题目描述
在有向图中, 我们从某个节点和每个转向处开始, 沿着图的有向边走。 如果我们到达的节点是终点 (即它没有连出的有向边), 我们停止。
现在, 如果我们最后能走到终点,那么我们的起始节点是最终安全的。 更具体地说, 存在一个自然数 (K), 无论选择从哪里开始行走, 我们走了不到 (K) 步后必能停止在一个终点。
哪些节点最终是安全的? 结果返回一个有序的数组。
该有向图有 N 个节点,标签为 0, 1, ..., N-1, 其中 N 是 graph 的节点数. 图以以下的形式给出: graph[i] 是节点 j 的一个列表,满足 (i, j) 是图的一条有向边。
示例:
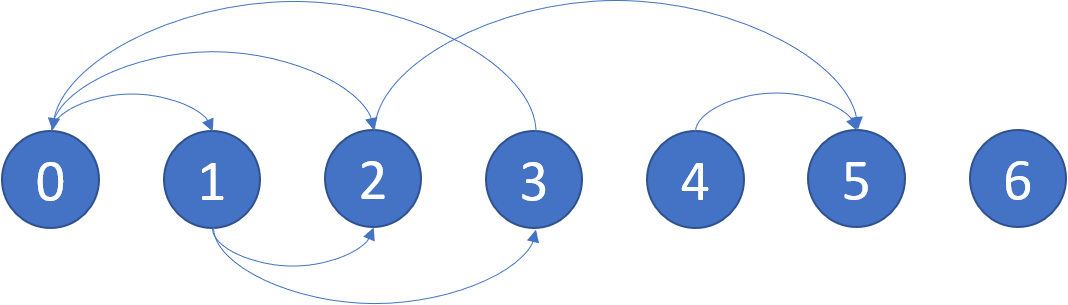
输入:graph = [[1,2],[2,3],[5],[0],[5],[],[]]
输出:[2,4,5,6]
这里是上图的示意图。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-eventual-safe-states
思路解析
- 定义安全节点:
没有出边的节点均为安全节点;
出边连接的节点均为安全节点的节点。 - 查找图的最终安全节点(没有出边的节点)
- 将图反向,得到
rGraph,依次查找仅与安全节点相连的节点,并存入队列
代码实现
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> eventualSafeNodes(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
// Find terminate
vector<int> terminates;
vector<int> degree;
for(int i = 0; i < graph.size(); i++) {
if(graph[i].empty())
terminates.push_back(i);
degree.push_back(graph[i].size());
}
// Reverse graph
vector<vector<int>> rGraph = reverseGraph(graph);
// Construct queue
queue<int> safeNodes;
for(auto node : terminates)
safeNodes.push(node);
while(!safeNodes.empty()) {
int curNode = safeNodes.front();
for(auto pNode : rGraph[curNode]) {
for(auto tNode : graph[pNode]) {
if(tNode == curNode) {
degree[pNode]--;
break;
}
}
if(degree[pNode] <= 0) {
safeNodes.push(pNode);
terminates.push_back(pNode);
}
/*
for(auto nt = graph[pNode].begin(); nt != graph[pNode].end(); nt++) {
if((*nt) == curNode)
graph[pNode].erase(nt);
if(nt == graph[pNode].end())
break;
}
if(graph[pNode].empty()) {
safeNodes.push(pNode);
terminates.push_back(pNode);
}
*/
}
safeNodes.pop();
}
sort(terminates.begin(), terminates.end());
return terminates;
}
vector<vector<int>> reverseGraph(vector<vector<int>> graph) {
vector<vector<int>> rGraph(graph.size(), vector<int>{});
for(int i = 0; i < graph.size(); i++)
for(auto tNode : graph[i])
rGraph[tNode].push_back(i);
return rGraph;
}
};