基础
字典
# 字典
me = {'height': 180}
print(me['height'])
me['weight'] = 18
print(me)
读取图片import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.image import imread
img = imread('lena.jpg')
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
类
# 类
class Man:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
print("Initilized!")
def hello(self):
print("Hello " + self.name)
def goodbye(self):
print("Good bye "+self.name+" !")
m = Man("David")
m.hello()
m.goodbye()
numpy使用
# numpy使用
import numpy as np
x = np.array([1.0, 2, 3]) # 生成数组
print(x)
print(type(x))
A = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
print(A)
print(A.shape) # 行、列数量
print(A.dtype)
B = np.array([10, 20])
C = A * B # 广播
print(C)
print(A[0]) # 第0行元素
for row in A:
print(row)
X = A.flatten() # 将 A 转换为一维数组
print(X)
matplotlib使用
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(0, 6, 0.1) # 以0.1为单位,成0到6的数据
y1 = np.sin(x)
y2 = np.cos(x)
plt.plot(x, y1, label = "sin") # label 为图例
plt.plot(x, y2, linestyle = "--", label = "cos")
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.title("sin & cos")
plt.legend() # 图例显示
plt.show()
感知机
与门
# 感知机
def AND(x1, x2):
# 与门
w1, w2, theta = 0.5, 0.5, 0.7
tmp = x1*w1 + x2*w2
if tmp <= theta:
return 0
elif tmp > theta:
return 1
import numpy as np
x = np.array([0, 1])
w = np.array([0.5, 0.5])
b = -0.7
print(w*x)
print(np.sum(w*x))
print(np.sum(w*x) + b)
def AND1(x1, x2):
x = np.array([x1, x2])
w = np.array([0.5, 0.5])
b = -0.7
tmp = np.sum(w*x) + b
if tmp <= 0:
return 0
else:
return 1
a = AND1(0.2, 0)
print(a)
与、非、或、与非、异或
import numpy as np
def AND(x1, x2):
# 与门
x = np.array([x1, x2])
w = np.array([0.5, 0.5])
b = -0.7
tmp = np.sum(w*x) + b
if tmp <= 0:
