并发
基本概念
并发和并行的区别




并发的解决






进程和线程


线程的状态


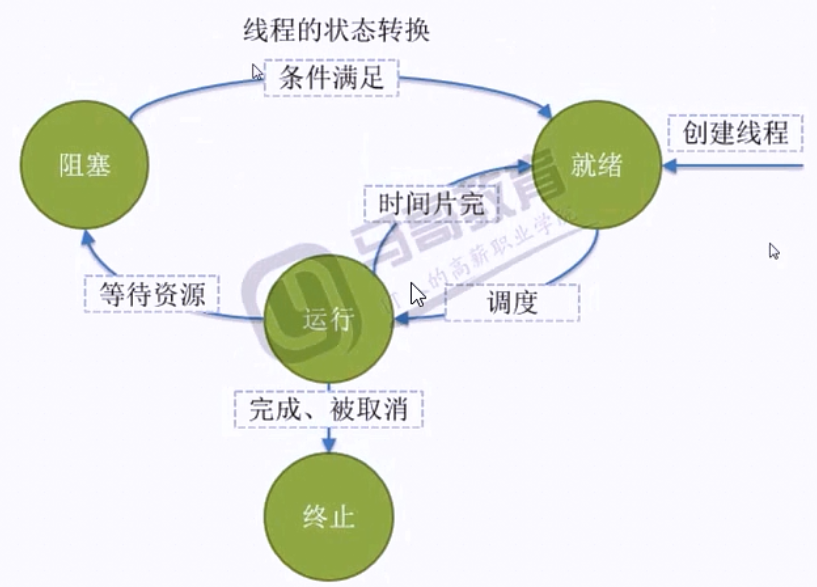
Python中的进程和线程
![]()
Python的线程开发
![]()
Thread类


线程启动
import threading import time #最简单的线程程序 def worker(): for _ in range(5): time.sleep(0.5) print('welcome ') print('Thread over') t = threading.Thread(target=worker)#线程对象 t.start()#启动

import threading import time #最简单的线程程序 def worker(): while True: time.sleep(0.5) print("I'm working") print('Thread over') t = threading.Thread(target=worker)#线程对象 t.start()#启动
线程退出

import threading import time def worker(): count = 0 while True: if (count>5): raise RuntimeError(count) time.sleep(1) print("I'm working") count += 1 t = threading.Thread(target=worker)#线程对象 t.start()#启动 print('===End===')

线程的传参
import threading import time def add(x,y): print(threading.current_thread()) print('{}+{}={} {}'.format(x,y,x+y,threading.current_thread().ident)) thread1 = threading.Thread(target=add,name='add1',args=(4,5))#线程对象 thread1.start() time.sleep(2) thread2 = threading.Thread(target=add,name='add2',args=(5,),kwargs={'y':4})#线程对象 thread2.start() time.sleep(2) thread3 = threading.Thread(target=add,name='add3',kwargs={'x':4,'y':5}) thread3.start()
![]()
threading的属性和方法

#示例1 import threading import time def worker(n=5): print("in",threading.current_thread()) print(threading.main_thread()) print(threading.active_count()) print(threading.enumerate()) for _ in range(n): time.sleep(0.5) print('welcome') print('Thread over') print("out",threading.current_thread()) t = threading.Thread(target=worker,name='w1') t.start() # t1 = threading.Thread(target=worker,name='w2') # t1.start() print(threading.enumerate()) #[<_MainThread(MainThread, started 18880)>, <Thread(w1, started 7404)>]或者 # [<_MainThread(MainThread, stopped 18720)>, <Thread(w1, started 22448)>]
#示例2 import threading import time def showthreadinfo(n=5): print("currentthread ={}".format(threading.current_thread())) print("main thread = {}".format(threading.main_thread())) print("active count ={}".format(threading.active_count())) print(threading.enumerate()) def worker(): count = 0 showthreadinfo() while True: if count>5: break time.sleep(0.5) count += 1 print("I'm working") t = threading.Thread(target=worker,name='worker')#线程对象 showthreadinfo() t.start() #此时输出如下: currentthread =<_MainThread(MainThread, started 18900)> main thread = <_MainThread(MainThread, started 18900)> active count =1 [<_MainThread(MainThread, started 18900)>] currentthread =<Thread(worker, started 19512)> main thread = <_MainThread(MainThread, stopped 18900)> active count =2 [<_MainThread(MainThread, stopped 18900)>, <Thread(worker, started 19512)>]
...
Thread实例的属性和方法

![]()
import threading import time def worker(): count = 0 while True: if count>5: break time.sleep(0.5) count += 1 print(threading.current_thread().name) t = threading.Thread(target=worker,name='worker')#线程对象 print(11,t.ident)#输出None,因为还未启动该线程 t.start() while True: time.sleep(1) if t.is_alive(): print('{} {} alive'.format(t.name,t.ident)) else: print('{} {} dead'.format(t.name,t.ident)) t.start()#可以否?#不可以,RuntimeError: threads can only be started once

![]()
start方法
import threading import time class MyThread(threading.Thread): def run(self): print('run') super().run() def start(self): print('start') return super().start() def worker(): count = 0 while True: if count>2: break time.sleep(0.5) count += 1 print('working') print('Thread over') t = MyThread(target=worker,name='w1') t.start() #输出如下: start run working working working Thread over
run方法
import threading import time class MyThread(threading.Thread): def run(self): print('run') super().run() def start(self): print('start') return super().start() def worker(): count = 0 while True: if count>2: break time.sleep(0.5) count += 1 print('working') print('Thread over') t = MyThread(target=worker,name='w1') t.run() #输出如下: run working working working Thread over

start和run的区别
![]()
import threading import time class MyThread(threading.Thread): def run(self): print('run') super().run() def start(self): print('start') return super().start() def worker(): count = 0 while True: if count>2: break time.sleep(0.5) count += 1 print('working') print('Thread over') print(threading.current_thread().name) t = MyThread(target=worker,name='worker') # t.run()#输出MainThread t.start()#输出worker

多线程
![]()
import threading import time def worker(): count = 0 while True: if count>5: break time.sleep(0.5) count += 1 print('working') print('Thread over') print(threading.current_thread().name,threading.current_thread().ident) class MyThread(threading.Thread): def run(self): print('run') super().run() def start(self): print('start') return super().start() t1 = MyThread(target=worker,name='worker1') t2 = MyThread(target=worker,name='worker2') t1.start() t2.start() # t1.run() # t2.run()


