线性规划算法
一、一般的线性规划问题
问题:求解下列线性规划问题
max z = 2x1 + 3x2 − 5x3
s.t. x1 + x2 + x3 = 7
2x1 −5x2 + x3 ≥10
x1 + 3x2 + x3 ≤12
x1, x2 , x3 ≥ 0
python解答(代码实现)
1 import numpy as np 2 from scipy import optimize #求线性规划用到的函数 3 def line_progress(): #不等式中的大于等于号要换成小于等于号 4 c = np.array([2,3,-5]) #所求的最终式子的系数(求最大值,要在后面求值时加负号) 5 A = np.array([[-2,5,-1],[1,3,1]]) #不等式中的系数 6 b = np.array([-10,12]) #不等式中的约束值(即右边的值) 7 Aeq = np.array([[1,1,1]]) #不等式中的变量 8 beq = np.array([7]) 9 line_result = optimize.linprog(-c,A,b,Aeq,beq)#优化求解 10 if line_result.success: 11 print("线性规划最小值的变量:") 12 print(line_result.x) 13 print("线性规划最小值:") 14 print(line_result.fun) 15 print("线性规划最大值:") 16 print(-line_result.fun) 17 else: 18 print("找不到线性规划最小值") 19 20 if __name__=='__main__': 21 line_progress()
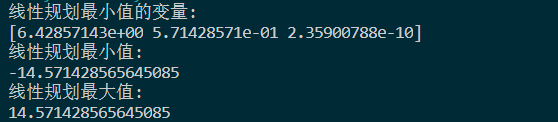
结果显示
MATLAB(代码实现)
c=[2;3;-5]; a=[-2,5,-1;1,3,1]; b=[-10;12]; aeq=[1,1,1]; beq=7; x=linprog(-c,a,b,aeq,beq,zeros(3,1)) value=c'*x
二、指派问题(选用匈牙利算法)
算法:如果系数矩阵C = (cij) 一行(或一列)中每一元素都加上或减去同一个数,得到一个新矩阵 B = (bij) ,则以C 或 B 为系数矩阵的
指派问题具有相同的最优指派。(一般是每一行或每一列该减去该行(该列)最小的的一个数)
上图最明了

解答最优指派
1-->2 2-->1 3-->3 4-->4
代码实现(其实小编也不懂,搬别人的过来的)有想了解的可以参照下面的链接
https://blog.csdn.net/jingshushu1995/article/details/80411325
import itertools import numpy as np from numpy import random from scipy.optimize import linear_sum_assignment # 任务分配类 class TaskAssignment: # 类初始化,需要输入参数有任务矩阵以及分配方式,其中分配方式有两种,全排列方法all_permutation或匈牙利方法Hungary。 def __init__(self, task_matrix, mode): self.task_matrix = task_matrix self.mode = mode if mode == 'all_permutation': self.min_cost, self.best_solution = self.all_permutation(task_matrix) if mode == 'Hungary': self.min_cost, self.best_solution = self.Hungary(task_matrix) # 全排列方法 def all_permutation(self, task_matrix): number_of_choice = len(task_matrix) solutions = [] values = [] for each_solution in itertools.permutations(range(number_of_choice)): each_solution = list(each_solution) solution = [] value = 0 for i in range(len(task_matrix)): value += task_matrix[i][each_solution[i]] solution.append(task_matrix[i][each_solution[i]]) values.append(value) solutions.append(solution) min_cost = np.min(values) best_solution = solutions[values.index(min_cost)] return min_cost, best_solution # 匈牙利方法 def Hungary(self, task_matrix): b = task_matrix.copy() # 行和列减0 for i in range(len(b)): row_min = np.min(b[i]) for j in range(len(b[i])): b[i][j] -= row_min for i in range(len(b[0])): col_min = np.min(b[:, i]) for j in range(len(b)): b[j][i] -= col_min line_count = 0 # 线数目小于矩阵长度时,进行循环 while (line_count < len(b)): line_count = 0 row_zero_count = [] col_zero_count = [] for i in range(len(b)): row_zero_count.append(np.sum(b[i] == 0)) for i in range(len(b[0])): col_zero_count.append((np.sum(b[:, i] == 0))) # 划线的顺序(分行或列) line_order = [] row_or_col = [] for i in range(len(b[0]), 0, -1): while (i in row_zero_count): line_order.append(row_zero_count.index(i)) row_or_col.append(0) row_zero_count[row_zero_count.index(i)] = 0 while (i in col_zero_count): line_order.append(col_zero_count.index(i)) row_or_col.append(1) col_zero_count[col_zero_count.index(i)] = 0 # 画线覆盖0,并得到行减最小值,列加最小值后的矩阵 delete_count_of_row = [] delete_count_of_rol = [] row_and_col = [i for i in range(len(b))] for i in range(len(line_order)): if row_or_col[i] == 0: delete_count_of_row.append(line_order[i]) else: delete_count_of_rol.append(line_order[i]) c = np.delete(b, delete_count_of_row, axis=0) c = np.delete(c, delete_count_of_rol, axis=1) line_count = len(delete_count_of_row) + len(delete_count_of_rol) # 线数目等于矩阵长度时,跳出 if line_count == len(b): break # 判断是否画线覆盖所有0,若覆盖,进行加减操作 if 0 not in c: row_sub = list(set(row_and_col) - set(delete_count_of_row)) min_value = np.min(c) for i in row_sub: b[i] = b[i] - min_value for i in delete_count_of_rol: b[:, i] = b[:, i] + min_value break row_ind, col_ind = linear_sum_assignment(b) min_cost = task_matrix[row_ind, col_ind].sum() best_solution = list(task_matrix[row_ind, col_ind]) return min_cost, best_solution # 生成开销矩阵 rd = random.RandomState(10000) task_matrix = rd.randint(0, 100, size=(5, 5)) # 用全排列方法实现任务分配 ass_by_per = TaskAssignment(task_matrix, 'all_permutation') # 用匈牙利方法实现任务分配 ass_by_Hun = TaskAssignment(task_matrix, 'Hungary') print('cost matrix = ', ' ', task_matrix) print('全排列方法任务分配:') print('min cost = ', ass_by_per.min_cost) print('best solution = ', ass_by_per.best_solution) print('匈牙利方法任务分配:') print('min cost = ', ass_by_Hun.min_cost) print('best solution = ', ass_by_Hun.best_solution)