public class StringInSwitchStatementExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String game = "Card-Games";
switch(game){
case "Hockey": case"Cricket": case"Football":
System.out.println("This is a outdoor game");
break;
case "Chess": case"Card-Games": case"Puzzles": case"Indoor basketball":
System.out.println("This is a indoor game");
break;
default:
System.out.println("What game it is?");
}
}
}
3. 自动资源分配 try(someresource),不需要再用try{...}finally{close()}
还可以用;分割来一次申请多个资源,比如: try(FileOutputStream fos = newFileOutputStream("movies.txt");DataOutputStream dos = newDataOutputStream(fos)) {
不过这些资源需要实现AutoCloseable接口(是java.io.Closeable的父接口)。
4. 引入数字常量中的下划线,比如1_000_000
5. 在一个catch中catch多种exception。catch(ExceptionOne | ExceptionTwo | ExceptionThree e)
6. 新的File System API(nio2.0)
比如:
Path path= Paths.get("c:Temp emp");
path.getNameCount();//2
path.getFileName();//temp.txt
path.getRoot();//c:
path.getParent();//c:Temp
Files.delete(path);
Files.deleteIfExists(path)
Files.copy(srcpath, despath)
Files.move(srcpath, despath)
Files.createSymbolicLink(symLink, srcpath)
能用WatchService来获取dir或者file变更的通知
WatchService watchService = FileSystems.getDefault().newWatchService(); dirToWatch.register(watchService, ENTRY_CREATE, ENTRY_MODIFY, ENTRY_DELETE); while(true) { WatchKey key = watchService.take(); for(WatchEvent<?> event : key.pollEvents()) { Kind<?> kind = event.kind(); //do sth }
key.reset(); }
7. ForkJoinTask & ForkJoinPool
ForkJoinTask可以是RecursiveAction或者RecursiveTask,这里前者不返回
ForkJoinPool Pool = new ForkJoinPool(proc); TaskA tk=new TaskA(arg1); T t = Pool.invoke(tk); Pool.awaitTermination(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); Pool.awaitQuiescence(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS); Pool.getActiveThreadCount(); Pool.getPoolSize(); Pool.isTerminating(); TaskA tk2=new TaskA(arg1); Pool.execute(tk2); // do not return Pool.getAsyncMode()//if FIFO Pool.submit(tk3); Pool.shutdown(); class TaskA extends RecursiveTask<T> { TaskA(T argT) { } protected T compute() { return new T(); } }
ForkJoinPool fpool = new ForkJoinPool(); TaskA tk = new TaskA(); ForkJoinTask<String> Sfpool = ForkJoinTask.adapt(tk,"OK"); fpool.invoke(Sfpool); if(Sfpool.isDone()) System.out.println(Sfpool.join()); //OK,功效相当于在tk结束之后返回一个OK
这里ForkJoinTask.adapt提供一个运行Runnable并且返回可选的预定result的新ForkJoinTask。
8. invokeDynamic,此外,Java 7引入了新的java.lang.invoke包,里面有MethodHandle和CallSite等功能。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long lengthyColors = List.of("Red", "Green", "Blue")
.stream().filter(c -> c.length() > 3).count();
}
}
javap -c -p Main // truncated // class names are simplified for the sake of brevity // for instance, Stream is actually java/util/stream/Stream 0: ldc #7 // String Red 2: ldc #9 // String Green 4: ldc #11 // String Blue 6: invokestatic #13 // InterfaceMethod List.of:(LObject;LObject;)LList; 9: invokeinterface #19, 1 // InterfaceMethod List.stream:()LStream; 14: invokedynamic #23, 0 // InvokeDynamic #0:test:()LPredicate; 19: invokeinterface #27, 2 // InterfaceMethod Stream.filter:(LPredicate;)LStream; 24: invokeinterface #33, 1 // InterfaceMethod Stream.count:()J 29: lstore_1 30: return
这里filter新建了一个Predicate实例,并且调用了invokedynamic。调用对象是一个匿名成员函数,在BootstrapMethod Table的第0个。
private static boolean lambda$main$0(java.lang.String);
Code:
0: aload_0
1: invokevirtual #37 // Method java/lang/String.length:()I
4: iconst_3
5: if_icmple 12
8: iconst_1
9: goto 13
12: iconst_0
13: ireturn
引用来自https://www.baeldung.com/java-invoke-dynamic
