CNN:
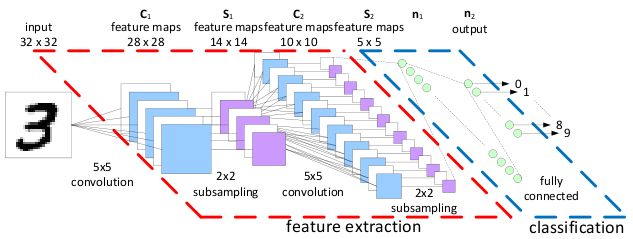
一张概览图可以很清楚的展示出CNN一步步学习的步骤:
#!/usr/bin/env python2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ tensorflow编写cnn """ import tensorflow as tf #导入手写数据集 from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True) def weight_variable(shape): #tf.truncated_normal(shape, mean, stddev) :shape表示生成张量的维度,mean是均值,stddev是标准差。 #这是一个截断的产生正太分布的函数,就是说产生正太分布的值如果与均值的差值大于两倍的标准差,那就重新生成。 initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1) return tf.Variable(initial) def bias_variable(shape): initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape) return tf.Variable(initial) #定义卷积层 #x为输入数据 #W为过滤窗口的大小,及卷积核 def conv2d(x,W): #stride [1, x_movement, y_movement, 1] 为过滤窗口每次移动的步长 #其中第一个参数和最后一个参数必须为1 # #padding的方式在tensorflow里分两种,一种是VALID,一种是SAME, #padding表示通俗的说就是是否在图片周围添加0 #same比较常用就是添加0,然后抽取出的图片和原来图片大小相等, valid不添加0,抽取的图片比原图片小 return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') #定义池化层,一般有两种,取最大值,获取平均值,进一步提取最重要的特征,属于subsampling,下采样 #窗口大小定义为2X2 def max_pool_2X2(x): #ksize就是定义窗口大小 return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1], padding='SAME') def compute_accuracy(v_xs, v_ys): global prediction y_pre = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: v_xs, keep_prob: 1}) correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_pre,1), tf.argmax(v_ys,1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) result = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={xs: v_xs, ys: v_ys, keep_prob: 1}) return result xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) # 28x28 ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) #输入图片的大小为28X28 #-1表示不考虑样本的维度,即样本的数量,1表示channel,黑白只有一个,RGB有多个 x_image = tf.reshape(xs,[-1, 28, 28, 1]) """ 定义层1 conv1 """ #过滤窗口大小为 5X5 ,输入的高度为1, 输出高度为32 W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32]) b_conv1 = bias_variable([32]) #试用relu做激活函数 #输出大小为28X28X32 h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1)+ b_conv1) #输出大小为14X14X32 h_pool1 = max_pool_2X2(h_conv1) """ 定义层2 conv2 不断缩小拉长 """ #过滤窗口大小为 5X5 ,输入的高度为32, 输出高度为64 W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64]) b_conv2 = bias_variable([64]) #试用relu做激活函数 #输出大小为14X14X64 h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2)+ b_conv2) #输出大小为7X7X64 h_pool2 = max_pool_2X2(h_conv2) """ 定义全连接层fully connected layer,神经网络中隐藏层,将卷积后的结果按普通神经网络求结果 func1 layer """ # 数据由[n_samples, 7, 7, 64] 压扁为一维 [n_samples, 7*7*64] h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64]) ##函数层,将数据由高维变成1维数据## W_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64,1024]) b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024]) h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1)+ b_fc1) h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob) """ 定义全连接层,输出结果为要预测数字的概率,所有输出为10 func2 layer """ W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10]) b_fc2 = bias_variable([10]) prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop,W_fc2)+b_fc2) #定义损失函数 cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(ys * tf.log(prediction), reduction_indices=[1])) # loss #添加训练步骤, 优化方法用adam优化器 train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy) sess = tf.Session() sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) for i in range(1000): batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: batch_xs, ys: batch_ys, keep_prob: 0.5}) if i % 50 == 0: print(compute_accuracy( mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels))