题记
感觉说的挺好的,值得学习
1 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。 2 本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/liujiaqi12345/article/details/88357041 3 Leetcode JAVA 题解: https://github.com/mJackie/leetcode 4 自己日常刷题经过是这样的: 5 6 拿到题目,看一眼Difficulty,然后自己思考一下解题思路。如果解不出来,就记下在哪里卡住了,难点在哪。 7 如果对应的题目有Solution,就看Solution,没有的话就点Discuss,按Most Votes排序,看排名最高的解法。 8 对比一下自己的解法与最优的解法的差别,总结一下为什么没想起来,记录下来这个思考的过程。 9 关掉别人的代码,开始Coding,Debug,Submit。 10 附上自己总结的几条经验: 11 12 先刷两个Top专题。Leetcode 上有个List选项,里边有两个专题,分别是Top 100 Liked Questions和Top Interview Questions。这两个List中有很多重复的题,加起来一共150道左右。都是经典的题目,将这150道刷完基本上所有的题型都见过了,而且多数经典题目都会涉及,是提升最快的一个方法。 13 14 注意记录、总结与复习。自己写过的代码一定要保存下来,刷题的时候也要记下主要思路和注意点,这样在复习的时候也能对比发现自己哪里还能改进,之前犯得错误有没有重犯。可以将相互关联的题目对比着一起看,方便总结与记忆。一定要时常复习刷过的题,复习比一味的追求数量更重要。 15 16 做好Easy,没必要死扣Hard。LeetCode上很多Easy的题目看似简单,实则想要写出Perfect的代码并非易事。多思考如何优化Easy,Medium的解法实际上比花精力解Hard题更能提高自己。况且面试的时候Hard被问的概率太小了。 17 18 切忌眼高手低。不要想着自己知道思路解法了就是会了,一定要亲自Coding,手撸出来。我在刷的过程中就经常在Debug的时候才发现自己忘记考虑了某些条件。不把代码写出来,只看别人的答案对自己是没有多大的提高的,只有亲自AC了题目,才能算做过一道题。 19 ———————————————— 20 版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「Jackie.Liu」的原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。 21 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/liujiaqi12345/article/details/88357041
还有这注释方式也不错,学习
-
语言: Java
-
说明: 每道题在代码头部都添加了我的解题思路和批注,Eg:
/***** * 287. Find the Duplicate Number * 题意:n+1个数属于[1~n],找出重复的那个数 * 难度:Medium * 分类:Array, Two Pointers, Binary Search * 思路:如果nums[i]不在对应位置,则和对应位置交换。如果对应位置上也为该数,说明这个数就是重复的数字。这个方法改变了数组。是错误的。 * 另一种方法,把问题转换成有环链表,找环的起始节点。O(n) O(1) lc142 * 二分查找,每次看一边数字的个数, O(nlog(n)) O(1) * Tips:剑指offer原题 */ -
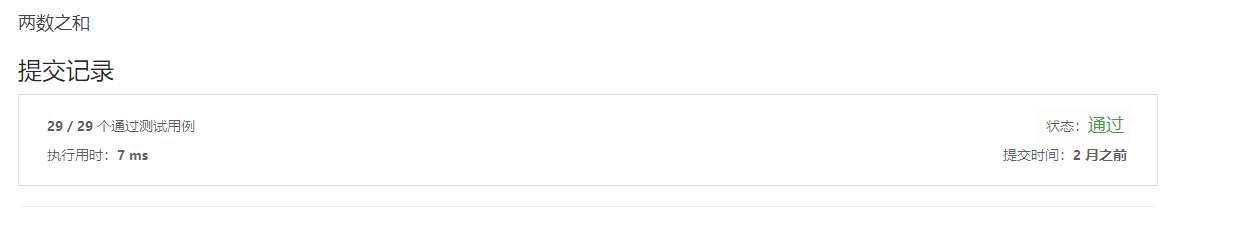
1. 两数之和
1 public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
2 int[] result = new int[2];
3 Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
4 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
5 if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
6 result[1] = i;
7 result[0] = map.get(target - nums[i]);
8 return result;
9 }
10 map.put(nums[i], i);
11 }
12 return result;
13
14 }
15
2. Add Two Numbers
/**
* Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4) Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8 Explanation: 342 +
* 465 = 807
*
* 题意:对于俩个链表。对应节点相加,满十进一
* 思路:先判断对应节点是否至少存在一个有值,有则相加,然后移动节点向下,循环如此,如果说最后一次相加,进位(carry)不为0,则要显示,其次,返回值要从返回链表的第二个几点开始
*
* @param l1
* @param l2
* @return
*/
public static ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode resultNode = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = l1, q = l2, curr = resultNode;
int carry = 0;
while (p != null || q != null) {
int x = p != null ? p.val : 0;
int y = q != null ? q.val : 0;
int sum = x + y + carry;
carry = sum / 10;
curr.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
curr = curr.next;
if (p != null) {
p = p.next;
}
if (q != null) {
q = q.next;
}
}
if (carry > 0) {
curr.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return resultNode.next;
}
3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
1 public static void main(String[] args) {
2 String s = "abbabc";
3 System.out.println(lengthOfLongestSubstring(s));
4 }
5
6 public static int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
7 int max = 0;
8 // ”记录当前重复字母的最新位置“
9 int j = 0;
10 HashMap<Character, Integer> resultMap = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
11 for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
12 if (resultMap.containsKey(s.charAt(i))) {
13 j = Math.max(resultMap.get(s.charAt(i)) + 1, j);
14 }
15 //”当前位置-上次重复的最大位置+1“
16 max = Math.max(i - j + 1, max);
17 resultMap.put(s.charAt(i), i);
18 }
19
20 return max;
21 }
7. 整数反转
1 public int reverse(int x) {
2 int ans = 0;
3 while (x != 0) {
4 int pop = x % 10;
5 if (ans > Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 || (ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 && pop > 7))
6 return 0;
7 if (ans < Integer.MIN_VALUE / 10 || (ans == Integer.MIN_VALUE / 10 && pop < -8))
8 return 0;
9 ans = ans * 10 + pop;
10 x /= 10;
11 }
12 return ans;
13 }
14
8. String to Integer (atoi)
1 public static int myAtoi(String str) { 2 3 // 1字符串非空判断 ""||" " 4 if (str.isEmpty() || str.trim().isEmpty()) { 5 return 0; 6 } 7 8 int index = 0; 9 int sign = 1; 10 int total = 0; 11 //1检测第一个非空字符串是什么 12 while (str.charAt(index) == ' ' && index < str.length()) { 13 index++; 14 } 15 16 //1判断这个数是正数还是负数 17 if (str.charAt(index) == '+' || str.charAt(index) == '-') { 18 sign = str.charAt(index) == '+' ? 1 : -1; 19 index++; 20 } 21 22 //1判断是否是数字,是否越界,如果越界就取越界的边界值 23 while (index < str.length()) { 24 int digit = str.charAt(index) - '0'; 25 if (digit < 0 || digit > 9) {
11. Container With Most Water