return 0
else:
return 1
def NAND(x1, x2):
# 与非门
x = np.array([x1, x2])
w = np.array([-0.5, -0.5])
b = 0.7
tmp = np.sum(w*x) + b
if tmp <= 0:
return 0
else:
return 1
def OR(x1, x2):
# 或门
x = np.array([x1, x2])
w = np.array([0.5, 0.5])
b = -0.2
tmp = np.sum(w*x) + b
if tmp <= 0:
return 0
else:
return 1
def XOR(x1, x2):
# 异或门
s1 = NAND(x1, x2)
s2 = OR(x1, x2)
y = AND(s1, s2)
return y
if __name__=="__main__":
for xs in [(0, 0), (1, 0), (0, 1), (1, 1)]:
y = AND(xs[0], xs[1])
print(str(xs) + " -> " + str(y))
for xs in[(0, 0), (1, 0), (0, 1), (1, 1)]:
y = NAND(xs[0], xs[1])
print(str(xs) + " -> " + str(y))
for xs in [(0,0), (1, 0), (0,1 ), (1, 1)]:
y = OR(xs[0], xs[1])
print(str(xs) + " -> " + str(y))
for xs in [(0, 0), (1, 0), (0, 1), (1, 1)]:
y = XOR(xs[0], xs[1])
print(str(xs) + " -> " + str(y))
神经网络
激活函数
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
def sigmoid(x):
g = 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
return g
def step_function(x):
g = np.array(x>0, dtype=np.int)
return g
x = np.arange(-5.0, 5.0, 0.1)
y1 = sigmoid(x)
y2 = step_function(x)
plt.plot(x, y1, label = 'sigmoid')
plt.plot(x, y2, 'k--', label = 'step_function')
# plt.ylim(-0.1, 1.1) # 指定 y 轴的范围
plt.legend()
plt.show()

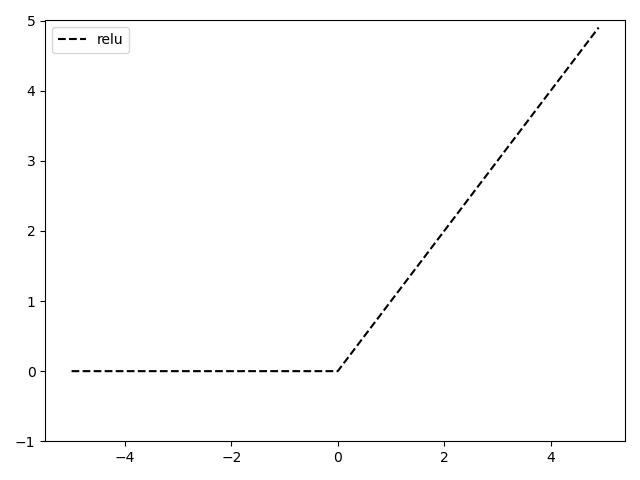
def relu(x): # relu函数 # x < 0 时 输出 0 # x > 0 时 直接输出 x g = np.maximum(0, x) return g x = np.arange(-5.0, 5.0, 0.1) y = relu(x) plt.plot(x,y,'k--',label = 'relu') plt.legend() plt.ylim(-1.0, 5.0) plt.show()
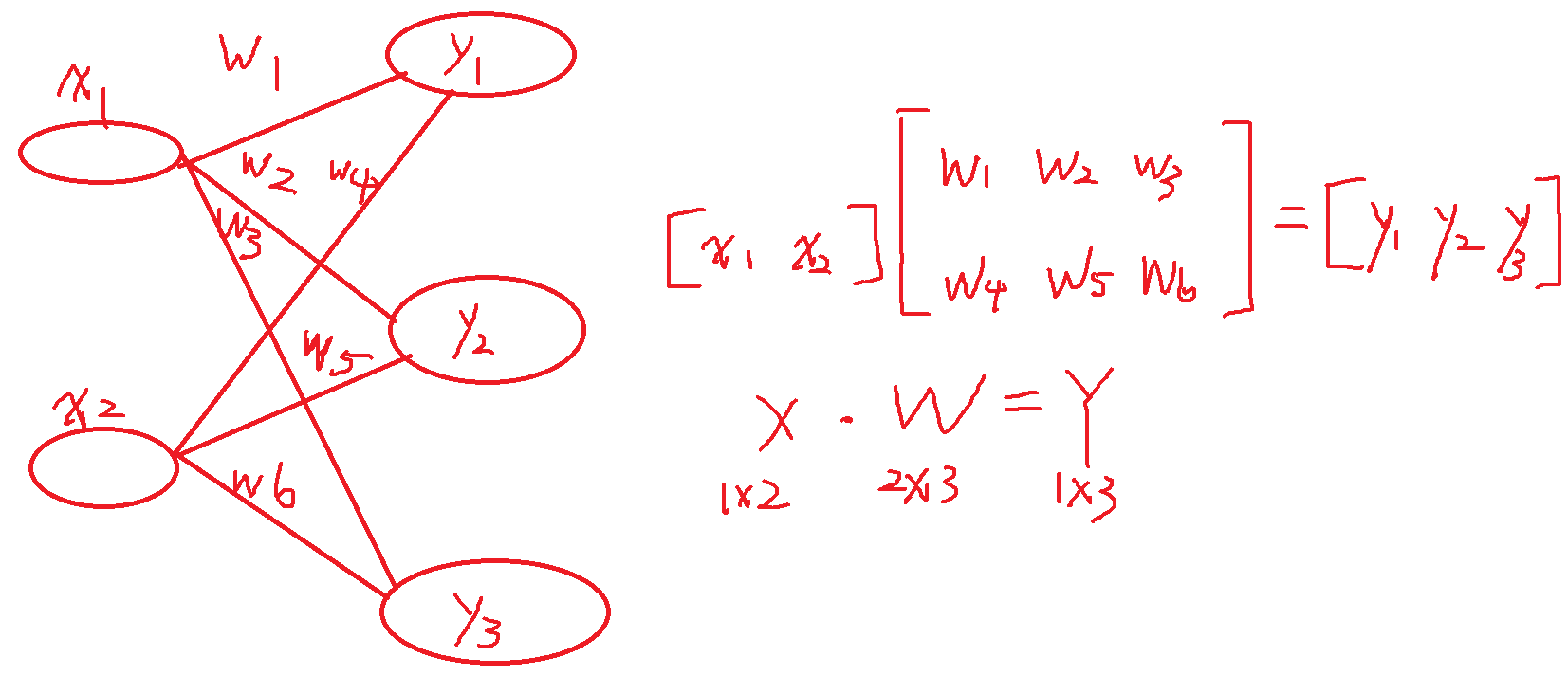
import numpy as np
def sigmoid(x):
# 激活函数
g = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
return g
def init_network():
network = {}
network['W1']= np.array([[0.1, 0.3, 0.5],