线程安全
![]()
import threading def worker(): for x in range(100): print("{} is running".format(threading.current_thread())) for x in range(5): threading.Thread(target=worker,name="worker{}".format(x+1)).start()

1.不让print打印换行
import threading def worker(): for x in range(100): print("{} is running ".format(threading.current_thread()),end='') for x in range(5): threading.Thread(target=worker,name="worker{}".format(x+1)).start()
2.使用logging
import threading import logging def worker(): for x in range(100): # print("{} is running ".format(threading.current_thread()),end='') logging.warning('{} is running'.format(threading.current_thread())) for x in range(5): threading.Thread(target=worker,name="worker{}".format(x+1)).start()
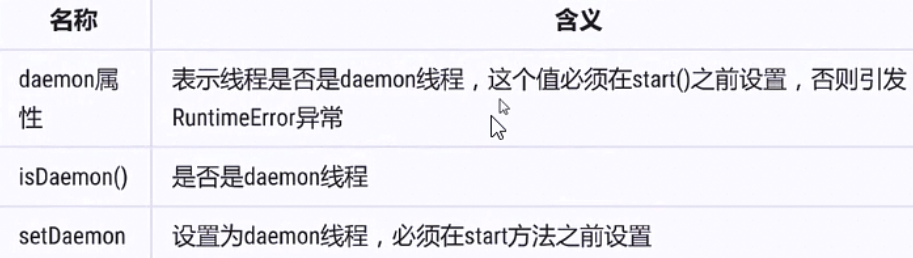
daemon线程和non-daemon线程

#源码Thread的__init__方法中 if daemon is not None: self._daemonic = daemon else: self._daemonic = current_thread().daemon

import time import threading def foo(): # time.sleep(2) for i in range(10): print(i) #主线程是non-daemon线程 t = threading.Thread(target=foo,daemon=False) t.start() print('Main Thread Exiting')

总结


import time import threading def bar(): time.sleep(5) print('bar') def foo(): for i in range(10): print(i) t = threading.Thread(target=bar,daemon=False) t.start() #主线程是non-daemon线程 t = threading.Thread(target=foo,daemon=True) t.start() print('Main Thread Exiting')
![]()
time.sleep(2) print('Main Thread Exiting')
![]()
import time import threading def foo(n): for i in range(n): print(i) time.sleep(1) #主线程是non-daemon线程 t1 = threading.Thread(target=foo,args=(10,),daemon=True)#调换10和20看看效果 t1.start() t2 = threading.Thread(target=foo,args=(20,),daemon=False) t2.start() time.sleep(2) print('Main Thread Exiting')

join方法
![]()
import threading import time def foo(n): for i in range(n): print(i) time.sleep(1) t = threading.Thread(target=foo,args=(10,),daemon=True) t.start() t.join()#设置join与取消join对比一下,可以理解为join(t) print('Main Thread Exiting')

daemon线程应用场景
![]()


import time import threading def bar(): while True: time.sleep(1) print('bar') def foo(): print("t1's daemon = {}".format(threading.current_thread().isDaemon())) t2 = threading.Thread(target=bar) t2.start() print("t2's daemon = {}".format(t2.isDaemon())) t1 = threading.Thread(target=foo,daemon=True) t1.start() time.sleep(3) print('Main Thread Exiting')
![]()
![]()
import time import threading def bar(): while True: time.sleep(1) print('bar') def foo(): print("t1's daemon = {}".format(threading.current_thread().isDaemon())) t2 = threading.Thread(target=bar) t2.start() print("t2's daemon = {}".format(t2.isDaemon())) t2.join() t1 = threading.Thread(target=foo,daemon=True) t1.start() t1.join() time.sleep(3) print('Main Thread Exiting')
threading.local类
import threading import time #局部变量实现 def worker(): x = 0 for i in range(100): time.sleep(0.0001) x += 1 print(threading.current_thread(),x) for x in range(10): threading.Thread(target=worker).start()

import threading import time class A: def __init__(self): self.x = 0 #全局对象 global_data = A() #局部变量实现 def worker(): global_data.x = 0 for i in range(100): time.sleep(0.0001) global_data.x += 1 print(threading.current_thread(),global_data.x) for x in range(10): threading.Thread(target=worker).start()

import threading import time #全局对象 global_data = threading.local() #局部变量实现 def worker(): global_data.x = 0 for i in range(100): time.sleep(0.0001) global_data.x += 1 print(threading.current_thread(),global_data.x) for x in range(10): threading.Thread(target=worker).start()

import threading import time X = 'abc' ctx = threading.local()#注意这个对象所处的线程 ctx.x = 123 print(ctx,type(ctx),ctx.x) #局部变量实现 def worker(): print(X) print(ctx) print(ctx.x) print('working') worker()#普通函数调用 print('===========') threading.Thread(target=worker).start()#AttributeError: '_thread._local' object has no attribute 'x'

定时器 Timer/延时执行

import threading import logging import time FORMAT = '%(asctime)s %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s' logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT) def worker(): logging.info('in worker') # time.sleep(2) t = threading.Timer(5,worker) t.setName('w1') t.start()#启动线程 print(threading.enumerate()) t.cancel()#取消,可以注释这一句看看如何定时执行 time.sleep(1) print(threading.enumerate())
![]()

![]()
import threading import logging import time FORMAT = '%(asctime)s %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s' logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT) def worker(): logging.info('in worker') # time.sleep(2) t = threading.Timer(5,worker) t.setName('w1') t.cancel()#提前取消 t.start()#启动线程 print(threading.enumerate()) time.sleep(1) print(threading.enumerate())
logging模块
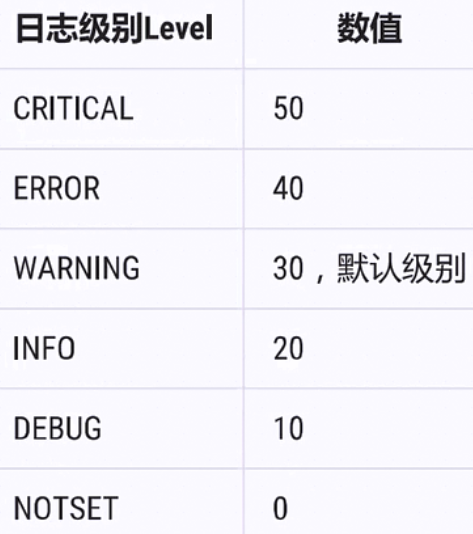
日志级别

import threading import logging logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO) def add(x,y): #只有设置的级别高于或等于上面的基准级别才会打印 logging.info("{} {}".format(threading.enumerate(),x+y)) #def __init__(self, interval, function, args=None, kwargs=None): t = threading.Timer(1,add,args=(4,5)) t.start()
格式字符串


