实验十六 线程技术
实验时间 2017-12-8
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握线程概念;
(2) 掌握线程创建的两种技术;
(3) 理解和掌握线程的优先级属性及调度方法;
(4) 掌握线程同步的概念及实现技术;
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:测试程序并进行代码注释。
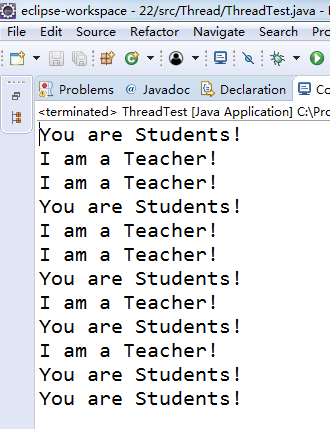
测试程序1:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行ThreadTest,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握线程概念;
l 掌握用Thread的扩展类实现线程的方法;
l 利用Runnable接口改造程序,掌握用Runnable接口创建线程的方法。
|
class Lefthand extends Thread { public void run() { for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) { System.out.println("You are Students!"); try{ sleep(500); } catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Lefthand error.");} } } } class Righthand extends Thread { public void run() { for(int i=0;i<=5;i++) { System.out.println("I am a Teacher!"); try{ sleep(300); } catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Righthand error.");} } } } public class ThreadTest { static Lefthand left; static Righthand right; public static void main(String[] args) { left=new Lefthand(); right=new Righthand(); left.start(); right.start(); } } |
package Thread; class Lefthand implements Runnable { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println("You are Students!"); try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Lefthand error."); } } } } class Righthand implements Runnable { public void run() { for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println("I am a Teacher!"); try { Thread.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Righthand error."); } } } } public class ThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { { Lefthand lefthand = new Lefthand(); //Runnable lefthand=new Lefthand(); Thread t=new Thread(lefthand); t.start(); Runnable righthand=new Righthand(); Thread t1=new Thread(righthand); t1.start(); } } }
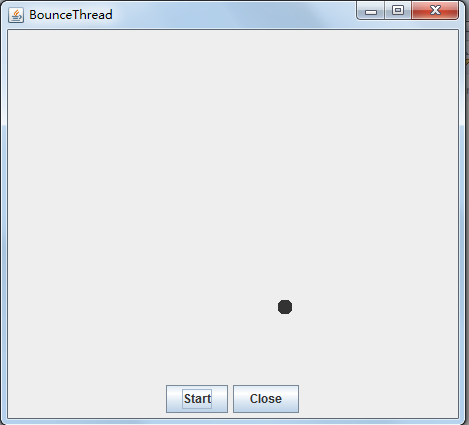
测试程序2:
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材625页程序14-1、14-2 、14-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材631页程序14-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 对比两个程序,理解线程的概念和用途;
l 掌握线程创建的两种技术。
第一个程序:必须运行结束以后才能关闭;
第二个程序:随时可以关闭;
测试程序3:分析以下程序运行结果并理解程序。
|
class Race extends Thread { public static void main(String args[]) { Race[] runner=new Race[4]; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) runner[i]=new Race( ); for(int i=0;i<4;i++) runner[i].start( ); runner[1].setPriority(MIN_PRIORITY); runner[3].setPriority(MAX_PRIORITY);} public void run( ) { for(int i=0; i<1000000; i++); System.out.println(getName()+"线程的优先级是"+getPriority()+"已计算完毕!"); } } |

package x; class Race extends Thread { public static void main(String args[]) { Race[] runner=new Race[4]; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) runner[i]=new Race( ); for(int i=0;i<4;i++) runner[i].start( ); runner[0].setPriority(MIN_PRIORITY); runner[3].setPriority(MAX_PRIORITY);} public void run( ) { for(int i=0; i<1000000; i++);//起延时作用 // 为了使其延时到( runner[0].setPriority(MIN_PRIORITY);runner[3].setPriority(MAX_PRIORITY);}) System.out.println(getName()+"线程的优先级是"+getPriority()+"已计算完毕!"); } }
测试程序4
l 教材642页程序模拟一个有若干账户的银行,随机地生成在这些账户之间转移钱款的交易。每一个账户有一个线程。在每一笔交易中,会从线程所服务的账户中随机转移一定数目的钱款到另一个随机账户。
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材642页程序14-5、14-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
综合编程练习
编程练习1
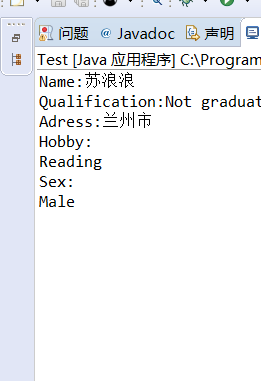
- 1. 设计一个用户信息采集程序,要求如下:
(1) 用户信息输入界面如下图所示:
(2) 用户点击提交按钮时,用户输入信息显示控制台界面;
(3) 用户点击重置按钮后,清空用户已输入信息;
(4) 点击窗口关闭,程序退出。
package a; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.event.*; public class Frame extends JFrame { private JPanel panel; private JPanel panel1; private JPanel panel2; private JPanel spanel2; private JPanel buttonPanel; private JComboBox<String> faceCombo; private JCheckBox Reading; private JCheckBox Singing; private JCheckBox Dancing; private JPanel panelDanXuan; private ButtonGroup option; private JRadioButton optionA; private JRadioButton optionB; private static final int DEFAULT_WITH = 750; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 350; public Frame() { panel = new JPanel(); panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,4)); //框架a panel1 = new JPanel(); panel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(300,80)); JLabel lab = new JLabel("Name: ", JLabel.CENTER); final JTextField jt = new JTextField(); JLabel lab1 = new JLabel("Qualification: ", JLabel.CENTER); faceCombo = new JComboBox<>(); faceCombo.addItem("Graduate"); faceCombo.addItem("Not graduated"); //b panel1 = new JPanel(); panel1.