前言:
自定义控件的三大方法:
测量: onMeasure(): 测量自己的大小,为正式布局提供建议
布局: onLayout(): 使用layout()函数对所有子控件布局
绘制: onDraw(): 根据布局的位置绘图
onDraw() 里面是绘制的操作,可以看下其他的文章,下面来了解 onMeasure()和onLayout()方法。
一、onMeasure()、测量
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
参数即父类传过来的两个宽高的"建议值",即把当前view的高设置为:heightMeasureSpec ;宽设置为:widthMeasureSpec
这个参数不是简单的整数类型,而是2位整数(模式类型)和30位整数(实际数值) 的组合
其中模式分为三种:
①、UNSPECIFIED(未指定),父元素部队自元素施加任何束缚,子元素可以得到任意想要的大小;UNSPECIFIED=00000000000000000000000000000000
②、EXACTLY(完全),父元素决定自元素的确切大小,子元素将被限定在给定的边界里而忽略它本身大小;EXACTLY =01000000000000000000000000000000
③、AT_MOST(至多),子元素至多达到指定大小的值。 他们对应的二进制值分别是: AT_MOST =10000000000000000000000000000000
最前面两位代表模式,分别对应十进制的0,1,2;
获取模式int值 和 获取数值int值的方法:
- int measureWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
- int measureHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
- int measureWidthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
- int measureHeightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
模式的值有:
MeasureSpec.AT_MOST = 2
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY = 1
MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED = 0
上面我们知道了 onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) 方法参数的意义
下面了解参数对应的三个模式分别对应的意义:
每一个模式都对应的xml布局中的一个值
wrap_content --- MeasureSpec.AT_MOST match_parent --- MeasureSpec.EXACTLY 具体值 --- MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED
注意:当模式是MeasureSpec.AT_MOST时,即wrap_content时,需要将大小设置一个数值。
二、onLayout() 、 布局
首先先了解几个需要用到的方法:
(1)、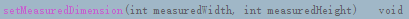
这个方法和onMeasure()方法类似。其实这个方法的作用就是 设置当前View的宽高。
(2)、
这个方法就和 方法类似了,不过少了第一个参数boolean changed
方法类似了,不过少了第一个参数boolean changed
这个方法的目的是用于当前ViewGroup中的子控件的布局
再看 方法,只要是继承ViewGroup的类都必须要重写该方法,来实现该控件内部子控件的布局情况。
方法,只要是继承ViewGroup的类都必须要重写该方法,来实现该控件内部子控件的布局情况。
我们写一个自定义类继承ViewGroup实现Linearlayout垂直排列的效果看下:
public class XViewGroup extends ViewGroup{ public XViewGroup(Context context) { super(context); } public XViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); } public XViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); } @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); int measureWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int measureHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); int measureWidthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int measureHeightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
// 计算所有子控件需要用到的宽高 int height = 0; //记录根容器的高度 int width = 0; //记录根容器的宽度 int count = getChildCount(); //记录容器内的子控件个数 for (int i=0;i<count;i++) { //测量子控件 View child = getChildAt(i); measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); //获得子控件的高度和宽度 int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); //得到最大宽度,并且累加高度 height += childHeight; width = Math.max(childWidth, width); } // 设置当前View的宽高 setMeasuredDimension((measureWidthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? measureWidth: width, (measureHeightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? measureHeight: height); } @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { int top = 0; int count = getChildCount(); for (int i=0;i<count;i++) { View child = getChildAt(i); int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); //该子控件在父容器的位置 , 高度是之前所有子控件的高度和开始 ,从上往下排列,就实现了类似Linearlayout布局垂直排列的布局 child.layout(0, top, childWidth, top + childHeight); //以父容器左上角为原点进行布局 top += childHeight; } } }