示例
默认级别
import threading import logging FORMAT = "%(asctime)-15s info:%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s" #logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT,datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") def add(x,y): #只有设置的级别高于或等于上面的基准级别才会打印 logging.info("My")#INFO不显示 logging.warning('I am {}'.format(20)) t = threading.Timer(1,add,args=(4,5)) t.start()
构建消息
import threading import logging FORMAT = "%(asctime)-15s info:%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s" logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT,datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") def add(x,y): #只有设置的级别高于或等于上面的基准级别才会打印 logging.info('I am {}'.format(20))#单一字符串 logging.info('I am %d %s',20,'years old.')#C风格 t = threading.Timer(1,add,args=(4,5)) t.start()

import threading import logging FORMAT = "%(asctime)-15s info:%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s %(school)s" logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT,datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") d = {'school':'STU'} def add(x,y): #只有设置的级别高于或等于上面的基准级别才会打印 logging.info('I am {}'.format(20),extra=d)#单一字符串 logging.info('I am %d %s',20,'years old.',extra=d)#C风格 t = threading.Timer(1,add,args=(4,5)) t.start()
修改日期格式
import logging FORMAT = "%(asctime)-15s info:%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s %(school)s" logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT,datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
输出到文件
import threading import logging FORMAT = "%(asctime)-15s info:%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s %(school)s" logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT,datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",filename='E:/test.log')
Logger类

构造

import logging #层级关系 FORMAT = "%(asctime)-15s info:%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s" logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT) root = logging.getLogger()#root 根logger print(root.name,type(root),root.parent,id(root)) logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)#模块级的logger print(logger.name,type(logger),id(logger),id(logger.parent)) logger1 = logging.getLogger(__name__+".ok") print(logger1.name,type(logger1),id(logger1),id(logger1.parent)) print(logger1.parent,id(logger1.parent)) #输出如下: root <class 'logging.RootLogger'> None 47432984 __main__ <class 'logging.Logger'> 43741368 47432984 __main__.ok <class 'logging.Logger'> 43741480 43741368 <Logger __main__ (INFO)> 43741368
级别设置
import logging FORMAT = "%(asctime)-15s info:%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s" logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT) logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)#模块级的logger print(logger.name,type(logger)) print(logger.getEffectiveLevel())#INFO 20 logger.info('hello1') logger.setLevel(28) print(logger.getEffectiveLevel())#INFO 28 logger.info('hello2') logger.warning('warning')

Handler

#在basicConfig的源码中 if handlers is None: filename = kwargs.pop("filename", None) mode = kwargs.pop("filemode", 'a') if filename: h = FileHandler(filename, mode) else: stream = kwargs.pop("stream", None) h = StreamHandler(stream) handlers = [h]


![]()
import logging FORMAT = "%(asctime)s %(name)s %(message)s" logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO) logger = logging.getLogger('test') print(logger.name,type(logger)) logger.info("line 1") handler = logging.StreamHandler()#创建handler print(handler.level)#0 logger.addHandler(handler) #line 2 #注意看控制台 logger.info('line 2')
日志流
level的继承
import logging FORMAT = "%(asctime)-15s info:%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s" logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT) root = logging.getLogger() log1 = logging.getLogger("s") log1.setLevel(logging.ERROR)#分别取INFO,WARNING,ERROR试一试 #没有设置任何handler、level #log2有效级别就是log1的ERROR log2 = logging.getLogger('s.s1') log2.warning('log2 warning')
![]()
import logging FORMAT = "%(asctime)-15s info:%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s" logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT) root = logging.getLogger() log1 = logging.getLogger("s") log1.setLevel(logging.WARNING)#ERROR试一试 print(log1.getEffectiveLevel()) h1 = logging.StreamHandler() h1.setLevel(logging.INFO) log1.addHandler(h1)#输出到控制台内容:log2 warning log2 error log2 = logging.getLogger('s.s1') print(log2.getEffectiveLevel())#继承父的level,WARNING h2 = logging.StreamHandler() h2.setLevel(logging.ERROR) log2.addHandler(h2)#输出到控制台内容:log2 error log2.warning('log2 warning') #输出到控制台内容:2019-05-09 22:49:52,299 info:5924 MainThread log2 warning log2.error('log2 error') #输出到控制台内容:2019-05-09 22:47:46,081 info:16104 MainThread log2 error #输出如下: # log2 warning # 30 # 2019-05-09 22:49:52,299 info:5924 MainThread log2 warning # 30 # log2 error # log2 error # 2019-05-09 22:49:52,299 info:5924 MainThread log2 error
总结


Formatter

import logging FORMAT = "%(asctime)-15s info:%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s" logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT) log1 = logging.getLogger("s") log1.setLevel(logging.WARNING)#ERROR试一试 h1 = logging.StreamHandler() h1.setLevel(logging.INFO) # fmt1 = logging.Formatter('log1-h1 %(message)s') # h1.setFormatter(fmt1) print('log1 formatter',h1.formatter) #设置formatter输出内容:log1-h1 log2 warning log1-h1 log2 error #不设置formatter输出内容: log2 warning log2 error log1.addHandler(h1) log2 = logging.getLogger('s.s1') print(log2.getEffectiveLevel())#继承父的level,WARNING #FileHandler为StreamHandler子类 h2 = logging.FileHandler('E:/test.log')#个性化将日志输出到指定文件 h2.setLevel(logging.ERROR) fmt2 = logging.Formatter('log2-h2 %(message)s') h2.setFormatter(fmt2) log2.addHandler(h2)#输出到文件内容:log2-h2 log2 error log2.warning('log2 warning') #输出内容:2019-05-09 23:00:13,680 info:15356 MainThread log2 warning log2.error('log2 error') #输出内容:2019-05-09 23:00:13,680 info:15356 MainThread log2 error log2.info('log2 info') #无显示内容
Filter

