今天写了个拦截器对一些mapping做了些处理,写完之后突然很想看看拦截器是怎么加进spring里面。对着源码debug了一遍。又有了新的收获。
1.拦截器的实现
1.实现HandlerInterceptor
public class MyHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("---------preHandle--------"); return true; } /** * controller执行之后,且页面渲染之前调用 * @param request * @param response * @param handler * @param modelAndView * @throws Exception */ @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("---------postHandle--------"); } /** * 页面渲染之后调用,一般用于资源清理操作 * @param request * @param response * @param handler * @param ex * @throws Exception */ @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("---------afterCompletion--------"); }
2.将拦截器加入到拦截链里面去,这里可以实现
WebMvcConfigurer
也可以继承
WebMvcConfigurerAdapter
只是 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter这个类在Springboot2.0已经 Deprecated了,这部分内容我们后面再讲
@Component public class MyWebMvcConfigurerAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { registry.addInterceptor(new MyHandlerInterceptor()); } }
接下来我们看看拦截是怎么被调用的,在 preHandle方法打断点
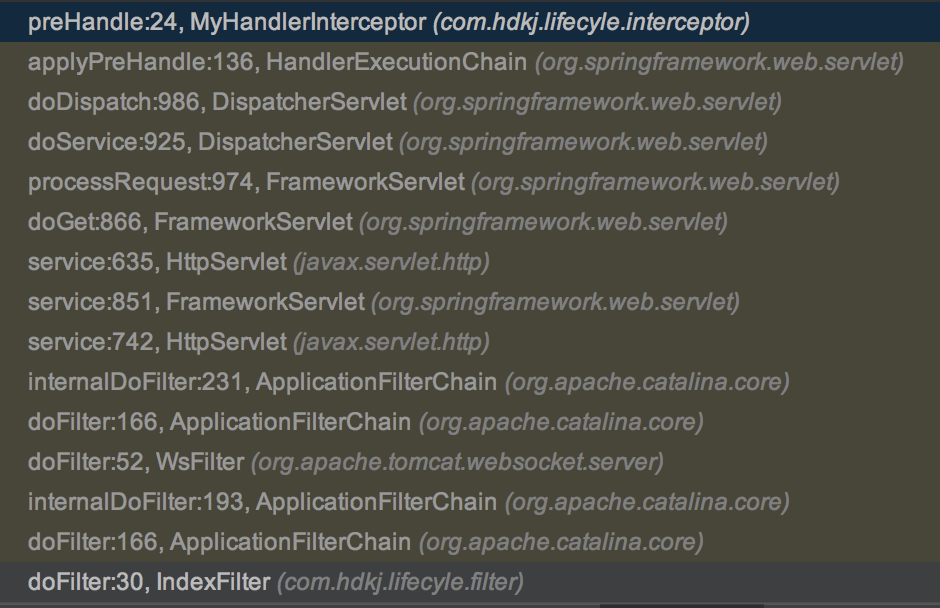
我们发现拦截器的获取在 org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExecutionChain#applyPreHandle 方法
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors(); if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) { for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) { HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i]; if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) { triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); return false; } this.interceptorIndex = i; } } return true; }
这里的 getInterceptors 如下所示
public HandlerInterceptor[] getInterceptors() { if (this.interceptors == null && this.interceptorList != null) { this.interceptors = this.interceptorList.toArray(new HandlerInterceptor[0]); } return this.interceptors; }
那现在的问题就是要找到 interceptors是怎么初始化的呢。我们找到了HandlerExecutionChain的构造方法,发现interceptors就是在这赋值的
public HandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, @Nullable HandlerInterceptor... interceptors) { if (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain) { HandlerExecutionChain originalChain = (HandlerExecutionChain) handler; this.handler = originalChain.getHandler(); this.interceptorList = new ArrayList<>(); CollectionUtils.mergeArrayIntoCollection(originalChain.getInterceptors(), this.interceptorList); CollectionUtils.mergeArrayIntoCollection(interceptors, this.interceptorList); } else { this.handler = handler; this.interceptors = interceptors; } }
再在这打个断点,找到了调用这个构造方法的类
org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping#getHandlerExecutionChain
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) { HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ? (HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler)); String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request); for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) { if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) { MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor; if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) { chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor()); } } else { chain.addInterceptor(interceptor); } } return chain; }
看到 AbstractHandlerMapping 差不多就知道是怎么一回事情了,这里再把调用的代码贴出来
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request); if (handler == null) { handler = getDefaultHandler(); } if (handler == null) { return null; } // Bean name or resolved handler? if (handler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) handler; handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request); if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) { CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.globalCorsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request); CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request); CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig); executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config); } return executionChain; }
这个getHandler方法 其实就是RequestMapping注解调用的地方,这里的handle可以想象成是一个controller,getHandlerExecutionChain 这个方法的作用就是给我们的controller加上一层拦截器的属性,从HandlerExecutionChain的构造方法也能看出,HandlerExecutionChain 就是 handle和interceptor的封装。
到这里,我们大概是知道了拦截器是怎么被调用的。但是,我们还不知道拦截器是怎么被加载进spring的呢?
