记录一次使用Ubuntu环境搭建svn服务器的详细步骤
一、查看是否已经安装svn
命令:svn
如果显示以下信息,说明已安装

二、卸载已安装的svn
命令:sudo apt-get remove --purge subversion
三、安装svn
1.安装svn
更新命令:sudo apt-get update
安装svn:sudo apt-get install subversion
2.创建svn版本库
在home目录下创建svn目录,然后在svn中创建repository目录
命令:sudo mkdir /home/svn
sudo mkdir /home/svn/repository
3.修改repository文件中权限
命令:sudo chmod -R 777 /home/svn/repository
4.创建版本库
命令:sudo svnadmin create /home/svn/repository
执行完毕之后,repository目录下会有如下文件

5.切换当前目录到repository
命令:cd /home/svn/repository
6.设置db文件的权限
命令:sudo chmod -R 777 db
7.切换当前目录打破conf
命令:cd conf
8.修改配置文件svnserve.conf
命令:sudo vi svnserve.conf
修改前:
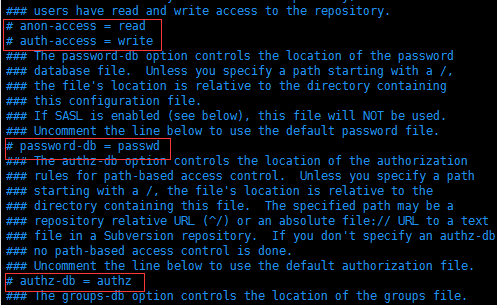
修改后:

说明:(去掉前面的#,并且顶格)
anon-access = none 匿名用户不可读
auth-access = write 权限用户可写
password-db = passwd 密码文件为passwd
authz-db = authz 权限文件为authz
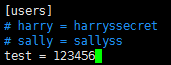
9.修改password文件,添加访问用户
命令:sudo vi passwd
新增用户格式:名字 = 密码
10.给用户test增加目录权限
命令:sudo vi authz
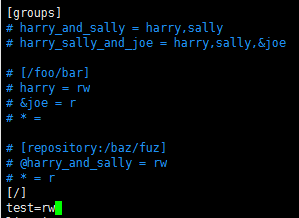
用户test拥有版本库根目录读写的权限
四、启动服务,并且监听81端口
命令:svnserve -d -r /home/svn --listen-port 81
如果提示:权限不够

切换到root权限
命令:sudo su
重试启动svn:svnserve -d -r /home/svn --listen-port 81
查看svn是否启动
命令:ps -ef | grep svnserve

五、停止服务
命令:killall svnserve
附:精确目录权限控制
[/]
A=rw
A拥有版本库根目录读写的权限
[/Android]
A=rw
B=r
A拥有Android目录读写的权限
B拥有Android目录读的权限,但没有写的权限
[/Android/Project1]
A=rw
*=r
A拥有/Android/Project1目录读写的权限
所有人都拥有/Android/Project1目录读的权限
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/daimengxiaoerge/p/10238503.html
六、获取当前最新修订版本号
svnlook youngest /home/svn/repository/

七、配置HTTP访问【暂时测试通不过,后面再测试】
1 安装apache
sudo apt-get install apache2
2 修改版本库权限
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data 版本库路径
例如:sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /home/svn/repository/db
3 配置apache2
sudo vi /etc/apache2/mods-available/dav_svn.conf
# dav_svn.conf - Example Subversion/Apache configuration # # For details and further options see the Apache user manual and # the Subversion book. # # NOTE: for a setup with multiple vhosts, you will want to do this # configuration in /etc/apache2/sites-available/*, not here. # <Location URL> ... </Location> # URL controls how the repository appears to the outside world. # In this example clients access the repository as http://hostname/svn/ # Note, a literal /svn should NOT exist in your document root. <Location /svn> # 配置svn的http路径,如这里配置了svn后路径为http://hostname/svn/ # Uncomment this to enable the repository DAV svn # Set this to the path to your repository #SVNPath /root/SVN/repo/ # Alternatively, use SVNParentPath if you have multiple repositories under # under a single directory (/var/lib/svn/repo1, /var/lib/svn/repo2, ...). # You need either SVNPath and SVNParentPath, but not both. SVNParentPath /home/svn # 当在一个父目录中有多个库时使用SVNParentPath SVNListParentPath On # 显示仓库根目录 # Access control is done at 3 levels: (1) Apache authentication, via # any of several methods. A "Basic Auth" section is commented out # below. (2) Apache <Limit> and <LimitExcept>, also commented out # below. (3) mod_authz_svn is a svn-specific authorization module # which offers fine-grained read/write access control for paths # within a repository. (The first two layers are coarse-grained; you # can only enable/disable access to an entire repository.) Note that # mod_authz_svn is noticeably slower than the other two layers, so if # you don't need the fine-grained control, don't configure it. # Basic Authentication is repository-wide. It is not secure unless # you are using https. See the 'htpasswd' command to create and # manage the password file - and the documentation for the # 'auth_basic' and 'authn_file' modules, which you will need for this # (enable them with 'a2enmod'). AuthType Basic # 基本权限验证功能 AuthName "Subversion Repository" # 权限名字,随便都行 AuthUserFile /etc/apache2/dav_svn.passwd # 保存授权用户的账户密码的文件路径 # To enable authorization via mod_authz_svn (enable that module separately): #<IfModule mod_authz_svn.c> #AuthzSVNAccessFile /etc/apache2/dav_svn.authz #</IfModule> # The following three lines allow anonymous read, but make # committers authenticate themselves. It requires the 'authz_user' # module (enable it with 'a2enmod'). # 除了以下描述的GET OPTIONS操作外,其他的HTTP操作都需要授权用户才可以 <LimitExcept GET PROPFIND OPTIONS REPORT> Require valid-user </LimitExcept> </Location>
4、修改端口
sudo vi /etc/apache2/ports.conf
# If you just change the port or add more ports here, you will likely also # have to change the VirtualHost statement in # /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf Listen 82 <IfModule ssl_module> Listen 443 </IfModule> <IfModule mod_gnutls.c> Listen 443 </IfModule>
5 启动Apache服务
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 restart