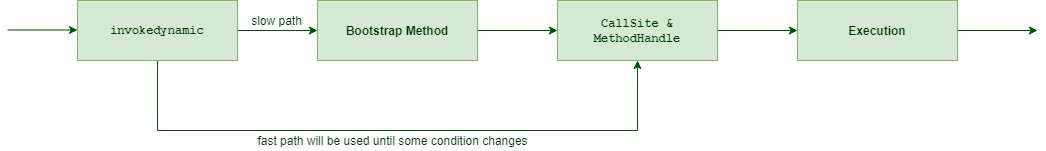
当JVM第一次看到invokeDynamic的时候会调用一个特殊的方法Bootstrap来进行初始化。Bootstrap是用来invocation process的,可以包含任何逻辑。当bootstrap调用完成之后,会返回一个CallSite实例,这个CallSite实例中封装了以下信息:
1. 指向JVM应当执行的实际逻辑的指针MethodHandle
2. 条件变量,用来指示CallSite是否可用。
之后JVM就不会再次调用bootstrap而是会直接用CallSite中的MethodHandle了。
与Reflection不同,JVM会试着优化MethodHandle中的代码。
此时列出BootstrapTable。可以看到,所有bootstrap method都存在LambdaMetafactory.metafactory里面。
javap -c -p -v Main
// truncated
// added new lines for brevity
BootstrapMethods:
0: #55 REF_invokeStatic java/lang/invoke/LambdaMetafactory.metafactory:
(Ljava/lang/invoke/MethodHandles$Lookup;
Ljava/lang/String;
Ljava/lang/invoke/MethodType;
Ljava/lang/invoke/MethodType;
Ljava/lang/invoke/MethodHandle;
Ljava/lang/invoke/MethodType;)Ljava/lang/invoke/CallSite;
Method arguments:
#62 (Ljava/lang/Object;)Z
#64 REF_invokeStatic Main.lambda$main$0:(Ljava/lang/String;)Z
#67 (Ljava/lang/String;)Z
注意bootstrap返回的是ConstantCallSite。此外,java还提供了MutableCallSite和VolatileCallSite功能,也能实现类似逻辑。
9. JDBC: 提供了RowSetFactory, RowSetProvider, RowSet,CachedRowSet, JdbcRowSet等。
import javax.sql.rowset.JdbcRowSet; import javax.sql.rowset.RowSetProvider; class JdbcExample{ public staticvoid main(String args[]) throws Exception{ try(// --------------try-with-resources begin-------------// // Creating connection JdbcRowSet jRS = RowSetProvider.newFactory().createJdbcRowSet(); )// --------------try-with-resources end--------------// { // ----------------try block begin---------------------// // Set database connection jRS.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student"); // Set database username jRS.setUsername("root"); // Set database password jRS.setPassword("mysql"); // Set sql query to execute jRS.setCommand("select * from user"); // Execute query jRS.execute(); // Getting 3rd row because it is scrollable by default jRS.absolute(3); System.out.println(jRS.getInt(1)+""+jRS.getString(2)+""+jRS.getString(3)); // Updating 3rd row jRS.updateString("name", "Neraj Kumar Singh"); jRS.updateRow(); // Fetching 3rd row again System.out.println(jRS.getInt(1)+""+jRS.getString(2)+""+jRS.getString(3)); // Set sql query to execute jRS.setCommand("select * from user"); // Execute query jRS.execute(); while(jRS.next()){ System.out.println(jRS.getInt(1)+""+jRS.getString(2)+""+jRS.getString(3)); } } // ----------------try block end----------------------// catch(Exception e){ // Exception handler System.out.println(e); } } }
Java 8
1. lambda expression,基本结构(args)->{dosth;return sth2;}
例子来自javatpoint.com
Sayable s2= name ->{ return "Hello, "+name; };
Addable ad2=(int a,int b)->(a+b);
list.forEach(
(n)->System.out.println(n)
);
Runnable r2=()->{
System.out.println("Thread2 is running...");
};
Thread t2=new Thread(r2);
t2.start();
Collections.sort(list,(p1,p2)->{
return p1.name.compareTo(p2.name);
});
Stream<Product> filtered_data = list.stream().filter(p -> p.price > 20000);
b.addActionListener(e-> {tf.setText("hello swing");});
2. Method Reference
a) Reference to a Static Method:基本语法Class::staticMethod
例如,可以定义一个functional interface,然后把一个参数构成相同的静态方法引用为该interface实例。
interface Sayable{ void say(); } public class MethodReference { public static void saySomething(){ System.out.println("Hello, this is static method."); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Referring static method Sayable sayable = MethodReference::saySomething; // Calling interface method sayable.say(); //Hello, this is static method. } }
以下实例则直接将静态方法转化为Runnable接口:
