一、pycharm 的下载与安装:
使用教程:https://www.cnblogs.com/jin-xin/articles/9811379.html
二、python的基础知识
1、变量与常量。
变量:就是将一些运算的中间结果暂存到内存中,以便后续代码调用。
1,必须由数字,字母,下划线任意组合,且不能数字开头。
2,不能是python中的关键字。
['and', 'as', 'assert', 'break', 'class', 'continue',
'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'exec',
'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import',
'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'print',
'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
3,变量具有可描述性。
4,不能是中文。
常量: 一直不变的量。 π
python 中的常量: BIR_OF_CHINA = 1949
2、注释。
方便自己方便他人理解代码。
单行注释:#
多行注释:'''被注释内容''' """被注释内容"""
python 中的多行注释若是被赋值,就变成字符串。
如: msg = ''' 我爱 python'''
3、基本数据类型
bool True False int +-*/ (加减乘除) %(取余) //(整除) **(幂) str : str =""
4、input 与 用户交互:
#格式化输出
name = input("请输入名字")
age = int(input("请输入年龄")) #需要强转,input为str 类型,转成 int 类型
height = int(input("请输入身高"))
msg = "我叫 %s ,今年 %d 岁 ,身高 %d , 学习任务的进度 50 %% , %%s" %( name , age , height
注意:如果格式化输出想输出 % ,则为 %% ,若是想输出 %s 则为 %%s
5、if :语句
1、 if 条件: 结果 2、 if 条件: 结果 else : 结果 3、 if 条件: 结果 elif 条件: 结果 else: 结果 4 if 条件: if 条件: 结果 else: 结果
6、while 语句
1、 while 条件: 结果 (循环的结束,break , 条件的改变) 2、while 条件: 结果 else: 结果
案例: while语句 不被 break 打断 , else 执行.如下代码
count = 1
while count < 5:
print('count :'+ str(count))
count += 1
else:
print('正常执行')
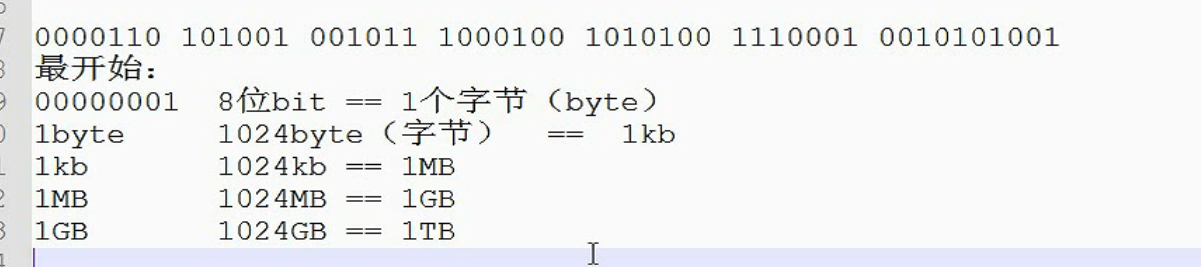
三、编码介绍
电脑传输文件 , 和 存储文件 是以 0 1 0 1 的形式存储的.
