一、JSON规范
2)功能强大,支持JDK的各种类型,包括JavaBean、Collection、Map、Date、Enum、泛型。
3)无依赖,不需要例外额外的jar,能够直接在JDK上运行。
4)开源,使用Apache License 2.0协议开源。
Issue Tracking:http://code.alibabatech.com/jira/browse/FASTJSON
public static final Object parse(String text); // 把JSON文本parse为JSONObject或者JSONArray public static final JSONObject parseObject(String text); // 把JSON文本parse成JSONObject public static final <T> T parseObject(String text, Class<T> clazz); // 把JSON文本parse为JavaBean public static final JSONArray parseArray(String text); // 把JSON文本parse成JSONArray public static final <T> List<T> parseArray(String text, Class<T> clazz); //把JSON文本parse成JavaBean集合 public static final String toJSONString(Object object); // 将JavaBean序列化为JSON文本 public static final String toJSONString(Object object, boolean prettyFormat); // 将JavaBean序列化为带格式的JSON文本 public static final Object toJSON(Object javaObject); //将JavaBean转换为JSONObject或者JSONArray
fastJson对于json格式字符串的解析主要用到了一下三个类:
1)JSON:fastJson的解析器,用于JSON格式字符串与JSON对象及javaBean之间的转换。
2)JSONObject:fastJson提供的json对象。我们可以把JSONObject当成一个Map<String,Object>来看,只是JSONObject提供了更为丰富便捷的方法,方便我们对于对象属性的操作。

3)JSONArray:fastJson提供json数组对象。同样我们可以把JSONArray当做一个List<Object>,可以把JSONArray看成JSONObject对象的一个集合。

由于JSONObject和JSONArray继承了JSON,所以说也可以直接使用两者对JSON格式字符串与JSON对象及javaBean之间做转换,不过为了避免混淆我们还是使用JSON。
示例1:JSON格式字符串与JSON对象之间的转换。
示例1.1-json字符串-简单对象型与JSONObject之间的转换
/** * json字符串-简单对象型与JSONObject之间的转换 */ public static void testJSONStrToJSONObject(){ JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR); //JSONObject jsonObject1 = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR); //因为JSONObject继承了JSON,所以这样也是可以的 System.out.println(jsonObject.getString("studentName")+":"+jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge")); }
示例1.2-json字符串-数组类型与JSONArray之间的转换
/** * json字符串-数组类型与JSONArray之间的转换 */ public static void testJSONStrToJSONArray(){ JSONArray jsonArray = JSON.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR); //JSONArray jsonArray1 = JSONArray.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR);//因为JSONArray继承了JSON,所以这样也是可以的
//遍历方式1 int size = jsonArray.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++){ JSONObject jsonObject = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i); System.out.println(jsonObject.getString("studentName")+":"+jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge")); } //遍历方式2 for (Object obj : jsonArray) { JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject) obj; System.out.println(jsonObject.getString("studentName")+":"+jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge")); } }
示例1.3-复杂json格式字符串与JSONObject之间的转换
/** * 复杂json格式字符串与JSONObject之间的转换 */ public static void testComplexJSONStrToJSONObject(){ JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR); //JSONObject jsonObject1 = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR);//因为JSONObject继承了JSON,所以这样也是可以的 String teacherName = jsonObject.getString("teacherName"); Integer teacherAge = jsonObject.getInteger("teacherAge"); JSONObject course = jsonObject.getJSONObject("course"); JSONArray students = jsonObject.getJSONArray("students"); }
示例2:JSON格式字符串与javaBean之间的转换。
首先,我们针对数据源所示的字符串,提供三个javaBean。
public class Student {
private String studentName;
private Integer studentAge;
public String getStudentName() {
return studentName;
}
public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public Integer getStudentAge() {
return studentAge;
}
public void setStudentAge(Integer studentAge) {
this.studentAge = studentAge;
}
}
public class Course { private String courseName; private Integer code; public String getCourseName() { return courseName; } public void setCourseName(String courseName) { this.courseName = courseName; } public Integer getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(Integer code) { this.code = code; } }
public class Teacher { private String teacherName; private Integer teacherAge; private Course course; private List<Student> students; public String getTeacherName() { return teacherName; } public void setTeacherName(String teacherName) { this.teacherName = teacherName; } public Integer getTeacherAge() { return teacherAge; } public void setTeacherAge(Integer teacherAge) { this.teacherAge = teacherAge; } public Course getCourse() { return course; } public void setCourse(Course course) { this.course = course; } public List<Student> getStudents() { return students; } public void setStudents(List<Student> students) { this.students = students; } }
json字符串与javaBean之间的转换推荐使用 TypeReference<T> 这个类,使用泛型可以更加清晰。
示例2.1-json字符串-简单对象型与javaBean之间的转换
/** * json字符串-简单对象与JavaBean_obj之间的转换 */ public static void testJSONStrToJavaBeanObj(){ Student student = JSON.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR, new TypeReference<Student>() {}); //Student student1 = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR, new TypeReference<Student>() {});//因为JSONObject继承了JSON,所以这样也是可以的 System.out.println(student.getStudentName()+":"+student.getStudentAge()); }
示例2.2-json字符串-数组类型与javaBean之间的转换