[0.2, 0.4, 0.6]])
network['b1'] = np.array([0.1, 0.2, 0.3])
network['W2'] = np.array([[0.1, 0.4],
[0.2, 0.5],
[0.3, 0.6]])
network['b2'] = np.array([0.1, 0.2])
network['W3'] = np.array([[0.1, 0.3],
[0.2, 0.4]])
network['b3'] = np.array([0.1, 0.2])
return network
def identity_function(x):
# 恒等函数
return x
def forward(network, x):
W1, W2, W3 = network['W1'], network['W2'], network['W3']
b1, b2, b3 = network['b1'], network['b2'], network['b3']
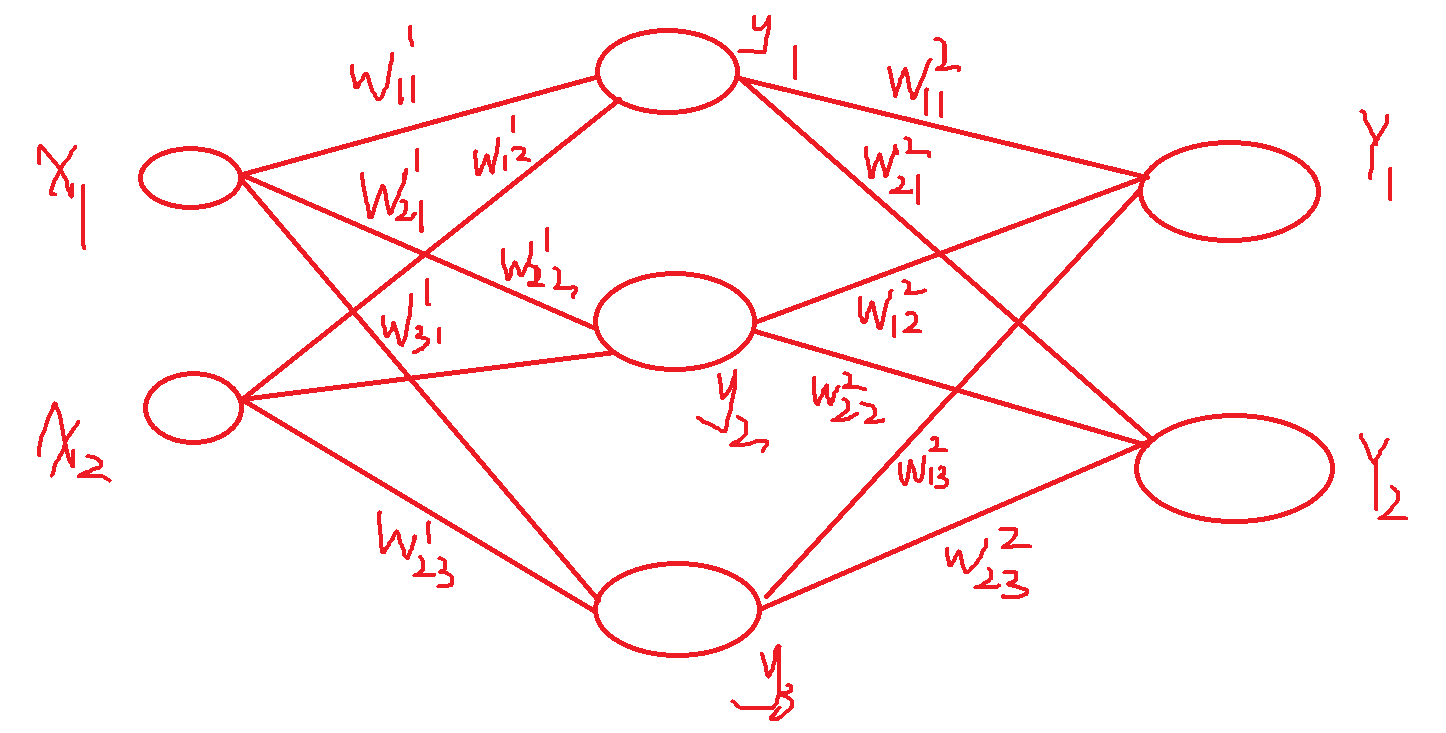
a1 = np.dot(x, W1) + b1
z1 = sigmoid(a1)
a2 = np.dot(a1, W2) + b2
z2 = sigmoid(a2)
a3 = np.dot(z2, W3) + b3
y = identity_function(a3)
return y
network = init_network()
x = np.array([1.0, 0.5])
y = forward(network, x)
print(y)
对输出函数进行改进
import numpy as np
def sigmoid(x):
# 激活函数
g = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
return g
def init_network():
network = {}
network['W1']= np.array([[0.1, 0.3, 0.5],
[0.2, 0.4, 0.6]])
network['b1'] = np.array([0.1, 0.2, 0.3])
network['W2'] = np.array([[0.1, 0.4],
[0.2, 0.5],
[0.3, 0.6]])
network['b2'] = np.array([0.1, 0.2])
network['W3'] = np.array([[0.1, 0.3],
[0.2, 0.4]])
network['b3'] = np.array([0.1, 0.2])
return network
def identity_function(x):
# 输出函数
# 恒等函数
return x
def softmax(a):
# 输出函数
# 对 溢出问题 进行改进
c = np.max(a)
exp_a = np.exp(a -c) # 溢出问题的对策
sum_exp_a = np.sum(exp_a)
y = exp_a/sum_exp_a
return y
def forward(network, x):
W1, W2, W3 = network['W1'], network['W2'], network['W3']
b1, b2, b3 = network['b1'], network['b2'], network['b3']
a1 = np.dot(x, W1) + b1
z1 = sigmoid(a1)
a2 = np.dot(a1, W2) + b2
z2 = sigmoid(a2)
a3 = np.dot(z2, W3) + b3
# y = identity_function(a3)
y = softmax(a3)
return y
network = init_network()
x = np.array([1.0, 0.5])