1 /** 2 * 解法1:俩边的边为起点,进行计算,如果左边的边比右边的小,左边第二条边和当前右边的边进行计算,如果右边的边小于左边的边,则右边的第二条便进行计算,依此类推 3 * 4 * @param height 5 * @return 6 */ 7 public static int maxArea(int[] height) { 8 int i = 0, j = height.length - 1, res = 0; 9 while (i < j) { 10 // ‘取最大值’ 11 res = Math.max(res, Math.min(height[i], height[j]) * (j - i)); 12 if (height[i] < height[j]) { 13 i++; 14 } else { 15 j--; 16 } 17 } 18 return res; 19 } 20 21 /** 22 * 解法2 遍历所有的可能结果n(n-1)/2中情况 23 * 24 * @param height 25 * @return 26 */ 27 public int maxArea1(int[] height) { 28 int max = 0; 29 for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) { 30 for (int j = i + 1; j < height.length; j++) { 31 max = Math.max(max, Math.min(height[i], height[j]) * (j - i)); 32 } 33 } 34 35 return max; 36 }
17. Letter Combinations of a Phone Number
1 public static List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) { 2 List<String> ret = new ArrayList<String>(); 3 Map<Character, String> map = new HashMap<Character, String>() { 4 { 5 put('2', "abc"); 6 put('3', "def"); 7 put('4', "ghi"); 8 put('5', "jkl"); 9 put('6', "mno"); 10 put('7', "pqrs"); 11 put('8', "tuv"); 12 put('9', "wxyz"); 13 } 14 }; 15 16 //‘非空校验’ 17 if (digits == null || "".equals(digits)) { 18 return ret; 19 } 20 dfs(digits, 0, "", map, ret); 21 22 return ret; 23 } 24 25 public static void dfs(String digits, int idx, String path, Map<Character, String> map, List<String> ret) { 26 if (digits.length() == path.length()) { 27 ret.add(path); 28 return; 29 } 30 //‘循环配合递归’ 31 for (int i = idx; i < digits.length(); i++) { 32 for (char c : map.get(digits.charAt(i)).toCharArray()) {//这里是第个数字的对应的字母 33 dfs(digits, i + 1, path + c, map, ret);//这里进行递归,对应的第二个数字的循环,和第一个字母进行拼接 34 } 35 } 36 }
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
1 public class ListNode { 2 int val; 3 ListNode next; 4 5 ListNode(int x) { 6 val = x; 7 } 8 9 /** 10 *‘本题思路:建立俩个链表,一个是dummy,复制原链表,另一个链表(first)为了计算链表长度;然后在用first链表指向dummy,删掉指定位置的元素’ 11 *‘注意,应为是dummy指向head,所以多了一个节点,在指定删除位置时不用减一;另外返回时应该返回dummy.next,第一个节点是我们自己定义的’ 12 * @param head 13 * @param n 14 * @return 15 */ 16 public static ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) { 17 ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); 18 dummy.next = head; 19 ListNode first = head; 20 int length = 0; 21 while (first != null) { 22 length++; 23 first = first.next; 24 } 25 int position = length - n; 26 first = dummy; 27 while (position > 0) { 28 position--; 29 first = first.next; 30 } 31 first.next = first.next.next; 32 return dummy.next; 33 34 } 35 36 public static void main(String[] args) { 37 ListNode a1 = new ListNode(1); 38 ListNode a2 = new ListNode(2); 39 ListNode a3 = new ListNode(3); 40 ListNode a4 = new ListNode(4); 41 ListNode a5 = new ListNode(5); 42 a1.next = a2; 43 a2.next = a3; 44 a3.next = a4; 45 a4.next = a5; 46 ListNode a6 = removeNthFromEnd(a1, 2); 47 while (a6 != null) { 48 System.out.println(a6.val); 49 a6 = a6.next; 50 } 51 } 52 }

20. Valid Parentheses
1 /** 2 * 题意:括号匹配,俩个匹配的括号之间是不允许有为匹配(也就是单个的)括号 3 * 解题思路:通过入栈的形式,如果未匹配就入栈,匹配就出栈,最后如果栈不为空或者栈顶元素不当前元素不匹配就返回false 4 * 5 * @param s 6 * @return 7 */ 8 public static boolean isValid(String s) { 9 Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>(); 10 for (char c : s.toCharArray()) { 11 if (c == '(') { 12 stack.push(')'); 13 } else if (c == '[') { 14 stack.push(']'); 15 } else if (c == '{') { 16 stack.push('}'); 17 } else if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.pop() != c) { 18 return false; 19 } 20 } 21 return stack.isEmpty(); 22 } 23 24 public static void main(String[] args) { 25 System.out.println(isValid("[")); 26 }
21. Merge Two Sorted Lists
1 int val; 2 ListNode next; 3 4 ListNode(int x) { 5 val = x; 6 } 7 8 /** 9 * 本题思路:‘将当前节点l1.next和L2的当前节点(第一个节点)进行比较,如果小于等于(注意:等于也是可以的),继续往下走,反之则进行节点替换(l1.next和l2进行替换),当l2为null时(也就是l1.next=null)结束循环’ 10 * @param l1 11 * @param l2 12 * @return 13 */ 14 public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { 15 if (l1 == null) { 16 return l2; 17 } 18 if (l2 == null) { 19 return l1; 20 } 21 //此处是为了保证第一个节点时最小值 22 ListNode tmp; 23 if (l1.val > l2.val) { 24 tmp = l2; 25 l2 = l1; 26 l1 = tmp; 27 } 28 ListNode newListNode = l1; 29 while (l2 != null) { 30 //遍历节点进行组合 31 while (newListNode.next != null && newListNode.next.val <= l2.val) { 32 newListNode = newListNode.next; 33 } 34 //比较排序 35 tmp = newListNode.next; 36 newListNode.next = l2; 37 l2 = tmp; 38 } 39 return l1; 40 41 } 42 43 //展示当前链表的值 44 public static void sysoListNode(ListNode l1) { 45 while (l1 != null) { 46 System.out.format("%d->", l1.val); 47 l1 = l1.next; 48 } 49 System.out.println("==================="); 50 } 51 52 /** 53 * 大神的解法:原理和上面一样,只是利用递归的原理 54 * @param l1 55 * @param l2 56 * @return 57 */ 58 public static ListNode mergeTwoLists2(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { 59 if (l1 == null) 60 return l2; 61 if (l2 == null) 62 return l1; 63 if (l1.val < l2.val) { 64 l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2); 65 //此处时为了更直观看当前链表的状态 66 sysoListNode(l1); 67 sysoListNode(l2); 68 return l1; 69 } else { 70 l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next); 71 //此处时为了更直观看当前链表的状态 72 sysoListNode(l1); 73 sysoListNode(l2); 74 return l2; 75 } 76 } 77 78 //测试数据 79 public static void main(String[] args) { 80 ListNode l1 = new ListNode(1); 81 ListNode l2 = new ListNode(2); 82 ListNode l3 = new ListNode(4); 83 l1.next = l2; 84 l2.next = l3; 85 86 ListNode r1 = new ListNode(1); 87 ListNode r2 = new ListNode(3); 88 ListNode r3 = new ListNode(4); 89 r1.next = r2; 90 r2.next = r3; 91 92 mergeTwoLists(l1, r1); 93 94 }