public class MethodReference2 {
public static void ThreadStatus(){
System.out.println("Thread is running...");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t2=new Thread(MethodReference2::ThreadStatus);
t2.start();
}
}
还能用静态方法来override另一个类中的静态方法。
import java.util.function.BiFunction; class Arithmetic{ public static int add(int a, int b){ return a+b; } public static float add(int a, float b){ return a+b; } public static float add(float a, float b){ return a+b; } } public class MethodReference4 { public static void main(String[] args) { BiFunction<Integer, Integer, Integer>adder1 = Arithmetic::add; BiFunction<Integer, Float, Float>adder2 = Arithmetic::add; BiFunction<Float, Float, Float>adder3 = Arithmetic::add; int result1 = adder1.apply(10, 20); float result2 = adder2.apply(10, 20.0f); float result3 = adder3.apply(10.0f, 20.0f); System.out.println(result1); System.out.println(result2); System.out.println(result3); } }
b) Ref to an instance method: obj::methodname
public class InstanceMethodReference2 { public void printnMsg(){ System.out.println("Hello, this is instance method"); } public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t2=new Thread(new InstanceMethodReference2()::printnMsg); t2.start(); } }
c) Ref to a Constructor: class::new
interface Messageable{ Message getMessage(String msg); } class Message{ Message(String msg){ System.out.print(msg); } } public class ConstructorReference { public static void main(String[] args) { Messageable hello = Message::new; hello.getMessage("Hello"); } }
3. 下划线变成了keyword,不能再直接用来当变量名了。
4. 提供了defaultStream和staticStream两个类。提供了takeWhile, dropWhile。
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class StreamExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list
= Stream.of(2,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10)
.takeWhile(i -> (i % 2 == 0)).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list); //[2,2]
}
}
dropwhile类似。
创建时也有两个值得一提的方法-ofNullable和iterate。
ofNullable,也就是Stream.of,当传入的是null的时候,返回empty stream,更方便处理null stream和NullPointerException。Stream<Integer> val = Stream.ofNullable(null);
iterate(seed; hasNext;next)
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class StreamExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.iterate(1, i -> i <= 10, i -> i*3)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
5. 引入Module,用来管理多个package。能够生成Modular JAR。这个JAR会包含一个用来描述信息的module-info.class。此外,还能生成JMOD格式,这个格式与JAR相似,但是能够包含源代码和config文件。
module-info.java的内容示例:
module com.javatpoint{
}
编译: javac -d mods --module-source-path src/ --module com.javatpoint
运行: java --module-path mods/ --module com.javatpoint/com.javatpoint.Hello
6. 引入JShell
7. 新的version命名格式: $MAJOR.$MINOR.$SECURITY.$PATCH
8. try-with-resource升级,现在可以在外面定义好:
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class FinalVariable {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
FileOutputStream fileStream=new FileOutputStream("javatpoint.txt");
try(fileStream){
String greeting = "Welcome to javaTpoint.";
byte b[] = greeting.getBytes();
fileStream.write(b);
System.out.println("File written");
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
9. Process API改进,例如:
public class ProcessApiExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProcessHandle currentProcess = ProcessHandle.current(); // Current processhandle
System.out.println("Process Id: "+currentProcess.pid()); // Process id
System.out.println("Direct children: "+ currentProcess.children()); // Direct children of the process