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(300,100)); JLabel lab2 = new JLabel("Adress: ", JLabel.CENTER); final JTextArea jt1 = new JTextArea(); JLabel lab3 = new JLabel("Hobby: ", JLabel.CENTER); panel2 = new JPanel(); panel2.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(220,20)); Reading = new JCheckBox("Reading"); Singing = new JCheckBox("Singing"); Dancing = new JCheckBox("Dancing "); //框架c spanel2 = new JPanel(); JLabel lab4 = new JLabel(" Sex: ", JLabel.CENTER); spanel2.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(300,60)); panelDanXuan = new JPanel(); option = new ButtonGroup(); optionA = new JRadioButton("Male"); optionB = new JRadioButton("Female"); //框架d buttonPanel = new JPanel(); buttonPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(0,50)); JButton jButton1 = new JButton("Validate"); JButton jButton2 = new JButton("Reset"); panel.add(lab); panel.add(jt); panel.add(lab1); panel.add(faceCombo); panel.add(lab2); panel.add(jt1); panel.add(lab3); panel2.add(Reading); panel2.add(Singing); panel2.add(Dancing); panel2.setLayout(new BoxLayout(panel2, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS)); panel.add(panel2); spanel2.add(lab4); option.add(optionA); option.add(optionB); panelDanXuan.add(optionA); panelDanXuan.add(optionB); panelDanXuan.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("")); panelDanXuan.setLayout(new BoxLayout(panelDanXuan, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS)); spanel2.add(panelDanXuan); buttonPanel.add(jButton1); buttonPanel.add(jButton2); add(panel, BorderLayout.NORTH); add(panel1, BorderLayout.CENTER); add(panel2, BorderLayout.EAST); add(spanel2, BorderLayout.WEST); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); setSize(DEFAULT_WITH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); jButton1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { String Name = jt.getText(); if (Name != null) { System.out.println("Name:"+Name); } String m = faceCombo.getSelectedItem().toString(); System.out.println("Qualification:"+m); String Adress = jt1.getText(); if (Adress != null) { System.out.println("Adress:"+Adress); } System.out.println("Hobby:"); if(Reading.isSelected()) { System.out.println(Reading.getText()); } if(Singing.isSelected()) { System.out.println(Singing.getText()); } if(Dancing.isSelected()) { System.out.println(Dancing.getText()); } System.out.println("Sex:"); if(optionA.isSelected()) { System.out.println(optionA.getText()); } if(optionB.isSelected()) { System.out.println(optionB.getText()); } } }); jButton2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { jt.setText(""); jt1.setText(""); faceCombo.setSelectedItem("Graduate"); Reading.setSelected(false); Singing.setSelected(false); Dancing.setSelected(false); option.clearSelection(); } }); } }
package a; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { Frame frame = new Frame(); frame.setTitle("Student Detail"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); frame.setResizable(false); }); } }

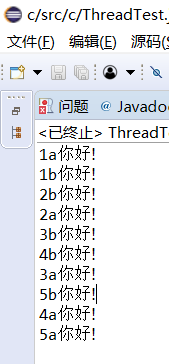
2.创建两个线程,每个线程按顺序输出5次“你好”,每个“你好”要标明来自哪个线程及其顺序号。
package c; import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.EventQueue; import java.awt.Toolkit; import javax.swing.JFrame; class Lefthand implements Runnable { public void run() { for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println(i+"a"+"你好!"); try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Lefthand error."); } } } } class Righthand implements Runnable { public void run() { for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { System.out.println(i+"b"+"你好!"); try { Thread.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Righthand error."); } } } } public class ThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { { Lefthand lefthand = new Lefthand(); //Runnable lefthand=new Lefthand(); Thread t=new Thread(lefthand); t.start(); Runnable righthand=new Righthand(); Thread t1=new Thread(righthand); t1.start(); } } }