y = forward(network, x)
print(y)
单层感知机
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# sign function
def sign(v):
if v > 0:
return 1
else:
return -1
# train function to get weight and bias
def training():
train_data1 = [[1, 3, 1], [2, 5, 1], [3, 8, 1], [2, 6, 1]] # positive sample
train_data2 = [[3, 1, -1], [4, 1, -1], [6, 2, -1], [7, 3, -1]] # negative sample
train_data = train_data1 + train_data2;
weight = [0, 0]
bias = 0
learning_rate = 0.1
train_num = int(input("train num:"))
for i in range(train_num):
train = random.choice(train_data)
x1, x2, y = train;
y_predict = sign(weight[0] * x1 + weight[1] * x2 + bias)
print("train data:x:(%d, %d) y:%d ==>y_predict:%d" % (x1, x2, y, y_predict))
if y * y_predict <= 0:
weight[0] = weight[0] + learning_rate * y * x1
weight[1] = weight[1] + learning_rate * y * x2
bias = bias + learning_rate * y
print("update weight and bias:")
print(weight[0], weight[1], bias)
print("stop training :")
print(weight[0], weight[1], bias)
# plot the train data and the hyper curve
plt.plot(np.array(train_data1)[:, 0], np.array(train_data1)[:, 1], 'ro')
plt.plot(np.array(train_data2)[:, 0], np.array(train_data2)[:, 1], 'bo')
x_1 = []
x_2 = []
for i in range(-10, 10):
x_1.append(i)
x_2.append((-weight[0] * i - bias) / weight[1])
plt.plot(x_1, x_2)
plt.show()
return weight, bias
# test function to predict
def test():
weight, bias = training()
while True:
test_data = []
data = input("enter q to quit,enter test data (x1, x2):")
if data == 'q':
break
test_data += [int(n) for n in data.split(',')]
predict = sign(weight[0] * test_data[0] + weight[1] * test_data[1] + bias)
print("predict==>%d" % predict)
if __name__ == "__main__":
test()