26 break;
27 }
28
29 if (Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 > total
30 || (Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 == total && Integer.MAX_VALUE % 10 >= digit)) {
31 total = total * 10 + digit;
32 index++;
33 } else {
34 return sign > 0 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : Integer.MIN_VALUE;
35 }
36 }
37 return total * sign;
38
39 }

20. 有效的括号
1 class Solution {
2 public boolean isValid(String s) {
3 int n = s.length();
4 for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
5 if (s.contains("{}"))
6 s = s.replace("{}", "");
7 if (s.contains("()"))
8 s = s.replace("()", "");
9 if (s.contains("[]"))
10 s = s.replace("[]", "");
11 }
12 if ("".equals(s)) {
13 return true;
14 }
15 return false;
16 }
17 }
26. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array
1 public static int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
2 int count = 1;
3 for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {//用当前的数字和上一个被比较的数字进行比较,如果大于他就替换,本题默认一排序
4 if (nums[i] > nums[count - 1]) {
5 nums[count++] = nums[i];
6 }
7 }
8 return count;
9
10 }

27. Remove Element
1 public static int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
2 if (nums == null) {
3 return -1;
4 } else if (nums.length == 0) {
5 return 0;
6 } else {
7 int count = 0;//统计几个不相同,同时作为新数组的下标
8 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
9 if (nums[i] != val) {
10 nums[count++] = nums[i];//注意count++的执行顺序
11 }
12 }
13 return count;
14 }
15
16 }
41. First Missing Positive
1 public static int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {
2 if (nums.length == 0) {
3 return 1;
4 }
5
6 Set<Integer> numsSet = new HashSet<Integer>();
7 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
8 if (nums[i] < 1) {
9 continue;
10 } else {
11 numsSet.add(nums[i]);
12 }
13 }
14 List<Integer> numsList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
15 numsSet.forEach(n -> numsList.add(n));
16
17 // 1筛选过后的数组为空
18 if (numsList.size() == 0) {
19 return 1;
20 }
21
22 numsList.sort((a, b) -> a.compareTo(b.intValue()));
23
24 int index = 0;// 1当前数组下标
25 for (int i = 1;; i++) {
26 // 1预防数组越界
27 if (index < numsList.size() && numsList.get(index) == i) {
28 index++;
29 } else {
30 return i;
31 }
32 }
33
34 }
46. Permutations
1 /** 2 * 本题目标:对于给定数组列出所有的可能排列组合 3 * 实现方法:利用递归的思路 4 * 举个例子,当数组为【1,2,3】;先考虑第一个数为1时,后面的可能性,以此类推 5 * 注意:后面的可能性要以递归的思路去考虑,或者入栈出栈的思路。 6 * @param nums 7 * @return 8 */ 9 public static List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) { 10 List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>(); 11 // Arrays.sort(nums); // not necessary 12 backtrack(list, new ArrayList<>(), nums); 13 return list; 14 } 15 16 private static void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> list, List<Integer> tempList, int[] nums) { 17 if (tempList.size() == nums.length) { 18 //注意这里的细节,是新声明一个集合去保存这个值,如果用tempList会导致最后list为空,原因就是堆被清空啦 19 list.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(tempList)); 20 } else { 21 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { 22 if (tempList.contains(nums[i])) { 23 continue; 24 } else { 25 tempList.add(nums[i]); 26 //注意是循环中调用递归 27 backtrack(list, tempList, nums); 28 //小算法,清空当前递归中的最后一个值 29 tempList.remove(tempList.size() - 1); 30 } 31 } 32 33 } 34 }
48. Rotate Image
1 /** 2 * 本体题意:顺时针反转90度 3 * 解题方法:找出通项公式 4 * @param matrix 5 */ 6 public static void rotate(int[][] matrix) { 7 int n = matrix.length; 8 int[][] rotate = new int[n][n]; 9 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 10 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { 11 //通项公式 12 rotate[i][j] = matrix[n - 1 - j][i]; 13 } 14 } 15 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 16 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { 17 //重新赋值 18 matrix[i][j] = rotate[i][j]; 19 } 20 } 21 }
49. Group Anagrams
1 /** 2 * 本题题意:将含有相同字母的字符串归类 3 * 4 * 解法:将字符串拆分成字符,然后排序作为key,最后map转化成list 5 */ 6 public static List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) { 7 if (strs.length == 0) { 8 return new ArrayList<List<String>>(); 9 } 10 Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<String, List<String>>(); 11 for (String s : strs) { 12 char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); 13 Arrays.sort(chars); 14 String key = String.valueOf(chars); 15 if (!map.containsKey(key)) { 16 map.put(key, new ArrayList<String>()); 17 } 18 map.get(key).add(s); 19 } 20 return new ArrayList<List<String>>(map.values()); 21 22 }