ASII码 最开始只有七位.开发者 远见,设计为8位.至今没有上,所以,asii码 最左变为0


四、基本运算符:
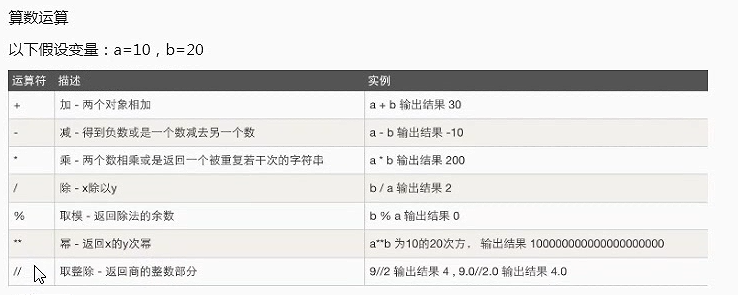
运算符:计算机可以进行的运算有很多种,可不只加减乘除。按运算种类可分为算数运算、比较运算、逻辑运算、赋值运算、成员运算、身份运算、位运算。
算数计算:
比较运算

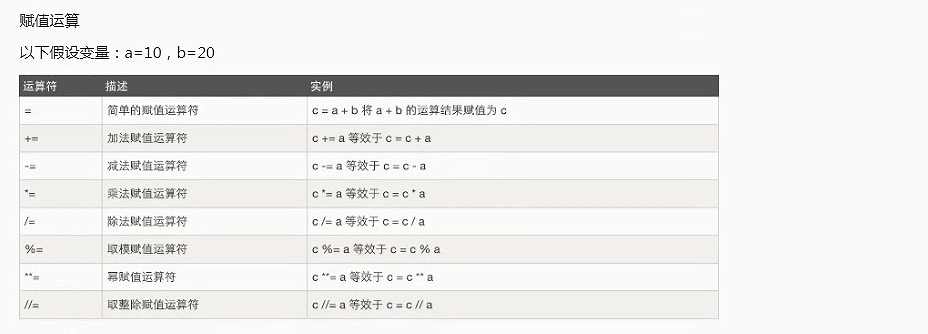
赋值运算
逻辑运算
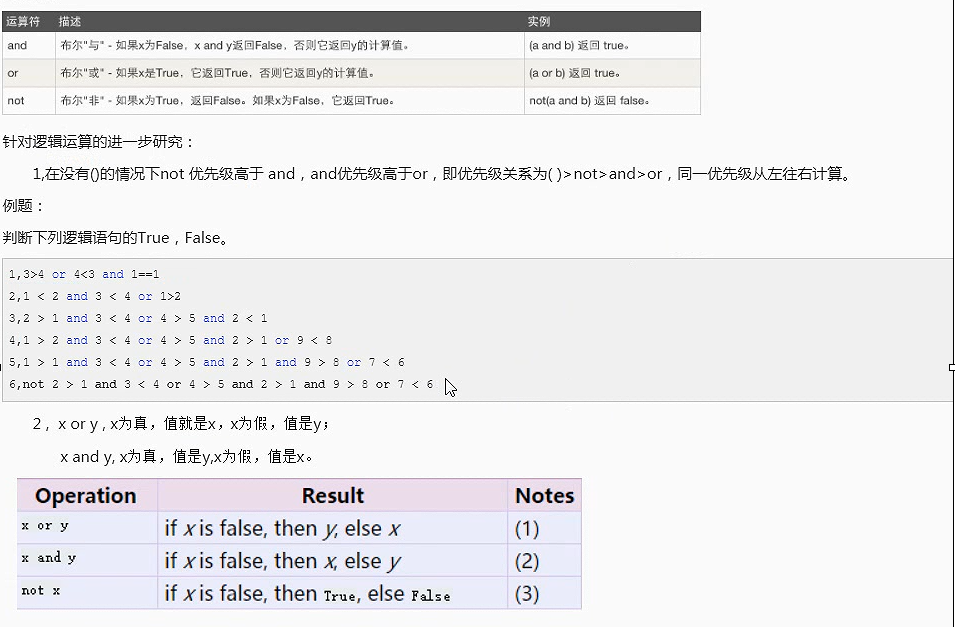
逻辑运算例题:
#and or not #优先级,()> not > and > or # print(2 > 1 and 1 < 4) # print(2 > 1 and 1 < 4 or 2 < 3 and 9 > 6 or 2 < 4 and 3 < 2) # T or T or F #T or F # print(3>4 or 4<3 and 1==1) # F # print(1 < 2 and 3 < 4 or 1>2) # T # print(2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 < 1) # T # print(1 > 2 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 or 9 < 8) # F # print(1 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6) # F # print(not 2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6) # F #ps int ----> bool 非零转换成bool True 0 转换成bool 是False # print(bool(2)) #T # print(bool(-2)) #T # print(bool(0)) #F # #bool --->int # print(int(True)) # 1 # print(int(False)) # 0 '''x or y x True,则返回x''' # print(1 or 2) # 1 # print(3 or 2) # 3 # print(0 or 2) # 2 # print(0 or 100) # 100 # print(2 or 100 or 3 or 4) # 2 # print(0 or 4 and 3 or 2) #3
'''x and y x True,则返回y''' # print(1 and 2) #2 # print(0 and 2) #0 print(2 or 1 < 3) # 2 print(3 > 1 or 2 and 2) #True