import logging FORMAT = "%(asctime)-15s info:%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s" logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT) log1 = logging.getLogger("s") log1.setLevel(logging.WARNING)#ERROR试一试 h1 = logging.StreamHandler() h1.setLevel(logging.INFO) fmt1 = logging.Formatter('log1-h1 %(message)s') h1.setFormatter(fmt1) log1.addHandler(h1)#输出内容:log1-h1 log2 warning log1-h1 log2 error log2 = logging.getLogger('s.s1') print(log2.getEffectiveLevel())#继承父的level,WARNING h2 = logging.StreamHandler() h2.setLevel(logging.WARNING) fmt2 = logging.Formatter('log2-h2 %(message)s') h2.setFormatter(fmt2) f2 = logging.Filter('s.s1')#过滤器 s s.s1 s.s2 h2.addFilter(f2) log2.addHandler(h2) log2.warning('log2 warning') #输出内容:2019-05-09 23:00:13,680 info:15356 MainThread log2 warning


线程同步
概念

Event***



from threading import Event,Thread import logging import time FORMAT = '%(asctime)s %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s' logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO) def boss(event:Event): logging.info("I'm boss,waitting for U.") #等待 event.wait() logging.info("Good job") def worker(event:Event,count=10): cups = [] logging.info("I'm working for U.") while True: logging.info('make 1') time.sleep(0.5) cups.append(1) if len(cups) >= count: #通知 event.set() break logging.info("I'm finished my job.cups={}".format(cups)) event = Event() w = Thread(target=worker,args=(event,)) b = Thread(target=boss,args=(event,)) w.start() b.start()

wait的使用
from threading import Event,Thread import logging import time logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO) def do(event:Event,interval:int): while not event.wait(interval):#等待interval时长,未等到则返回False logging.info('do sth.') e = Event() Thread(target=do,args=(e,3)).start() # time.sleep(3)#输出: main exit e.wait(3)#输出:INFO:root:do sth. main exit e.set() print('main exit')
![]()
Event练习

#思路实现 from threading import Event,Thread import logging import datetime logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO) def add(x:int,y:int): logging.info(x+y) class Timer: def __init__(self,interval,fn,*args,**kwargs): self.interval = interval self.fn = fn self.args = args self.kwargs = kwargs self.event = Event() def start(self): Thread(target=self.__run).start() def cancel(self): self.event.set() def __run(self): start = datetime.datetime.now() logging.info('waitting') self.event.wait(self.interval) if not self.event.is_set(): self.fn(*self.args,**self.kwargs) delta = (datetime.datetime.now()-start).total_seconds() logging.info('finished {}'.format(delta)) t = Timer(5,add,4,50) t.start() e = Event() e.wait(4) # t.cancel()
Lock***


#Lock import threading from threading import Thread,Lock import logging import time FORMAT = '%(asctime)s %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s' logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO) cups = [] def worker(count=10): logging.info("I'm working for U") flag = False while True: if len(cups) >= count: flag = True time.sleep(0.001)#为了看出线程切换的效果 if not flag: cups.append(1) if flag: break logging.info("{} finished. cups={}".format(threading.current_thread().name,len(cups))) for _ in range(10): Thread(target=worker,args=(1000,)).start() #输出结果: ... 2019-05-11 22:45:23,507 Thread-10 18944 Thread-10 finished. cups=1009 2019-05-11 22:45:23,507 Thread-5 23256 Thread-5 finished. cups=1009


![]()
#Lock import threading from threading import Thread,Lock import logging import time FORMAT = '%(asctime)s %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s' logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO) cups = [] lock = threading.Lock() def worker(count=10): logging.info("I'm working for U") flag = False while True: lock.acquire() if len(cups) >= count: flag = True #lock.release() #这里释放锁? time.sleep(0.001)#为了看出线程切换的效果 if not flag: cups.append(1) lock.release() #这里释放锁? if flag: break logging.info("{} finished. cups={}".format(threading.current_thread().name,len(cups))) for _ in range(10): Thread(target=worker,args=(1000,)).start() #输出结果: # ... # 2019-05-11 22:50:05,331 Thread-1 22564 Thread-1 finished. cups=1000 # 2019-05-11 22:50:05,332 Thread-9 1764 Thread-9 finished. cups=1000


import threading from threading import Thread,Lock import time class Counter: def __init__(self): self._val = 0 @property def value(self): return self._val def inc(self): self._val += 1 def dec(self): self._val -= 1 def run(c:Counter,count=100): for _ in range(count): for i in range(-50,50): if i<0: c.dec() else: c.inc() c = Counter() c1 = 10 c2 = 1000 for i in range(c1): threading.Thread(target=run,args=(c,c2)).start() print(c.value)

加锁、解锁


![]()
import threading from threading import Thread,Lock import time class Counter: def __init__(self): self.__val = 0 self.__lock = Lock() @property def value(self): with self.__lock: return self.__val def inc(self): try: self.__lock.acquire() self.__val += 1 finally: self.__lock.release() def dec(self): with self.__lock: self.__val -= 1 def run(c:Counter,count=100): for _ in range(count): for i in range(-50,50): if i<0: c.dec() else: c.inc() c = Counter() c1 = 10 c2 = 1000 for i in range(c1): threading.Thread(target=run,args=(c,c2)).start() print(c.value)#这一句合适吗?
![]()
while True: time.sleep(1) if threading.active_count() == 1:#即保证只有主线程存在 print(threading.enumerate()) print(c.value) else: print(threading.enumerate())
锁的应用场景