System.out.println("Class name: "+currentProcess.getClass()); // Class name
System.out.println("All processes: "+ProcessHandle.allProcesses()); // All current processes
System.out.println("Process info: "+currentProcess.info()); // Process info
System.out.println("Is process alive: "+currentProcess.isAlive());
System.out.println("Process's parent "+currentProcess.parent()); // Parent of the process
}
}
10. List, Set, Map都能够使用Java9的静态工厂类方法来创建,比如:
import java.util.Map;
public class FactoryMethodsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer,String> map = Map.of(101,"JavaFX",102,"Hibernate",103,"Spring MVC");
for(Map.Entry<Integer, String> m : map.entrySet()){
System.out.println(m.getKey()+" "+m.getValue());
}
}
}
import java.util.Set;
public class FactoryMethodsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = Set.of("Java","JavaFX","Spring","Hibernate","JSP");
for(String l:set) {
System.out.println(l);
}
}
}
11. @SafeVarargs
12. 允许在接口中创建private方法。
interface Sayable{
default void say() {
saySomething();
}
// Private method inside interface
private void saySomething() {
System.out.println("Hello... I'm private method");
}
}
public class PrivateInterface implements Sayable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sayable s = new PrivateInterface();
s.say();
}
}
13. Anonymous Inner Class创建也能自动推测泛型。
abstract class ABCD<T>{
abstract T show(T a, T b);
}
public class TypeInferExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ABCD<String> a = new ABCD<>() { // diamond operator is empty
String show(String a, String b) {
return a+b;
}
};
String result = a.show("Java","9");
System.out.println(result);
}
}
Java 10
1. 局部变量类型推断升级
var list = new ArrayList<String>(); // ArrayList<String> var stream = list.stream(); // Stream<String>
2. 整合JDK代码仓库
3. 统一GC接口,为 G1 引入多线程并行 GC
4. 增加了Application Class-Data Sharing,允许将应用类放置在共享存档中,能够让服务快速启动改善系统响应时间。
5. Thread-Local Handshakes, 能够单独对某个JVM线程操作-允许在不运行全局JVM安全点的情况下实现线程回调,由线程本身或者JVM线程来执行,同时保持线程处于阻塞状态,这种方式使得停止单个线程变成可能
6. 变更命名机制: $FEATURE.$INTERIM.$UPDATE.$PATCH
7. 提供默认的根证书认证
8. 实验性质的JIT编译器Graal。-XX:+ UnlockExperimentalVMOptions -XX:+ UseJVMCICompiler
9. 拓展了Unicode
java.text.DateFormat::get*Instance
java.text.DateFormatSymbols::getInstance
java.text.DecimalFormatSymbols::getInstance
java.text.NumberFormat::get*Instance
java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter::localizedBy
java.time.format.DateTimeFormatterBuilder::getLocalizedDateTimePattern
java.time.format.DecimalStyle::of
java.time.temporal.WeekFields::of
java.util.Calendar::{getFirstDayOfWeek,getMinimalDaysInWeek}
java.util.Currency::getInstance
java.util.Locale::getDisplayName
java.util.spi.LocaleNameProvider
10 .Heap Allocation on Alternative Memory Devices
11. Optional
Optional<String> name = Optional.ofNullable(str); // New API added - is preferred option then get() method name.orElseThrow();
Java 11
1. 为lambda参数的类型推断
Function<String, String> append = (var string) -> string + " ";
2. String::lines
multiline.lines()
// we now have a `Stream<String>`
.map(line -> "// " + line)
.forEach(System.out::println);
3. 新字符
4. Standard HTTP Client-jdk.incubator.http
5. File的新方法: ‘writeString()’, ‘readString()’ and ‘isSameFile()’. ‘writeString()’
6. ‘-XX: +UseDynamicNumberOfCompilerThreads.’ 动态分配编译器线程,每个type只产生一个thread
7. Z garbage Collector: 保证停顿不会超过10ms
8. jceks.key.serialFilte
9. Low-overhead Heap Profiling
10. Epsilon Garbage Collector: 用于处理没有实现任何内存回收机制的分配的内存
11. .toArray(IntFunction)