53. Maximum Subarray
1 /** 2 * 题意:找出一组 最大的数组和,作为结果的数组长度不限但小于等于给定的数组 3 * 解决方法:二步; 4 * 第一步找到当前最大(通过(当前最大的+a[i+1]) + a[i+1]比较,找出最大的)(类似贪心) 5 * 第二步找到当前最大的和之前最大的进行比较,选出最大的 6 * 注意:maxSum初始值一定要定义最小,可能为负数,如果初始化成0就不行啦 7 * @param A 8 * @return 9 */ 10 public static int maxSubArray(int[] A) { 11 if (A == null || A.length == 0) { 12 throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 13 } 14 // ‘记录当前数据的最大值’;‘理解成新生成的最大值 和 旧的(已知的最大值比较)’ 15 int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE; 16 // ‘记录(当前)和(当前加下一位)的最大值’ 17 int maxCurrentSum = 0; 18 for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) { 19 maxCurrentSum = Math.max(maxCurrentSum + A[i], A[i]); 20 maxSum = Math.max(maxCurrentSum, maxSum); 21 } 22 return maxSum; 23 24 } 25 26 /** 27 * 这个解决思路很好,也很好理解 28 * 解决思路:‘如果上一次结果为负数,则上一次结果置0,加下一次数’ 29 * 也不需要考虑最小值的问题啦 30 * @param nums 31 * @return 32 */ 33 public static int maxSubArray2(int[] nums) { 34 int max = nums[0], tmp = max; 35 for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) { 36 if (tmp < 0) tmp = 0;//‘精髓’ 37 tmp += nums[i]; 38 max = Math.max(tmp, max); 39 } 40 return max; 41 } 42 43 public static void main(String[] args) { 44 int[] a = {-1,1}; 45 System.out.println(maxSubArray2(a)); 46 }
55. Jump Game
1 /** 2 * 题意:从a[0]开始跳转当前索引对应数值的步数,看能否跳到最后一步 解题方法:通过 3 * (i(当前索引)+nums[i](能跳转的最大长度))和当前索引进行比较;如果可达到的位置小于当前位置;则可以判断不可到达 4 * 5 * @param nums 6 * @return 7 */ 8 public static boolean canJump(int[] nums) { 9 int reachable = 0; 10 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { 11 if (i > reachable) { 12 return false; 13 } 14 // i(当前索引)+nums[i](能跳转的最大长度) 15 reachable = Math.max(reachable, i + nums[i]); 16 } 17 return true; 18 } 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 int[] nums = { 3, 2, 1, 0, 4 };// false 22 // int[] nums = { 2, 3, 1, 1, 4 };//true 23 canJump(nums); 24 }
75. Sort Colors
1 /** 2 * 题目:‘将红白蓝归类排序;其实就是012归类排序’ 3 * 解决方法:‘我这里用的冒泡排序,可以尝试一下别的排序方法’ 4 * @param nums 5 */ 6 public static void sortColors(int[] nums) { 7 //‘注意下标’ 8 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) { 9 //‘注意下标’ 10 for (int j = 0; j < nums.length - 1; j++) { 11 if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) { 12 int temp = nums[j]; 13 nums[j] = nums[j + 1]; 14 nums[j + 1] = temp; 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 int[] nums = { 2, 0, 2, 1, 1, 0 }; 22 sortColors(nums); 23 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { 24 System.out.println(nums[i]); 25 } 26 }

78. Subsets
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; /** * Given a set of distinct integers, nums, return all possible subsets (the * power set). * * Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets. * * Example: * * Input: nums = [1,2,3] Output: [ [3], [1], [2], [1,2,3], [1,3], [2,3], [1,2],[]] * *给予一个不重复的整数集合,返回所有的可能的子集 */ public class Lc78 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = new int[3]; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { nums[i] = i + 1; } for (List<Integer> lists : subsets2(nums)) { for (Integer i : lists) { System.out.print(i); } System.out.println(); } } /** * 利用深度优先搜索(dfs) */ private static List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>(); public static List<List<Integer>> subsets2(int[] nums) { dfs(nums, 0, new LinkedList<>()); return results; } private static void dfs(int[] nums, int start, LinkedList<Integer> list) { results.add(new ArrayList<>(list)); for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) { list.addLast(nums[i]); dfs(nums, i + 1, list); //遍历之后删除该节点避免重复 list.removeLast(); } } }

80. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II
1 public static int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
2 int count = 2;
3 for (int i = 2; i < nums.length; i++) {
4 if (nums[i] > nums[count - 2]) {
5 nums[count++] = nums[i];
6 }
7 }
8 return count;
9 }
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.List; 3 import java.util.Stack; 4 5 public class TreeNode { 6 int val; 7 TreeNode left; 8 TreeNode right; 9 10 TreeNode(int x) { 11 val = x; 12 } 13 14 /** 15 * 题目:‘有序遍历:给你一个二叉树,有序遍历他的节点;有序遍历意味着先便利左子树,之后依次倒叙遍历右子树; 16 * ’最好集合solution的动图,入栈出栈的形式更好理解 17 * 18 * ‘解决方法:利用入栈出栈的形式 19 * 20 * @param root 21 * @return 22 */ 23 public static List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { 24 List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 25 //声明一个栈来存取节点 26 Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>(); 27 TreeNode curr = root; 28 //如果节点没有遍历完或者说栈不为空就继续一下流程 29 while (curr != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { 30 //如果当前节点不为空,就继续将当前节点压入栈 31 while (curr != null) { 32 stack.push(curr); 33 curr = curr.left; 34 } 35 //如果当前节点为空,意味着左子树遍历完了,那就出栈存值,然后遍历当前节点的右子树 36 curr = stack.pop(); 37 res.add(curr.val); 38 curr = curr.right; 39 } 40 return res; 41 } 42 43 public static void main(String[] args) { 44 // [1,null,2,3] 45 TreeNode treeNode = new TreeNode(1); 46 TreeNode treeNode1 = new TreeNode(2); 47 TreeNode treeNode2 = new TreeNode(3); 48 treeNode.right = treeNode1; 49 treeNode1.left = treeNode2; 50 inorderTraversal(treeNode); 51 } 52 53 }