非阻塞锁使用
import threading import logging import time FORMAT = '[%(threadName)s,%(thread)d] %(message)s' logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format=FORMAT) def worker(tasks): for task in tasks: time.sleep(0.001) if task.lock.acquire(False):#获取锁则返回True logging.info('{} {} begin to start'.format(threading.current_thread(),task.name)) else: #适当时机释放锁,为了演示不释放 logging.info('{} {} is working'.format(threading.current_thread(),task.name)) class Task: def __init__(self,name): self.name = name self.lock = threading.Lock() #构造10个任务 tasks = [Task('task-{}'.format(x)) for x in range(10)] #启动5个线程 for i in range(5): threading.Thread(target=worker,name='worker-{}'.format(i),args=(tasks,)).start()
可重入锁RLock

import threading import time lock = threading.RLock() print(lock.acquire()) print('===========') print(lock.acquire(blocking=False)) print(lock.acquire()) print(lock.acquire(timeout=3.55)) print(lock.acquire(blocking=False)) # print(lock.acquire(blocking=False,timeout=10))#异常 lock.release() lock.release() lock.release() lock.release() lock.release() # lock.release()#RuntimeError: cannot release un-acquired lock print('----------') def sub(lock): print('{}:{}'.format(threading.current_thread(),lock.acquire())) print('{}:{}'.format(threading.current_thread(),lock.acquire(False))) lock.release() lock.release() threading.Timer(2,sub,args=(lock,)).start()# 传入同一个lock对象 print('+++++++++++++') print()
Condition
![]()


from threading import Thread,Event import logging import random FORMAT = '%(asctime)s %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s' logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO) #此例只是为了演示,不考虑线程安全问题 class Dispatcher: def __init__(self): self.data = None self.event = Event()#event只是为了使用方便,与逻辑无关 def produce(self,total): for _ in range(total): data = random.randint(0,100) logging.info(data) self.data = data self.event.wait(1) self.event.set() def consume(self): while not self.event.is_set(): logging.info("received {}".format(self.data)) self.data = None self.event.wait(0.5) d = Dispatcher() p = Thread(target=d.produce,args=(10,),name='producer') c = Thread(target=d.consume,name='consumer') c.start() p.start()

from threading import Thread,Event,Condition import logging import random FORMAT = '%(asctime)s %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s' logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO) #此例只是为了演示,不考虑线程安全问题 class Dispatcher: def __init__(self): self.data = None self.event = Event()#event只是为了使用方便,与逻辑无关 self.cond = Condition() def produce(self,total): for _ in range(total): data = random.randint(0,100) with self.cond: logging.info(data) self.data = data self.cond.notify_all() self.event.wait(1)#模拟产生数据速度 self.event.set() def consume(self): while not self.event.is_set(): with self.cond: self.cond.wait()#阻塞等通知 logging.info("received {}".format(self.data)) self.data = None self.event.wait(0.5)#模拟消费者的速度 d = Dispatcher() p = Thread(target=d.produce,args=(10,),name='producer') c = Thread(target=d.consume,name='consumer') c.start() p.start()

from threading import Thread,Event,Condition import logging import random FORMAT = '%(asctime)s %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s' logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO) #此例只是为了演示,不考虑线程安全问题 class Dispatcher: def __init__(self): self.data = None self.event = Event()#event只是为了使用方便,与逻辑无关 self.cond = Condition() def produce(self,total): for _ in range(total): data = random.randint(0,100) with self.cond: logging.info(data) self.data = data self.cond.notify(2) self.event.wait(1)#模拟产生数据速度 self.event.set() def consume(self): while not self.event.is_set(): with self.cond: self.cond.wait()#阻塞等通知 logging.info("received {}".format(self.data)) # self.data = None self.event.wait(0.5)#模拟消费者的速度 d = Dispatcher() p = Thread(target=d.produce,args=(10,),name='producer') #增加消费者 for i in range(5): Thread(target=d.consume,name='consumer-{}'.format(i)).start() p.start()

Condition总结

Barrier


Barrier实例
import threading import logging #输出格式定义 FORMAT = '%(asctime)s-15s [%(threadName)s,%(thread)d] %(message)s' logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO) def worker(barrier:threading.Barrier): # print(barrier.n_waiting) logging.info('waitting for {} threads.'.format(barrier.n_waiting))#个人感觉这个显示有问题,应该是线程切换的原因 try: barrier._id = barrier.wait() logging.info('after barrier {}'.format(barrier._id)) except threading.BrokenBarrierError: logging.info('Broken Barrier') barrier = threading.Barrier(3) for x in range(6):#改成4,5,6,试试 threading.Thread(target=worker,name='worker-{}'.format(x),args=(barrier,)).start() # 输出如下: 2019-05-13 10:28:49,408-15s [worker-0,10696] waitting for 0 threads. 2019-05-13 10:28:49,408-15s [worker-1,11624] waitting for 1 threads. 2019-05-13 10:28:49,408-15s [worker-2,10328] waitting for 2 threads. 2019-05-13 10:28:49,408-15s [worker-2,10328] after barrier 2 2019-05-13 10:28:49,408-15s [worker-0,10696] after barrier 0 2019-05-13 10:28:49,408-15s [worker-1,11624] after barrier 1 2019-05-13 10:28:49,408-15s [worker-3,10068] waitting for 0 threads. 2019-05-13 10:28:49,409-15s [worker-4,6276] waitting for 0 threads. 2019-05-13 10:28:49,409-15s [worker-5,8256] waitting for 2 threads. 2019-05-13 10:28:49,409-15s [worker-5,8256] after barrier 2 2019-05-13 10:28:49,409-15s [worker-3,10068] after barrier 0 2019-05-13 10:28:49,410-15s [worker-4,6276] after barrier 1


import threading import logging #输出格式定义 FORMAT = '%(asctime)s-15s [%(threadName)s,%(thread)d] %(message)s' logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO) def worker(barrier:threading.Barrier): # print(barrier.n_waiting) logging.info('waitting for {} threads.'.format(barrier.n_waiting)) try: barrier._id = barrier.wait() logging.info('after barrier {}'.format(barrier._id)) except threading.BrokenBarrierError: logging.info('Broken Barrier') barrier = threading.Barrier(3) for x in range(0,9): if x==2: barrier.abort() elif x==6: barrier.reset() threading.Event().wait(1) threading.Thread(target=worker,name='worker-{}'.format(x),args=(barrier,)).start()
![]()
![]()
wait方法超时实例
![]()
import threading import logging #输出格式定义 FORMAT = '%(asctime)s-15s [%(threadName)s,%(thread)d] %(message)s' logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO) def worker(barrier:threading.Barrier,i:int): logging.info('waitting for {} threads.'.format(barrier.n_waiting)) try: logging.info(barrier.broken)#是否broken if i<3: barrier_id = barrier.wait(1)#1秒后超时,屏障处于broken状态 else: if i==6: barrier.reset()#恢复屏障 barrier_id = barrier.wait() logging.info('after barrier {}'.format(barrier_id)) except threading.BrokenBarrierError: logging.info('Broken Barrier') barrier = threading.Barrier(3) for x in range(0,9): threading.Event().wait(2) threading.Thread(target=worker,name='worker-{}'.format(x),args=(barrier,x)).start()
Barrier应用
![]()