/** * json字符串-数组类型与JavaBean_List之间的转换 */ public static void testJSONStrToJavaBeanList(){ ArrayList<Student> students = JSON.parseObject(JSON_ARRAY_STR, new TypeReference<ArrayList<Student>>() {}); //ArrayList<Student> students1 = JSONArray.parseObject(JSON_ARRAY_STR, new TypeReference<ArrayList<Student>>() {});//因为JSONArray继承了JSON,所以这样也是可以的 for (Student student : students) { System.out.println(student.getStudentName()+":"+student.getStudentAge()); } }
示例2.3-复杂json格式字符串与与javaBean之间的转换
/**
* 复杂json格式字符串与JavaBean_obj之间的转换
*/
public static void testComplexJSONStrToJavaBean(){
Teacher teacher = JSON.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR, new TypeReference<Teacher>() {});
//Teacher teacher1 = JSON.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR, new TypeReference<Teacher>() {});//因为JSONObject继承了JSON,所以这样也是可以的
String teacherName = teacher.getTeacherName();
Integer teacherAge = teacher.getTeacherAge();
Course course = teacher.getCourse();
List<Student> students = teacher.getStudents();
}
对于TypeReference<T>,由于其构造方法是使用 protected修饰,所以在其他包下创建其对象时,要用其实现类的子类:new TypeReference<Teacher>() {}
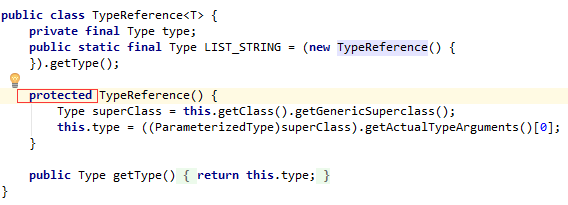
此外:
1)对于JSON对象与JSON格式字符串的转换可以直接用 toJSONString()这个方法。
2)javaBean与JSON格式字符串之间的转换要用到:JSON.toJSONString(obj);
3)javaBean与json对象间的转换使用:JSON.toJSON(obj),然后使用强制类型转换,JSONObject或者JSONArray。
package jsonArrayjsonObject; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; // JsonObject和JsonArray区别就是JsonObject是对象形式,JsonArray是数组形式 public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { test(); } // 创建jsonObject的第一种方式 static void createJsonObject1(){ JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(); jsonObject.put("name", "zhangsan"); jsonObject.put("age", "11"); jsonObject.put("sex", "男"); System.out.println(jsonObject); System.out.println(jsonObject.toJSONString()); System.out.println(jsonObject.toString()); } // 创建jsonObject的第二种方式 ---map转jsonObject static void createJsonObject2(){ HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("name", "lisi"); map.put("age", 22); JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(map); System.out.println(jsonObject); } // 创建jsonObject的第三种方式 ---map强转jsonObject static void createJsonObject3(){ HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("name", "lisi"); map.put("age", 22); Object json = JSON.toJSON(map); JSONObject o = (JSONObject) json; System.out.println(o); Object json2 = JSONObject.toJSON(map); System.out.println(json2); Object json3 = JSONArray.toJSON(map); System.out.println(json3); } // 创建JsonArray方法1 static void createJsonArray1(){ JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray(); jsonArray.add(0, "zjj"); jsonArray.add(1, "男"); jsonArray.add(2, 28); System.out.println(jsonArray); System.out.println(jsonArray.toJSONString()); System.out.println(jsonArray.toString()); } // 创建JsonArray方法2 ----list转jsonArray static void createJsonArray2(){ List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("xioali"); list.add(1, "xiaozhang"); JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray(list); System.out.println(jsonArray); } // 创建JsonArray方法3 ----list强转jsonArray static void createJsonArray3(){ List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("xioali"); String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(list); String jsonString2 = JSONObject.toJSONString(list); String jsonString3 = JSONArray.toJSONString(list); System.out.println(jsonString); System.out.println(jsonString2); System.out.println(jsonString3); JSONArray parseArray = JSON.parseArray(jsonString); JSONArray parseArray2 = JSONArray.parseArray(jsonString2); JSONArray parseArray3 = JSONObject.parseArray(jsonString3); System.out.println(parseArray); System.out.println(parseArray2); System.out.println(parseArray3); Object object = parseArray.get(1); System.out.println(object); } //解析JSON字符串 static void test(){ String jsonString = "{\"age\":33,\"sex\":\"男\",\"name\":\"zjj\"}"; // 先将对象型json字符串转换为json对象 JSONObject parseObject = JSON.parseObject(jsonString); // JSONObject与JSONArray均继承JSON JSONObject parseObject2 = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonString); JSONObject parseObject3 = JSONArray.parseObject(jsonString); // 从对象中取值 Object ob1 = parseObject.get("age"); Object ob2 = parseObject2.get("age"); Object ob3 = parseObject3.get("age"); System.out.println(ob1); System.out.println(ob2); System.out.println(ob3); // JSONObject转map Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map = parseObject; Object object = map.get("age"); System.out.println("map:" + object); String jsonString2 = "[\"z\",\"j\",\"j\"]"; // 先将数组型json字符串转换为json数组 JSONArray parseArray = JSON.parseArray(jsonString2); // JSONObject与JSONArray均继承JSON JSONArray parseArray2 = JSONArray.parseArray(jsonString2); JSONArray parseArray3 = JSONObject.parseArray(jsonString2); // 从数组中取值 Object object1 = parseArray.get(0); Object object2 = parseArray2.get(1); Object object3 = parseArray3.get(2); System.out.println(object1); System.out.println(object2); System.out.println(object3); // JSONArray转list List<Object> list = parseArray; Object object4 = list.get(0); System.out.println("list:" + object4); }
}
五、参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhenmingliu/archive/2011/12/29/2305775.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/cdf-opensource-007/p/7106018.html
六、高级应用
http://blog.csdn.net/pearyangyang/article/details/49451581