101. Symmetric Tree
1 public class TreeNode { 2 int val; 3 TreeNode left; 4 TreeNode right; 5 6 TreeNode(int x) { 7 val = x; 8 } 9 10 /** 11 * 题意:’判断给定的二叉树是不是对称的二叉树 12 * 解决方法:‘递归,理解简单。通过递归判断所有的节点是否对称; 13 * 思路:’将一个给定的二叉树‘复制一份’,从根节点开始,判断对应的节点(以根节点为对称轴)是否相同; 14 * @param t1 15 * @param t2 16 * @return 17 */ 18 public static boolean isMirro(TreeNode t1,TreeNode t2) { 19 if(t1 ==null && t2==null) { 20 return true; 21 } 22 if(t1 == null || t2 == null) { 23 return false; 24 } 25 //判断当前节点以及当前节点的左右树 26 return (t1.val == t2.val) && isMirro(t1.left, t2.right) && isMirro(t1.right, t2.left); 27 } 28 29 public static boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) { 30 return isMirro(root, root); 31 } 32 33 public static void main(String[] args) { 34 // [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 35 TreeNode t1 = new TreeNode(1); 36 TreeNode t2 = new TreeNode(2); 37 TreeNode t3 = new TreeNode(2); 38 TreeNode t4 = new TreeNode(3); 39 TreeNode t5 = new TreeNode(4); 40 TreeNode t6 = new TreeNode(4); 41 TreeNode t7 = new TreeNode(3); 42 t1.left = t2;t1.right = t3; 43 t2.left = t4;t2.right = t5; 44 t3.left = t6;t3.right = t7; 45 System.out.println(isSymmetric(t1)); 46 } 47 48 }
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
1 public class TreeNode { 2 int val; 3 TreeNode left; 4 TreeNode right; 5 6 TreeNode(int x) { 7 val = x; 8 } 9 10 /** 11 * 题意:遍历二叉树得到最大路径的长度 12 * 解题:遍历可以用递归或者是栈;这里用的是递归,栈我没用明白, 13 * @param root 14 * @return 15 */ 16 public static int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { 17 if(root == null) { 18 return 0; 19 } 20 return 1+Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)); 21 } 22 23 public static void main(String[] args) { 24 // [0,2,4,1,null,3,-1,5,1,null,6,null,8] 25 TreeNode t1 = new TreeNode(0); 26 TreeNode t2 = new TreeNode(2); 27 TreeNode t3 = new TreeNode(4); 28 TreeNode t4 = new TreeNode(1); 29 TreeNode t5 = new TreeNode(3); 30 TreeNode t6 = new TreeNode(-1); 31 TreeNode t7 = new TreeNode(5); 32 TreeNode t8 = new TreeNode(1); 33 TreeNode t9 = new TreeNode(6); 34 TreeNode t10 = new TreeNode(8); 35 t1.left = t2; 36 t1.right = t3; 37 t2.left = t4; 38 t4.left = t7; 39 t4.right = t8; 40 t3.left = t5; 41 t3.right = t6; 42 t5.left = t9; 43 t6.left = t10; 44 System.out.println(maxDepth(t1)); 45 } 46 47 }
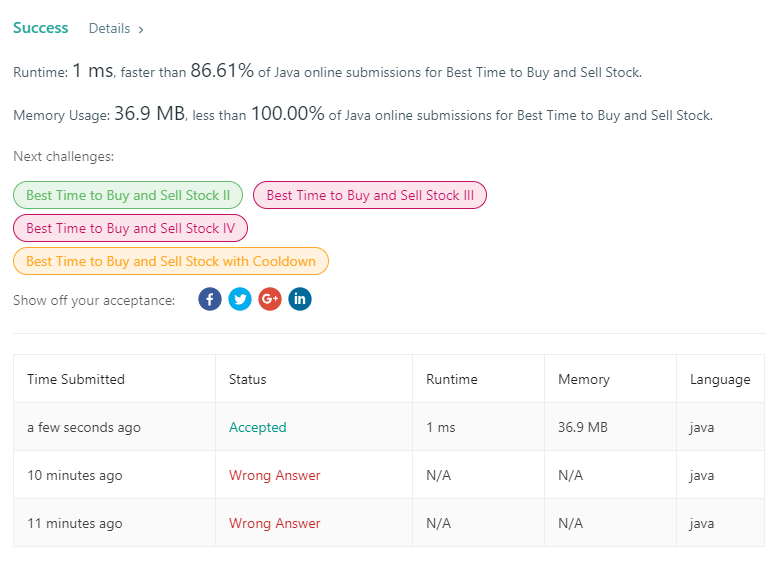
121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
1 public class oneHundredone { 2 /** 3 * 题目:卖股票 小卖大卖 4 * 解题方法:动态找到当前最小的,然后一次判断当前的最大利润 5 * @param prices 6 * @return 7 */ 8 public static int maxProfit(int prices[]) { 9 //初始化, 10 int minPrice = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 11 int maxProfit = 0; 12 for (int i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) { 13 //找到最小的买入值 14 minPrice = Math.min(minPrice, prices[i]); 15 //找到最大的卖出值 16 maxProfit = Math.max(maxProfit, prices[i] - minPrice); 17 } 18 return maxProfit; 19 20 } 21 22 public static void main(String[] args) { 23 int[] stock = { 7, 6, 4, 3, 1 }; 24 System.out.println(maxProfit(stock)); 25 } 26 27 }
136. Single Number
1 public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
2
3
4 Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
5
6 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
7 if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
8 map.remove(nums[i]);
9 } else {
10 map.put(nums[i], 1);
11 }
12
13 }
14
15 Integer result = 0;
16 for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
17 result = key;
18 break;
19 }
20
21 return result;
22
23
24 }
137. Single Number II
1 public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
2
3
4 Map<Integer, Boolean> map = new HashMap<Integer, Boolean>();
5
6 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
7 if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
8 map.put(nums[i], false);
9 } else {
10 map.put(nums[i], true);
11 }
12
13 }
14
15 List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
16 map.forEach((k, v) -> {
17 if (v) {
18 result.add(k);
19 }
20 });
21 return result.get(0);
22
23
24 }
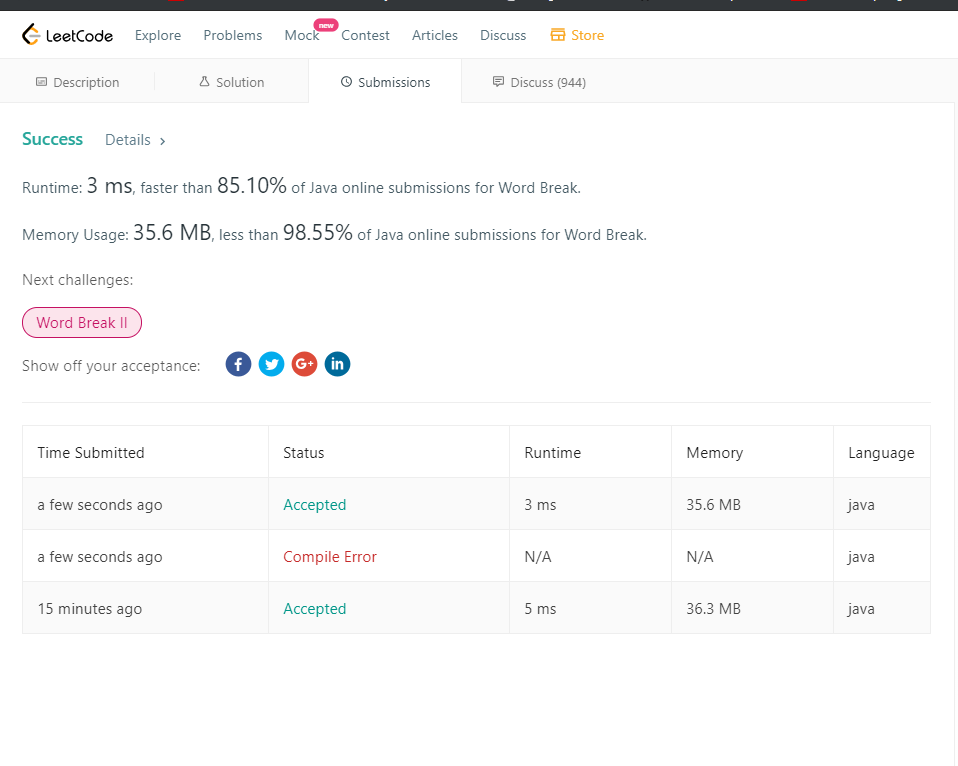
139. Word Break
1 import java.util.ArrayList;
2 import java.util.List;
3
4 /**
5 * 题意:根据给定的字典判断字符串是否可以完全根据字典拆解 思路:利用dp(动态规划:把问题分解成原子级别,求解每个问题的最优解,最后汇聚就是问题的最优解)
6 *
7 *
8 */
9 public class WordBreak {
10 /**
11 * dp1 比较容易理解
12 *