semaphore信号量


![]()
#-*- codeing:utf-8 -*- import threading import logging logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format="%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s") import time def work(s:threading.Semaphore): logging.info("in sub") s.acquire() logging.info("end sub") s = threading.Semaphore(3) logging.info(s.acquire()) logging.info(s.acquire()) logging.info(s.acquire()) threading.Thread(target=work,args=(s,)).start() print('-------') time.sleep(2) logging.info(s.acquire(False)) logging.info(s.acquire(timeout=1)) s.release() print('end main')
应用举例

# Author: Baozi #-*- codeing:utf-8 -*- # import threading # import logging # logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format="%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s") # import time class Conn: def __init__(self,name): self.name = name class Pool: def __init__(self,count:int): self.count = count #池中是连接对象的列表 self.pool = [Conn("conn-{}".format(x))for x in range(self.count)] def get_conn(self): #从池中拿走一个连接 if len(self.pool)>0: return self.pool.pop() def return_conn(self,conn:Conn): #向池中添加一个连接 self.pool.append(conn)

import threading import logging logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format="%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s") import random class Conn: def __init__(self,name): self.name = name def __repr__(self): return self.name class Pool: def __init__(self,count:int): self.count = count #池中是连接对象的列表 self.pool = [Conn("conn-{}".format(x))for x in range(self.count)] self.semaphore = threading.Semaphore(count) def get_conn(self): #从池中拿走一个连接 self.semaphore.acquire() return self.pool.pop() def return_conn(self,conn:Conn): #向池中添加一个连接 self.pool.append(conn) self.semaphore.release() #连接池初始化 pool = Pool(3) def worker(pool:Pool): conn = pool.get_conn() logging.info(conn) #模拟使用了一段时间 threading.Event().wait(random.randint(3,6)) pool.return_conn(conn) for i in range(6): threading.Thread(target=worker,name="worker-{}".format(i),args=(pool,)).start()

问题

不需要,原因如下:

import logging import threading sema = threading.Semaphore(3) logging.warning(sema.__dict__) for i in range(3): sema.acquire() logging.warning('~~~~~~~') logging.warning(sema.__dict__) for i in range(4): sema.release() logging.warning(sema.__dict__) for i in range(3): sema.acquire() logging.warning('======') logging.warning(sema.__dict__) sema.acquire() logging.warning('------') logging.warning(sema.__dict__)

BoundedSemaphore类

![]()
self.pool.append(conn)
self.semaphore.release()

![]()
![]()

信号量和锁

数据结构和GIL

GIL全局解释器锁(进程级别锁)

IO密集型:多访问文件系统,里面可能会有wait()语句。
CPU密集型:大量使用CPU的计算资源。


#1 import datetime import logging logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format="%(threadName)s %(message)s") start = datetime.datetime.now() #计算 def calc(): sum = 0 for _ in range(1000000000): sum += 1 calc() calc() calc() calc() calc() delta = (datetime.datetime.now()-start).total_seconds() logging.info(delta)#239.750713
#2 import threading import logging logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,format="%(thread)d %(threadName)s %(message)s") import datetime def calc(): sum = 0 for _ in range(1000000000): sum += 1 start = datetime.datetime.now() lst = [] for _ in range(5): t = threading.Thread(target=calc) t.start() lst.append(t) for t in lst: t.join() delta = (datetime.datetime.now()-start).total_seconds() logging.info(delta)

多进程

multiprocessing
Process类

#多进程 import multiprocessing import datetime def calc(i): sum = 0 for _ in range(1000000000): sum += 1 if __name__ == '__main__': start = datetime.datetime.now() ps = [] for i in range(5): p = multiprocessing.Process(target=calc,args=(i,),name="calc-{}".format(i)) ps.append(p) p.start() for p in ps: p.join() delta = (datetime.datetime.now() - start).total_seconds() print(delta) print("end")