3. 完善实验十五 GUI综合编程练习程序。
package c; import java.awt.Font; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Scanner; import javax.swing.*; import java.math.*; public class D extends JFrame { private String[] c=new String[10]; private String[] c1=new String[11]; private int[] list=new int[10]; int i=0,i1=0,sum = 0; private PrintWriter out = null; private JTextArea text,text1; private int counter; public D() { JPanel Panel = new JPanel();Panel.setLayout(null); JLabel JLabel1=new JLabel("...");JLabel1.setBounds(500, 800, 400, 30);JLabel1.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35)); JButton Button = new JButton("题目");Button.setBounds(50,150,150,50);Button.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20)); Button.addActionListener(new Action()); JButton Button2 = new JButton("确定");Button2.setBounds(300,150,150,50);Button2.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20));Button2.addActionListener(new Action1()); JButton Button3 = new JButton("读出文件");Button3.setBounds(500,150,150,50);Button3.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20));Button3.addActionListener(new Action2()); text=new JTextArea(30,80);text.setBounds(30, 50, 200, 50);text.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35)); text1=new JTextArea(30,80);text1.setBounds(270, 50, 200, 50);text1.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35)); Panel.add(text); Panel.add(text1); Panel.add(Button); Panel.add(Button2); Panel.add(Button3); Panel.add(JLabel1); add(Panel); } private class Action implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { text1.setText("0"); if(i<11) { int a = 1+(int)(Math.random() * 99); int b = 1+(int)(Math.random() * 99); int m= (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3); switch(m) { case 1: while(a<b){ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } c[i]=((i+1)+":"+a+"/"+b+"="); list[(i+1)]=Math.floorDiv(a, b); text.setText((i+1)+":"+a+"/"+b+"="); i++; break; case 2: c[i]=((i+1)+":"+a+"*"+b+"="); list[(i+1)]=Math.multiplyExact(a, b); text.setText((i+1)+":"+a+"*"+b+"="); i++; break; case 3: c[i]=((i+1)+":"+a+"+"+b+"="); list[(i+1)]=Math.addExact(a, b); text.setText((i+1)+":"+a+"+"+b+"="); i++; break ; case 4: while(a<=b){ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } c[i]=((i+1)+":"+a+"-"+b+"="); text.setText((i+1)+":"+a+"-"+b+"="); list[(i+1)]=Math.subtractExact(a, b); i++; break ; } } } } private class Action1 implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { if(i<10) { String daan=text1.getText().toString().trim(); int a = Integer.parseInt(daan); if(text1.getText()!=" ") { if(list[i1]==a) sum+=10; } c1[i1]=daan; i1++; } } } private class Action2 implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { try { out = new PrintWriter("text.txt"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } for(int counter=0;counter<10;counter++) { out.println(c[counter]+c1[counter]); } out.println("成绩"+sum); out.close(); } } }
package c; import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.EventQueue; import java.awt.Toolkit; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class N { public static void main (String args[]) { Toolkit t=Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit(); Dimension s=t.getScreenSize(); EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new D(); frame.setBounds(0, 0,(int)s.getWidth()/2,(int)s.getHeight()/2); frame.setTitle("大师"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }
加减乘除的代码完善。
实验总结: 这个周知道了什么 是线程、 掌握了线程创建的两种技术(继承Thread类、实现步骤:1.自定义类继承Thread 2.覆盖Thread中的run()方法3.创建该类的对象,调用start()方法,开启线程并调用run方法。
这个周知道了什么 是线程、 掌握了线程创建的两种技术(继承Thread类、实现步骤:1.自定义类继承Thread 2.覆盖Thread中的run()方法3.创建该类的对象,调用start()方法,开启线程并调用run方法。
理解和掌握线程的优先级属性及调度方法:线程的调度策略分为3个:SCHED_OTHER,SCHED_FIFO,SCHED_RR。
掌握线程同步的概念及实现技术:线程“同步”(也叫线程“并发”)指多个线程访问同一份资源时,需要确保这份资源的安全;
1:同步方法------在方法名前加关键字synchronized
2:同步块-------即synchronized{……}
大概就这么多的东西吧!练习二在室友的帮助下也基本完成了,但并未达到样图所示 嗯差不多了,完了。
嗯差不多了,完了。