13 * 遍历给定字符串的每一个字符,和字典机型比较,如果符合条件(wordDict.contains(sub) && (j == 0 || dp[j -
14 * 1])),就将该位置设置成true 若遍历所有之后,dp的最后一位是true,代表字符串按照字段拆解完全
15 *
16 * @param s
17 * @param wordDict
18 * @return
19 */
20 public static boolean wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
21 if (s == null || "".equals(s)) {
22 return false;
23 }
24 int n = s.length();
25 boolean[] dp = new boolean[s.length()];
26 for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
27 for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
28 String sub = s.substring(j, i + 1);
29 if (wordDict.contains(sub) && (j == 0 || dp[j - 1])) {
30 dp[i] = true;
31 }
32 }
33 }
34 return dp[n - 1];
35 }
36
37 /**
38 * dp2
39 * 和dp1思路一样,只是优化了匹配过程,第二次直接遍历字段进行匹配,优化了3ms
40 * @param s
41 * @param wordDict
42 * @return
43 */
44 public static boolean wordBreak2(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
45 int n = s.length();
46 boolean[] dp = new boolean[n + 1];
47 dp[0] = true;
48 for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) {
49 for (String word : wordDict) {
50 int len = word.length();
51 if (i >= len && dp[i - len] && s.substring(i - len, i).equals(word)) {
52 dp[i] = true;
53 }
54 }
55 }
56 return dp[n];
57
58 }
59
60 /**
61 * dp3递归加dp,还没有完全理解,不过思路都很相似
62 * @param s
63 * @param wordDict
64 * @return
65 */
66 public static boolean wordBreak3(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
67 boolean[] memo = new boolean[s.length()];
68 return wordBreakHelper(s, wordDict, memo, 0);
69 }
70
71 public static boolean wordBreakHelper(String s, List<String> wordDict, boolean[] memo, int i) {
72 if (i >= s.length()) {
73 return true;
74 }
75 if (memo[i]) {
76 return false;
77 }
78 for (String word : wordDict) {
79 if (!s.startsWith(word, i)) {
80 continue;
81 }
82 boolean result = wordBreakHelper(s, wordDict, memo, i + word.length());
83 if (result) {
84 return true;
85 }
86 memo[i] = true;
87 }
88 return false;
89 }
90
91 public static void main(String[] args) {
92 String s = "leetcode";
93 List<String> dict = new ArrayList<String>();
94 dict.add("leet");
95 dict.add("code");
96 // System.out.println(wordBreak(s, dict));
97 System.out.println(wordBreak2(s, dict));
98 }
99 }
152. Maximum Product Subarray
1 /** 2 * Given an integer array nums, find the contiguous subarray within an array 3 * (containing at least one number) which has the largest product. 4 * 5 * 给一整数,求解最大的连续乘积,数组包含至少一个整数 6 * 7 */ 8 public class Lc152 { 9 /** 10 * 思路:dp 11 * 最优子结构,之前最大值乘当前值为最大值 12 * 边界值,初始值为nums[0] 13 *公式: 最大值 为 当前值 和 之前最大值乘以当前值 中的一个 14 * @param nums 15 * @return 16 */ 17 public static int maxProduct(int[] nums) { 18 if (nums.length == 1) { 19 return 0; 20 } 21 22 int max = nums[0]; 23 int dpMax = nums[0]; 24 int dpMin = nums[0]; 25 for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) { 26 dpMax = Math.max(nums[i], Math.max(dpMax * nums[i], dpMin * nums[i])); 27 dpMin = Math.min(nums[i], Math.min(dpMax * nums[i], dpMin * nums[i])); 28 max = Math.max(max, dpMax); 29 } 30 31 return max; 32 } 33 34 public static void main(String[] args) { 35 int[] nums = { 2, 3, -2, 4 }; 36 System.out.println(maxProduct(nums)); 37 } 38 }

167. Two Sum II - Input array is sorted
1 public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
2
3 int[] position = new int[2];
4 for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
5 for (int j = i + 1; j < numbers.length; j++) {
6 if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] == target) {
7 position[0] = ++i;
8 position[1] = ++j;
9 break;
10 }
11 }
12 }
13
14 return position;
15
16 }
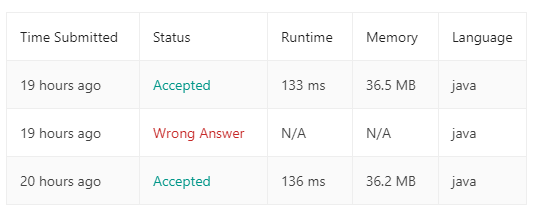
169. Majority Element
1 import java.util.Arrays; 2 3 public class majorityElement { 4 /** 5 * 题目: Given an array of size n, find the majority element. The majority element 6 * is the element that appears more than ⌊ n/2 ⌋ times. 7 * 8 * You may assume that the array is non-empty and the majority element always 9 * exist in the array. 10 * 11 * 解题: 利用测试用例数据 12 * 13 * @param nums 14 * @return 15 */ 16 public static int majorityElement(int[] nums) { 17 Arrays.sort(nums); 18 return nums[nums.length / 2]; 19 } 20 21 /** 22 * 摩尔投票 是你就给你加一,不是你就减一,如果你是0就替换 23 */ 24 public static int majorityElement2(int[] nums) { 25 int res = nums[0]; 26 int count = 1; 27 for (int i : nums) { 28 if (i == res) { 29 count++; 30 } else { 31 count--; 32 } 33 if (count == 0) { 34 res = i; 35 count++; 36 } 37 } 38 return res; 39 } 40 41 public static void main(String[] args) { 42 int a[] = { 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2 }; 43 // System.out.println(majorityElement(a)); 44 System.out.println(majorityElement2(a)); 45 } 46 47 }
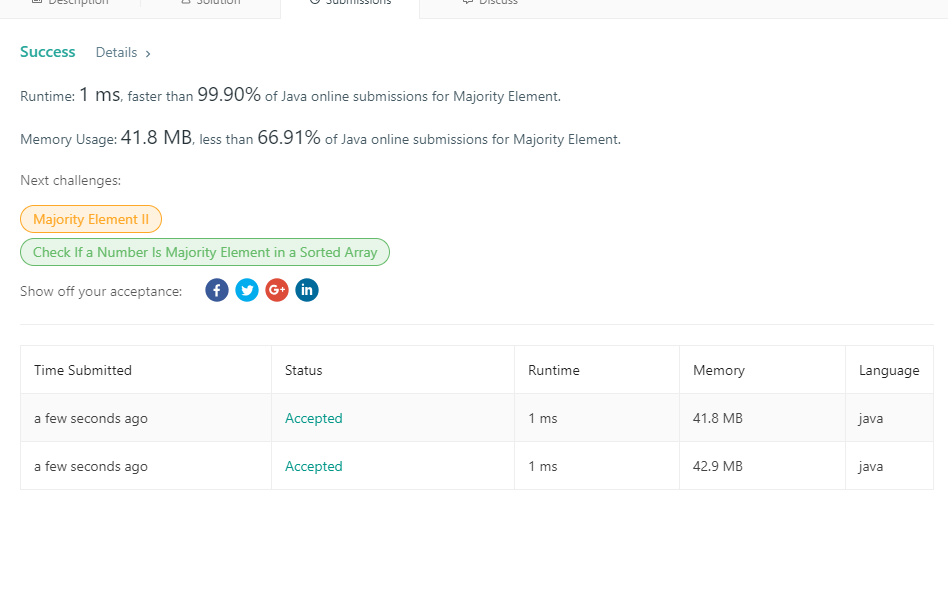
198. House Robber