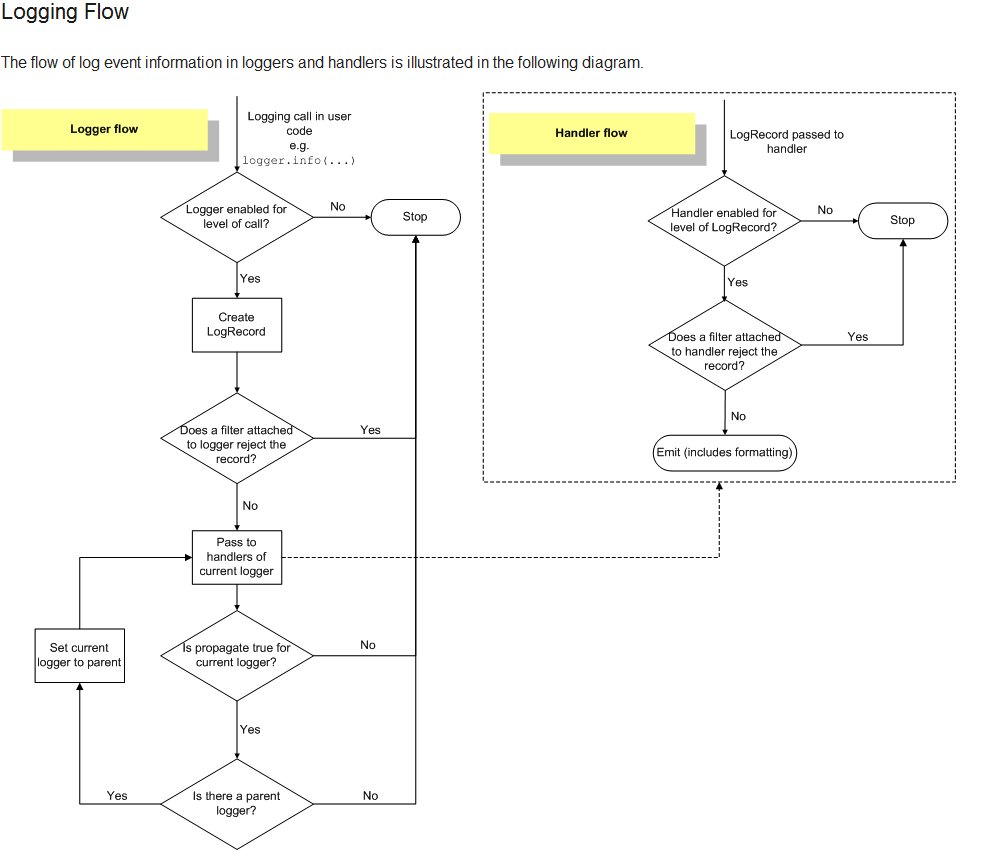
进程间同步

进程池
![]()
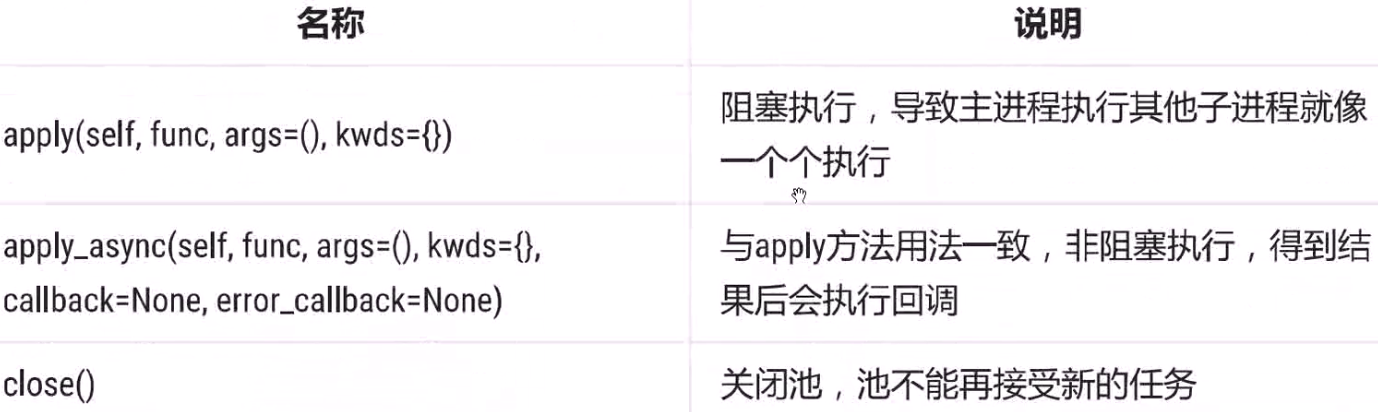
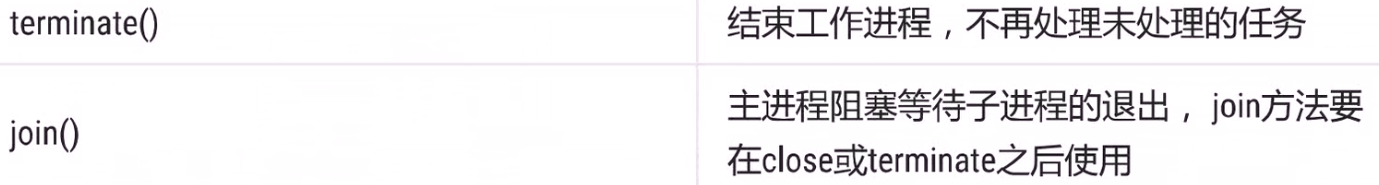
from multiprocessing import Process,Pool import datetime import logging FORMAT="%(asctime)s %(processName)s %(process)d %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s" logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO) start = datetime.datetime.now() def calc(i): sum = 0 for _ in range(100000000): sum += 1 res = sum + i logging.info(res) return res def callback(result): logging.info(result) if __name__ == '__main__': pool = Pool() for i in range(5): pool.apply_async(calc,(i,),callback=callback) #异步方法 # pool.apply(calc,(i,)) #异步方法 print('==============') pool.close() pool.join()#阻塞 delta = (datetime.datetime.now() - start).total_seconds() print(delta) print("end") #输出如下: # ============== # ============== # ============== # ============== # ============== # 2019-05-14 10:19:30,117 SpawnPoolWorker-5 8096 MainThread 11532 100000004 # 2019-05-14 10:19:30,117 MainProcess 10772 Thread-3 11852 100000004 # 2019-05-14 10:19:30,183 SpawnPoolWorker-1 4128 MainThread 11660 100000001 # 2019-05-14 10:19:30,183 MainProcess 10772 Thread-3 11852 100000001 # 2019-05-14 10:19:30,214 SpawnPoolWorker-2 7096 MainThread 7384 100000000 # 2019-05-14 10:19:30,214 MainProcess 10772 Thread-3 11852 100000000 # 2019-05-14 10:19:30,222 SpawnPoolWorker-4 12060 MainThread 11932 100000002 # 2019-05-14 10:19:30,222 MainProcess 10772 Thread-3 11852 100000002 # 2019-05-14 10:19:30,315 SpawnPoolWorker-3 6952 MainThread 6376 100000003 # 2019-05-14 10:19:30,315 MainProcess 10772 Thread-3 11852 100000003 # 7.69844 # end #将apply_async换成apply后输出如下 # 2019-05-14 10:17:58,961 SpawnPoolWorker-2 10128 MainThread 6944 100000000 # ============== # 2019-05-14 10:18:03,503 SpawnPoolWorker-1 6648 MainThread 1108 100000001 # ============== # 2019-05-14 10:18:08,074 SpawnPoolWorker-3 7180 MainThread 5764 100000002 # ============== # 2019-05-14 10:18:12,649 SpawnPoolWorker-5 7108 MainThread 9108 100000003 # ============== # 2019-05-14 10:18:17,225 SpawnPoolWorker-6 6668 MainThread 3384 100000004 # ============== # 23.522345 # end
多进程、多线程的选择