这里我们将重点放在 getHandlerExecutionChain 的 this.adaptedInterceptors 属性
我们找到了这个方法
protected void initInterceptors() { if (!this.interceptors.isEmpty()) { for (int i = 0; i < this.interceptors.size(); i++) { Object interceptor = this.interceptors.get(i); if (interceptor == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Entry number " + i + " in interceptors array is null"); } this.adaptedInterceptors.add(adaptInterceptor(interceptor)); } } }
这里的interceptor又是从interceptors获取而来,interceptors 的初始化是通过以下代码
public void setInterceptors(Object... interceptors) { this.interceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); }
我们在这里打个断点,最终找到了
org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport#requestMappingHandlerMapping
public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping() { RequestMappingHandlerMapping mapping = createRequestMappingHandlerMapping(); mapping.setOrder(0); mapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors()); mapping.setContentNegotiationManager(mvcContentNegotiationManager()); mapping.setCorsConfigurations(getCorsConfigurations());
protected final Object[] getInterceptors() { if (this.interceptors == null) { InterceptorRegistry registry = new InterceptorRegistry(); addInterceptors(registry); registry.addInterceptor(new ConversionServiceExposingInterceptor(mvcConversionService())); registry.addInterceptor(new ResourceUrlProviderExposingInterceptor(mvcResourceUrlProvider())); this.interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(); } return this.interceptors.toArray(); }
还记最开始我们说的 将拦截器加入到拦截链里面的方法么。就是在这里调用的。
public class MyWebMvcConfigurerAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { registry.addInterceptor(new MyHandlerInterceptor()); } }
到这里我们大概的就知道了拦截器是怎么加入spring的。还剩最后一个问题,requestMappingHandlerMapping 是由怎么触发的呢?
我们找到了方法的调用
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration.EnableWebMvcConfiguration#requestMappingHandlerMapping
@Bean @Primary @Override public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping() { // Must be @Primary for MvcUriComponentsBuilder to work return super.requestMappingHandlerMapping(); }
这个方法在 WebMvcAutoConfiguration里面,看到这个类名就知道这是个自动配置类。那么他一定和@EnableAutoconfigure 注解有关。我在 org/springframework/boot/spring-boot-autoconfigure/2.0.4.RELEASE/spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.0.4.RELEASE.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories 这个文件里面找到了AutoConfig的配置。所以 requestMappingHandlerMapping 是通过springboot自动配置扫描bean加载的。
# Auto Configure org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration= org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,
最后 我们再看下 WebMvcAutoConfiguration这个类的几个注解
@Configuration @ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET) @ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class }) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class) @AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10) @AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class }) public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
ConditionalOnMissingBean这个注解表明 只有不存在 WebMvcConfigurationSupport 这个bean才可以配置加载,所以这也是为什么我们在将拦截器加入到拦截链里面的方法里面是实现 WebMvcConfigurer 而不是继承WebMvcConfigurationSupport。
最后我们再总结下
1.项目启动的时候springboot会自动扫描相关配置类触发requestMappingHandlerMapping方法
2.requestMappingHandlerMapping会将系统的各个拦截添加到拦截器数组中,真正的http请求过来后会调用getHandler方法将过滤器和handle封装成HandlerExecutionChain。
3.按照过滤器添加顺序依次执行过滤器
以上,就是对拦截器的分析
转载请注明出处 https://www.cnblogs.com/xmzJava/p/9550535.html