/** * You are a professional robber planning to rob houses along a street. Each * house has a certain amount of money stashed, the only constraint stopping you * from robbing each of them is that adjacent houses have security system * connected and it will automatically contact the police if two adjacent houses * were broken into on the same night. * * Given a list of non-negative integers representing the amount of money of * each house, determine the maximum amount of money you can rob tonight without * alerting the police. * * @author 5109v12458 * */ public class HouseRobbe { /** * 每次求得的now都是相隔的俩个数相加 * @param nums * @return */ public static int rob(int[] nums) { int last = 0; int now = 0; int temp = 0; //an = (a(n-1)+n,an) for (int i : nums) { temp = now; now = Math.max(last + i, now); last = temp; } return now; } public static void main(String[] args) { int nums[] = { 1, 2, 4, 6 }; System.out.println(rob(nums)); } }

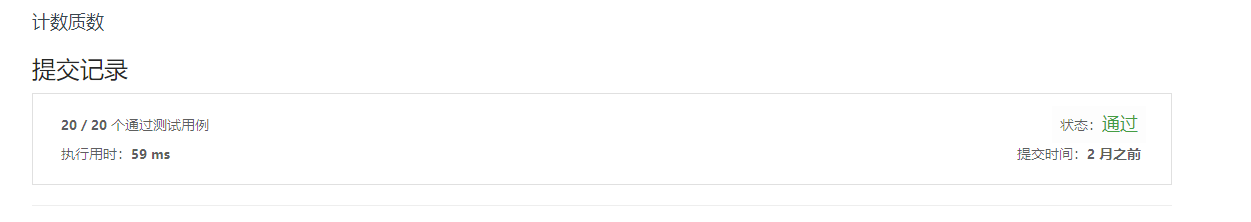
204. 计数质数
1 class Solution {
2 public int countPrimes(int n) {
3 int[] num = new int[n];
4
5 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
6 num[i] = 1;
7 }
8
9 for (int j = 2; j < n; j++) {
10 if (num[j] == 1) {
11 for (int k = 2; k * j < n; k++) {
12 num[j * k] = 0;
13 }
14 }
15 }
16 int sum = 0;
17 for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
18 if (num[i] == 1) {
19 sum++;
20 }
21 }
22 return sum;
23 }
24
25 }
206. Reverse Linked List
1 /** 2 * Reverse a singly linked list. 3 * 4 * Example: 5 * 6 * Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL Output: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL Follow up: 7 * 8 * A linked list can be reversed either iteratively or recursively. Could you 9 * implement both? 10 * 11 */ 12 public class ReverseLinkedList { 13 public static class ListNode { 14 int val; 15 ListNode next; 16 17 ListNode(int x) { 18 val = x; 19 } 20 } 21 22 /** 23 * 解法,通过另一条链表实现反转链表 24 * @param head 25 * @return 26 */ 27 public static ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { 28 ListNode prev = null; 29 ListNode curr = head; 30 while (curr != null) { 31 ListNode temp = curr.next; 32 /* 33 * 目的是将当前节点的下一个几点作为prev的上一个节点,当前节点作为prev的当前节点 34 * 其他的步骤就是单纯的置换 35 */ 36 curr.next = prev; 37 prev = curr; 38 curr = temp; 39 } 40 return prev; 41 } 42 43 public static void main(String[] args) { 44 ListNode node = new ListNode(0); 45 ListNode node1 = new ListNode(1); 46 ListNode node2 = new ListNode(2); 47 48 node.next = node1; 49 node1.next = node2; 50 51 reverseList(node); 52 } 53 }
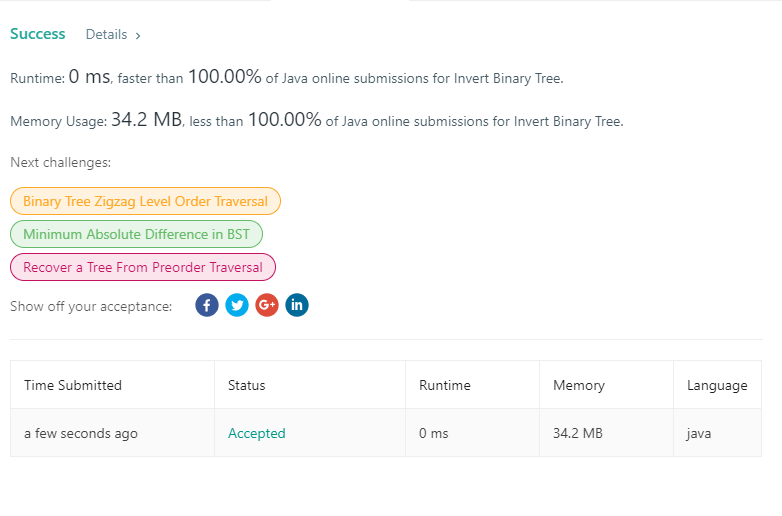
226. Invert Binary Tree
Invert a binary tree. Example: Input: 4 / 2 7 / / 1 3 6 9 Output: 4 / 7 2 / / 9 6 3 1
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. public class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode * left; TreeNode right; TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } } */ class Lc226 { public static class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } } /** * * 反转二叉树:先按照左子树反转,在右子树反转,在左右字数反转 * * @return */ public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return null; } TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left); TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right); root.left = right; root.right = left; return root; } }
260. Single Number III
1 public int[] singleNumber(int[] nums) {
2
3 Map<Integer, Boolean> map = new HashMap<Integer, Boolean>();
4
5 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
6 if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
7 map.put(nums[i], false);
8 } else {
9 map.put(nums[i], true);
10 }
11
12 }
13
14 List<Integer> resultTemp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
15
16 map.forEach((k, v) -> {
17 if (v) {
18 resultTemp.add(k);
19 }
20 });
21
22 int[] result = new int[resultTemp.size()];
23
24 for (int i = 0; i < resultTemp.size(); i++) {
25 result[i] = resultTemp.get(i);
26 }
27 return result;
28
29 }
283. Move Zeroes
1 public static void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
2 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
3 if (nums[i] != 0) {
4 continue;
5 } else {
6 int count = 0;
7 do {
8 swap(nums, i);//如果当前位置为0,则置换到最后一位
9 count++;
10 } while (nums[i] == 0 && count < nums.length - i);//如果当前位置是0,并且之前也没有0啦,则终止循环,终止条件有待优化
11 }
12 }
13 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
14 System.out.print(nums[i]);
15 }
16 }
17
18 public static void swap(int[] nums, int position) {//普通的置换算法,冒泡排序里的一段
19 for (int i = position; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
20 int temp = nums[i];
21 nums[i] = nums[i + 1];
22 nums[i + 1] = temp;
23 }
24 }
412. Fizz Buzz
1 class Solution {
2 public List<String> fizzBuzz(int n) {
3 List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
4 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
5 if (i % 3 == 0 && i % 5 == 0) {
6 result.add("FizzBuzz");
7 } else if (i % 3 == 0) {
8 result.add("Fizz");