应用

concurrent包
concurrent.futures

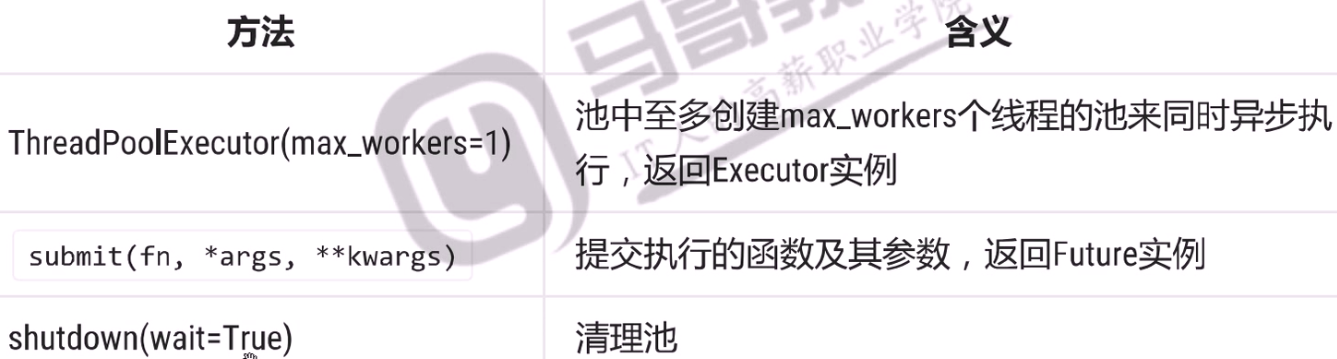
ThreadPoolExecutor对象
![]()
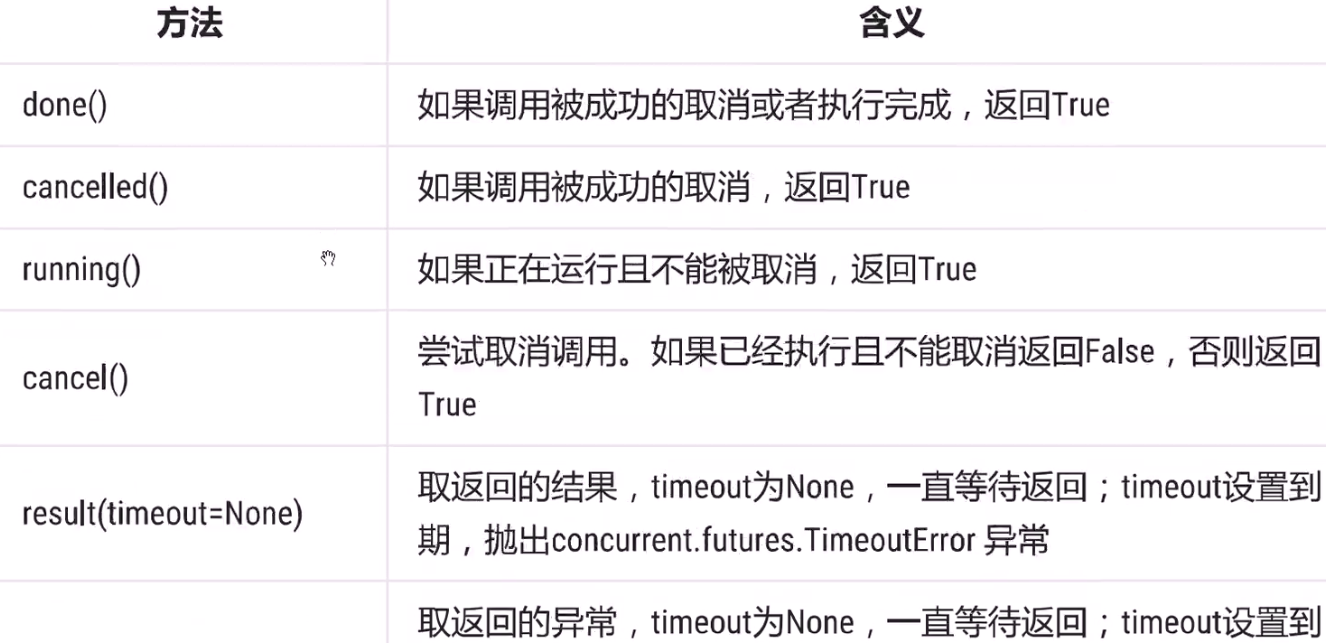
Future类
![]()
import threading import time import logging from concurrent import futures FORMAT="%(asctime)s %(processName)s %(process)d %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s" logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO) def worker(): logging.info('begin') time.sleep(5) logging.info("end") if __name__ == '__main__': # executor = futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=3) executor = futures.ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers=3) fs = [] for i in range(3): future = executor.submit(worker) fs.append(future) for i in range(3,6): future = executor.submit(worker)#不阻塞 print('~~~~~~~~~') fs.append(future) while True: time.sleep(2) logging.info("````") flag = True for f in fs:#判断是否还有未完成的任务 logging.info(f.done()) flag = flag and f.done() # if not flag:#注释if看得更清楚 # break print('-'*20) if flag: executor.shutdown()#清理池,池中线程全部杀掉 logging.info(threading.enumerate())#多进程时看主线程已经没有必要了 break
支持上下文管理

with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=1) as executor: furture = executor.submit(pow,323,1325) print(future.result())
![]()
import threading import time import logging from concurrent import futures FORMAT="%(asctime)s %(processName)s %(process)d %(threadName)s %(thread)d %(message)s" logging.basicConfig(format=FORMAT,level=logging.INFO) def worker(): logging.info('begin') time.sleep(5) logging.info("end") if __name__ == '__main__': # executor = futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=3) with futures.ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers=3) as executor: fs = [] for i in range(3): future = executor.submit(worker) fs.append(future) for i in range(3,6): future = executor.submit(worker)#不阻塞 print('~~~~~~~~~') fs.append(future) while True: time.sleep(2) logging.info("````") flag = True for f in fs:#判断是否还有未完成的任务 logging.info(f.done()) flag = flag and f.done() # if not flag:#注释if看得更清楚 # break print('-'*20) if flag: break
总结
