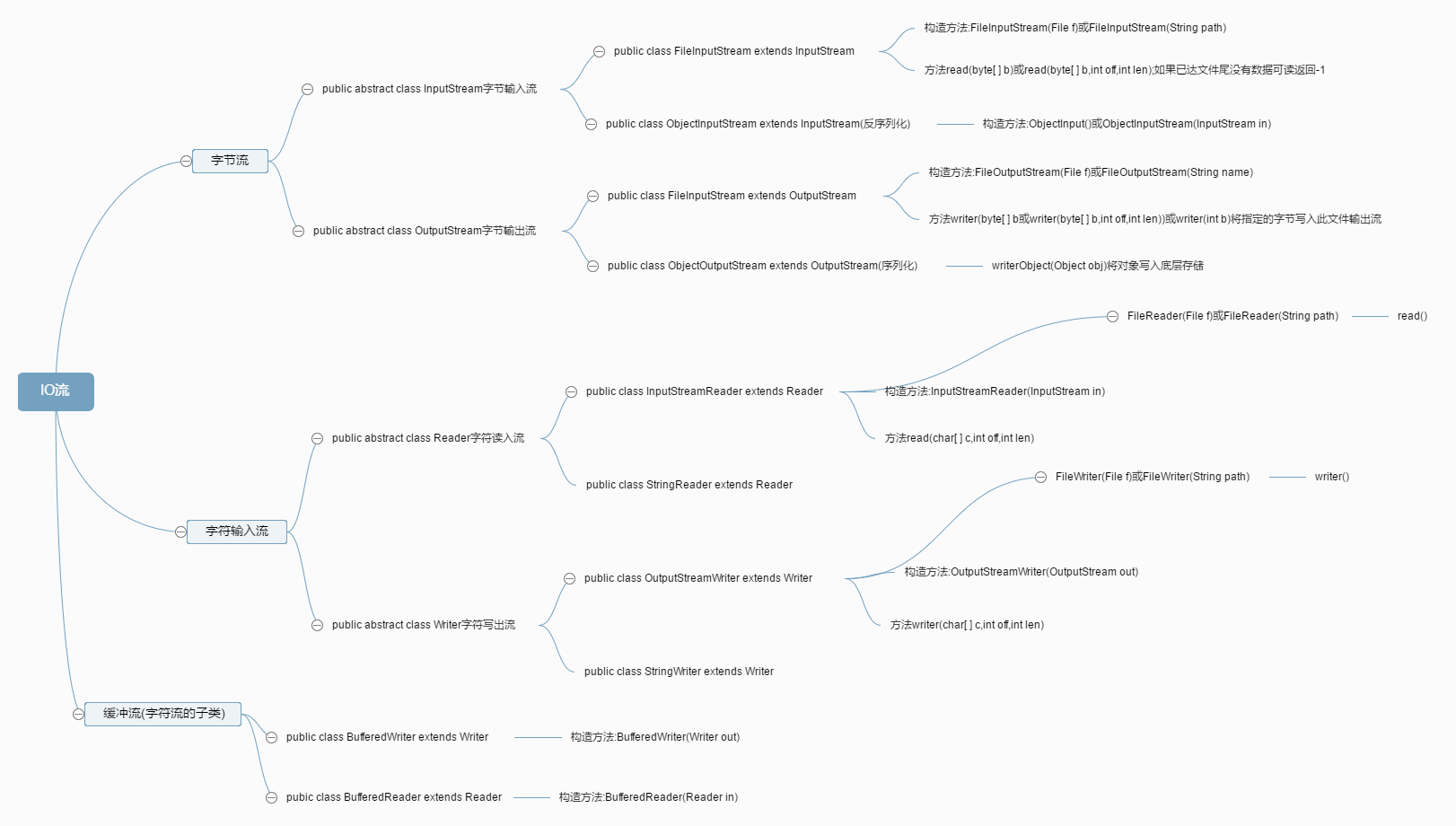
1.用FileInputStream读文件内容,然后再用OutputStream来向文件中写入内容
1 public class IO1 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 4 File file=new File("G://ha_xie/a.txt"); 5 InputStream in=new FileInputStream(file); 6 //读 里面的参数是 从此输入流读取的估计字节数 7 byte[] b=new byte[in.available()]; 8 in.read(b); 9 //将字节数组转换成字符串 10 String str=new String(b,0,b.length); 11 System.out.println(str); 12 13 OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("G://ha_xie/b.txt"); 14 out.write(b);//将数组中的字节写入此输出流 15 } 16 }
2.使用InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter
1 public class IO2 { 2 public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { 3 File file=new File("G://ha_xie/a.txt"); 4 InputStream in=null; 5 in=new FileInputStream(file); 6 InputStreamReader is = new InputStreamReader(in); 7 char[] c=new char[30]; 8 is.read(c); 9 //字符数组在转换成字符串 10 String str=new String(c); 11 System.out.println(str); 12 // in.close(); 13 // is.close(); 14 //写到c.txt 15 OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("G://ha_xie/d.txt"); 16 OutputStreamWriter os1=new OutputStreamWriter(out); 17 os1.write(str); 18 os1.close();//这个必须关闭,才能向文件里面写入内容 19 } 20 }
3.使用FileReader和FileWriter
1 public class IO3 { 2 public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { 3 Reader r= new FileReader("G://ha_xie/a.txt"); 4 char[] c=new char[20]; 5 r.read(c); 6 System.out.println(new String(c)); 7 8 Writer w=new FileWriter("G://ha_xie/bb.txt"); 9 w.write(c); 10 w.close(); 11 } 12 }
4.使用BufferedReader和BufferedWriter
1 public class IO4 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 3 //字节流 4 InputStream in=new FileInputStream("G://ha_xie./a.txt"); 5 //字符流 6 InputStreamReader r=new InputStreamReader(in); 7 //缓冲流 8 Reader reader1=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("G://ha_xie/b.txt")); 9 Reader reader=new BufferedReader(r); 10 /*String str=((BufferedReader) reader).readLine();//按行读 11 System.out.println(str);*/ 12 /*String s; 13 int i=0; 14 while((s=((BufferedReader) reader).readLine())!=null){ 15 System.out.println(s); 16 i++; 17 } 18 System.out.println(i);*/ 19 String string = ((BufferedReader) reader).readLine(); 20 String string2 = ((BufferedReader) reader).readLine(); 21 System.out.println(string); 22 System.out.println(string2); 23 //关闭资源 24 reader.close(); 25 r.close(); 26 in.close(); 27 //写 28 BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("G://ha_xie/oo.txt")); 29 bw.write("谢军帅谢军帅"); 30 bw.newLine();//换行,写入一个行分隔符 31 bw.newLine(); 32 bw.write("xiejunshuaixiejunshuai"); 33 bw.flush();//刷新 34 bw.close();//关闭此流,但要先刷新它 35 } 36 } 37 //我的理解:是缓冲中的数据,输出一行少一行
注意:使用完流对象之后,要关闭!!!要不然会存在写不进去的情况。