周赛地址(英):weekly contest 193
周赛地址(中):第 193 场周赛
仓库地址:week-Leetcode
1480. Running Sum of 1d Array
Given an array nums. We define a running sum of an array as runningSum[i] = sum(nums[0]…nums[i]).
Return the running sum of nums.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [1,3,6,10]
Explanation: Running sum is obtained as follows: [1, 1+2, 1+2+3, 1+2+3+4].
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,1,1]
Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
Explanation: Running sum is obtained as follows: [1, 1+1, 1+1+1, 1+1+1+1, 1+1+1+1+1].
Example 3:
Input: nums = [3,1,2,10,1]
Output: [3,4,6,16,17]
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 1000
- -10^6 <= nums[i] <= 10^6
题解
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number[]}
*/
const runningSum = function(nums) {
let curr=0
const res= nums.map(item=>{
curr+=item
return curr;
})
return res
};
1481. Least Number of Unique Integers after K Removals
Given an array of integers arr and an integer k. Find the least number of unique integers after removing exactly k elements.
Example 1:
Input: arr = [5,5,4], k = 1
Output: 1
Explanation: Remove the single 4, only 5 is left.
Example 2:
Input: arr = [4,3,1,1,3,3,2], k = 3
Output: 2
Explanation: Remove 4, 2 and either one of the two 1s or three 3s. 1 and 3 will be left.
Constraints:
- 1 <= arr.length <= 10^5
- 1 <= arr[i] <= 10^9
- 0 <= k <= arr.length
题解
/**
* @param {number[]} arr
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
const findLeastNumOfUniqueInts = function(arr, k) {
let obj={}
for(let item of arr){
if(obj[item]){
obj[item]++
}else{
obj[item]=1
}
}
let enObj=Object.entries(obj).sort((a,b)=>a[1]-b[1]);
let len=enObj.length;
for(let item of enObj){
if(k>=item[1]){
k-=item[1]
len--;
}else {
break;
}
}
return len;
};
1482. Minimum Number of Days to Make m Bouquets
Given an integer array bloomDay, an integer m and an integer k.
We need to make m bouquets. To make a bouquet, you need to use k adjacent flowers from the garden.
The garden consists of n flowers, the ith flower will bloom in the bloomDay[i] and then can be used in exactly one bouquet.
Return the minimum number of days you need to wait to be able to make m bouquets from the garden. If it is impossible to make m bouquets return -1.
Example 1:
Input: bloomDay = [1,10,3,10,2], m = 3, k = 1
Output: 3
Explanation: Let's see what happened in the first three days. x means flower bloomed and _ means flower didn't bloom in the garden.
We need 3 bouquets each should contain 1 flower.
After day 1: [x, _, _, _, _] // we can only make one bouquet.
After day 2: [x, _, _, _, x] // we can only make two bouquets.
After day 3: [x, _, x, _, x] // we can make 3 bouquets. The answer is 3.
Example 2:
Input: bloomDay = [1,10,3,10,2], m = 3, k = 2
Output: -1
Explanation: We need 3 bouquets each has 2 flowers, that means we need 6 flowers. We only have 5 flowers so it is impossible to get the needed bouquets and we return -1.
Example 3:
Input: bloomDay = [7,7,7,7,12,7,7], m = 2, k = 3
Output: 12
Explanation: We need 2 bouquets each should have 3 flowers.
Here's the garden after the 7 and 12 days:
After day 7: [x, x, x, x, _, x, x]
We can make one bouquet of the first three flowers that bloomed. We cannot make another bouquet from the last three flowers that bloomed because they are not adjacent.
After day 12: [x, x, x, x, x, x, x]
It is obvious that we can make two bouquets in different ways.
Example 4:
Input: bloomDay = [1000000000,1000000000], m = 1, k = 1
Output: 1000000000
Explanation: You need to wait 1000000000 days to have a flower ready for a bouquet.
Example 5:
Input: bloomDay = [1,10,2,9,3,8,4,7,5,6], m = 4, k = 2
Output: 9
Constraints:
- bloomDay.length == n
- 1 <= n <= 10^5
- 1 <= bloomDay[i] <= 10^9
- 1 <= m <= 10^6
- 1 <= k <= n
题解
const minDays = function(bloomDay, m, k) {
if (m * k > bloomDay.length) return -1;
let left = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER, right = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
for (let item of bloomDay) {
left = Math.min(left, item);
right = Math.max(right, item);
}
while (left <= right) {
let mid = left + parseInt((right - left) / 2);
if (isValid(bloomDay, k, m, mid)) right = mid - 1;
else left = mid + 1;
}
return left;
};
const isValid=function(bloomDay, size,count,day) {
let curcount = 0, cursize = 0;
for (let item of bloomDay) {
if (item <= day) cursize++;
else cursize = 0;
if (cursize == size) { cursize = 0; curcount++; }
if (curcount == count) return true;
}
return false;
}
1483. Kth Ancestor of a Tree Node
You are given a tree with n nodes numbered from 0 to n-1 in the form of a parent array where parent[i] is the parent of node i. The root of the tree is node 0.
Implement the function getKthAncestor(int node, int k) to return the k-th ancestor of the given node. If there is no such ancestor, return -1.
The k-th ancestor of a tree node is the k-th node in the path from that node to the root.
Example:
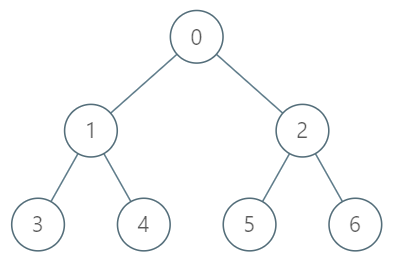
Input:
["TreeAncestor","getKthAncestor","getKthAncestor","getKthAncestor"]
[[7,[-1,0,0,1,1,2,2]],[3,1],[5,2],[6,3]]
Output:
[null,1,0,-1]
Explanation:
TreeAncestor treeAncestor = new TreeAncestor(7, [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]);
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(3, 1); // returns 1 which is the parent of 3
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(5, 2); // returns 0 which is the grandparent of 5
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(6, 3); // returns -1 because there is no such ancestor
Constraints:
- 1 <= k <= n <= 5*10^4
- parent[0] == -1 indicating that 0 is the root node.
- 0 <= parent[i] < n for all 0 < i < n
- 0 <= node < n
- There will be at most 5*10^4 queries.
题解
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[]} parent
*/
const TreeAncestor = function(n, parent) {
this.parent=parent;
this.n=n;
};
/**
* @param {number} node
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
TreeAncestor.prototype.getKthAncestor = function(node, k) {
let cnt =0
let val=-1, arrInd= node
while(k!==cnt){
val = this.parent[arrInd]
if (val === -1) return -1
arrInd = val
cnt++
}
return val
};
/**
* Your TreeAncestor object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new TreeAncestor(n, parent)
* var param_1 = obj.getKthAncestor(node,k)
*/