9 } else if (i % 5 == 0) {
10 result.add("Buzz");
11 } else {
12 result.add("" + i);
13 }
14
15 }
16 return result;
17 }
18 }
448. Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array
1 public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
2
3
4 Map<Integer, Integer> numsMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
5 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
6 numsMap.put(nums[i], i);
7 }
8
9 // 1给定数组应该有的大小
10 int size = nums.length;
11
12 List<Integer> disappearedNumbers = new ArrayList<Integer>();
13 for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
14 if (!numsMap.containsKey(i)) {
15 disappearedNumbers.add(i);
16 }
17 }
18
19 return disappearedNumbers;
20
21 }

442. Find All Duplicates in an Array
1 public List<Integer> findDuplicates(int[] nums) {
2
3 // 1对于给定数组进行排序
4 Map<Integer, Integer> numsMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
5 for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
6 if(numsMap.containsKey(nums[i])) {
7 numsMap.put(nums[i], 2);
8 }else {
9 numsMap.put(nums[i], 1);
10 }
11 }
12
13 List<Integer> disappearedNumbers = new ArrayList<Integer>();
14 numsMap.forEach((k,v)->{
15 if(v==2) {
16 disappearedNumbers.add(k);
17 }
18 });
19
20 return disappearedNumbers;
21
22
23 }
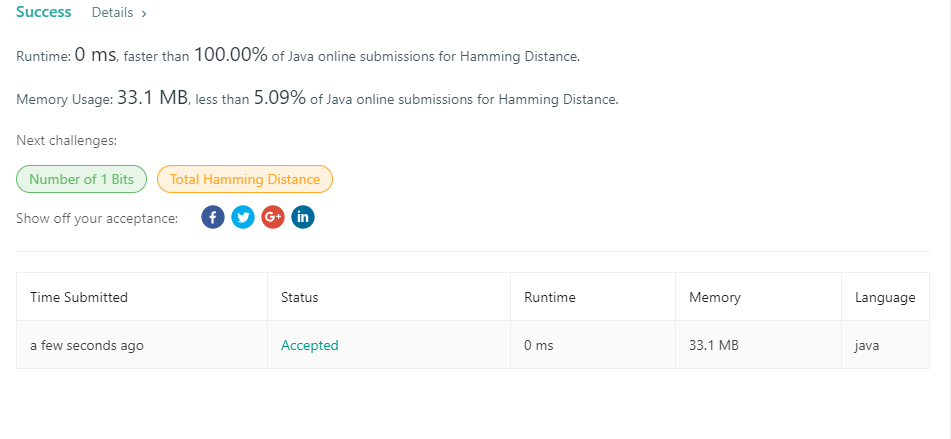
461. Hamming Distance
/** * Hamming Distance * * The Hamming distance between two integers is the number of positions at which * the corresponding bits are different. Given two integers x and y, calculate * the Hamming distance. * * 转换为2进制,有几个位置上的值不同,就叫做Hamming distance * */ public class Lc461 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(hammingDistance(1, 4)); } public static int hammingDistance(int x, int y) { int sum = x ^ y; int res = 0; res += sum % 2; sum /= 2; return res; } }
560. Subarray Sum Equals K
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** *找出最大连续子序列的个数 * */ public class Lc560 { /** * 如果存在 sum-k=subArrayCount,則存在对应count的连续子序列 * * @param nums * @param k * @return */ public static int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) { int count = 0; int sum = 0; Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();// map<sum,count(该sum-k出现的次数)> map.put(0, 1); for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { sum += nums[i]; if (map.containsKey(sum - k)) { count += map.get(sum - k); } map.put(sum, map.getOrDefault(sum, 0) + 1); } return count; } public static void main(String[] args) { int nums[] = { 3, 4, 7, 2, -3, 1, 4, 2 }; System.out.println(subarraySum(nums, 7)); } }
581. Shortest Unsorted Continuous Subarray
import java.util.Arrays; /* * 581. Shortest Unsorted Continuous Subarray * 题意:找出数组中需要排序的长度 * 难度:Easy * 分类:Array * 思路: * Tips:可以考虑八大排序 */ public class Lc581 { public static int findUnsortedSubarray(int[] nums) { int copyFromNums[] = new int[nums.length]; for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { copyFromNums[i] = nums[i]; } Arrays.sort(copyFromNums); int startPosition = 0; int endPosition = 0; for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { if (copyFromNums[i] != nums[i]) { startPosition = i; break; } } for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { if (copyFromNums[i] != nums[i]) { endPosition = i; } } int count = 0; if (endPosition != startPosition) { count = endPosition - startPosition + 1; } return count; } public static void main(String[] args) { int nums[] = { 2, 6, 4, 8, 10, 9, 15 }; System.out.println(findUnsortedSubarray(nums)); } }

617. Merge Two Binary Trees
1 /**
2 * 题意:将俩个二叉树及进行合并,如果同一位置节点都存在,则合并,否则旧直接放上去
3 * 思路:相同位置进行合并,有则相加,无责这届放上去,注意用递归
4 * @param t1
5 * @param t2
6 * @return
7 */
8 public static TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
9 if (t1 == null && t2 == null) {
10 return null;
11 }
12 if (t1 == null) {
13 return t2;
14 }
15 if (t2 == null) {
16 return t1;
17 }
18
19 TreeNode t = new TreeNode(t1.val + t2.val);
20 t.left = mergeTrees(t1.left, t2.left);
21 t.right = mergeTrees(t1.right, t2.right);
22 return t;
23 }
771. Jewels and Stones
public class Lc771 { public static int numJewelsInStones(String J, String S) { String[] strJ = convertToAscall(J); String[] strS = convertToAscall(S); int count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < strS.length; i++) { for (int k = 0; k < strJ.length; k++) { if (strS[i].equals(strJ[k])) { count++; break; } } } return count; } private static String[] convertToAscall(String s) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); for (char c : chars) { sb.append((int) c).append(","); } return sb.toString().split(","); } public static void main(String[] args) { String S = "aAAbbbddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddb"; String J = "addddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddddA"; System.out.println(numJewelsInStones(J, S)); } }