ServerBootstrapAcceptor
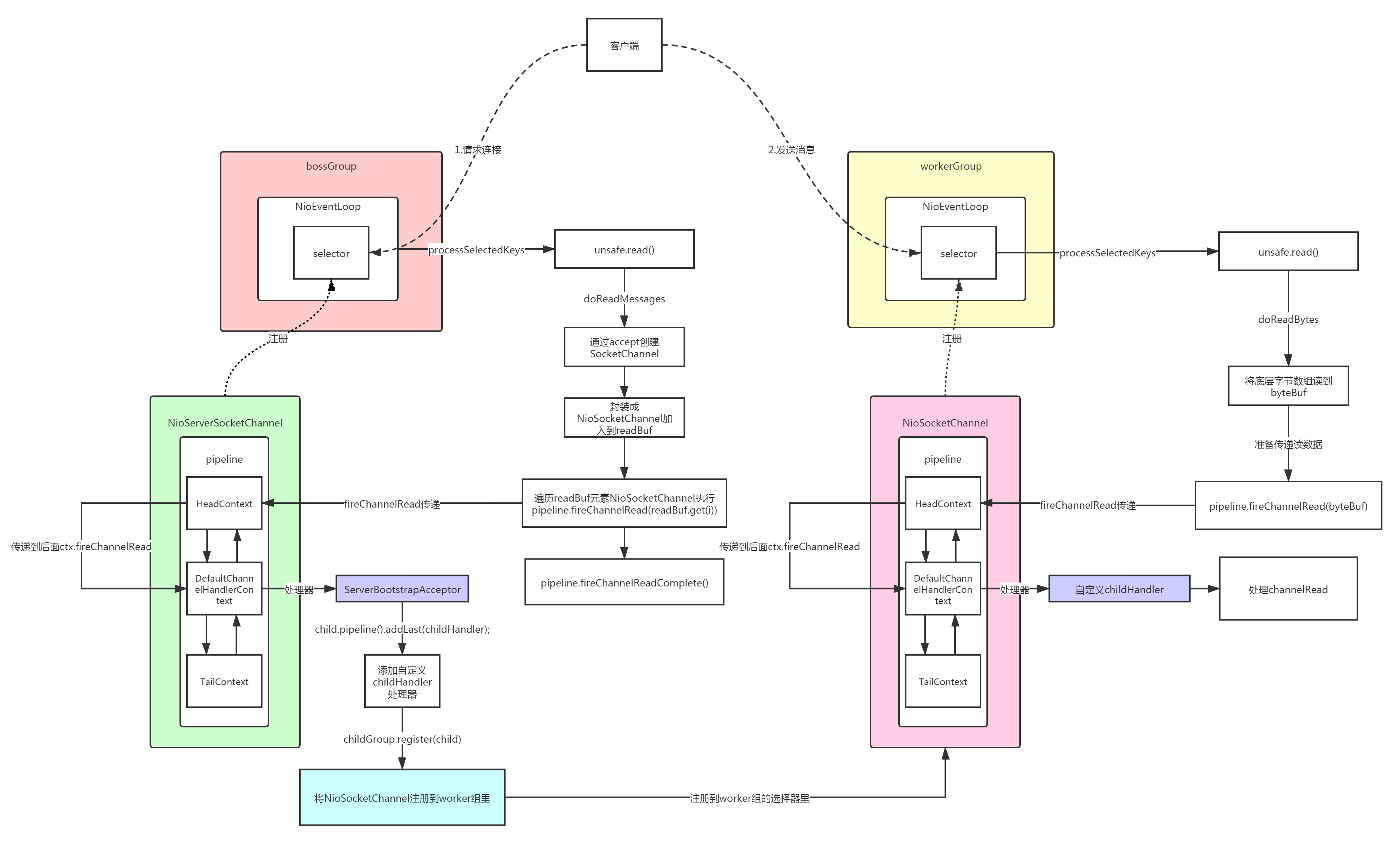
书接上文,讲到SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();即NioEventLoop.run()方法。
服务器启动后,等待事件,如果有连接事件,strategy为1。就会去执行processSelectedKeys方法。
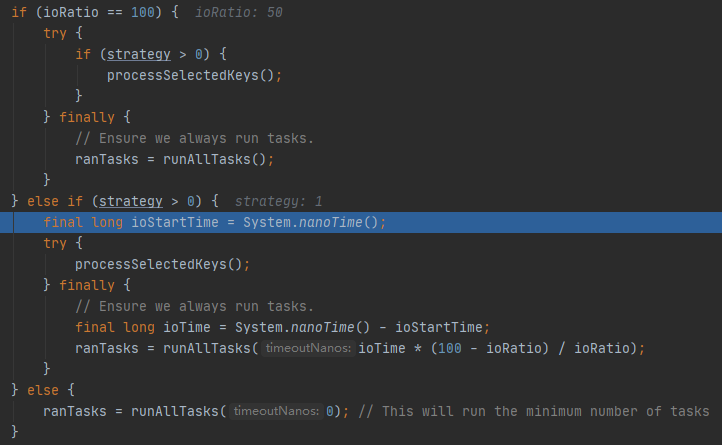
这里的selectedKeys是做了封装的,类型是SelectedSelectionKeySet,方便操作。
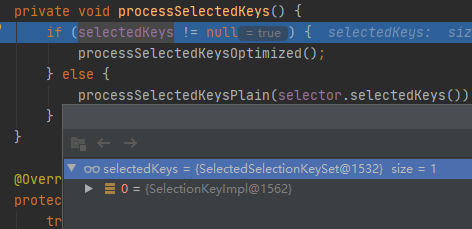
processSelectedKeysOptimized();
private void processSelectedKeysOptimized() { for (int i = 0; i < selectedKeys.size; ++i) { final SelectionKey k = selectedKeys.keys[i]; // null out entry in the array to allow to have it GC'ed once the Channel close // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2363 selectedKeys.keys[i] = null;//拿出来后设为null一旦通道关闭就可以释放,否则可能内存泄露 final Object a = k.attachment();//从附件中获得通道 if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) { processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);//处理key } else { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask<SelectableChannel>) a; processSelectedKey(k, task); } if (needsToSelectAgain) { // null out entries in the array to allow to have it GC'ed once the Channel close // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2363 selectedKeys.reset(i + 1); selectAgain(); i = -1; } } }
processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);
找到读或者事件,然后读取数据,这里的unsafe是io.netty.channel.nio.AbstractNioMessageChannel.NioMessageUnsafe类型,通道创建的时候创建的。
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) { final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe(); if (!k.isValid()) { final EventLoop eventLoop; try { eventLoop = ch.eventLoop(); } catch (Throwable ignored) { // If the channel implementation throws an exception because there is no event loop, we ignore this // because we are only trying to determine if ch is registered to this event loop and thus has authority // to close ch. return; } // Only close ch if ch is still registered to this EventLoop. ch could have deregistered from the event loop // and thus the SelectionKey could be cancelled as part of the deregistration process, but the channel is // still healthy and should not be closed. // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/5125 if (eventLoop == this) { // close the channel if the key is not valid anymore unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise()); } return; } try { int readyOps = k.readyOps(); // We first need to call finishConnect() before try to trigger a read(...) or write(...) as otherwise // the NIO JDK channel implementation may throw a NotYetConnectedException. if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) { // remove OP_CONNECT as otherwise Selector.select(..) will always return without blocking // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/924 int ops = k.interestOps(); ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT; k.interestOps(ops); unsafe.finishConnect(); } // Process OP_WRITE first as we may be able to write some queued buffers and so free memory. if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) { // Call forceFlush which will also take care of clear the OP_WRITE once there is nothing left to write ch.unsafe().forceFlush(); } // Also check for readOps of 0 to workaround possible JDK bug which may otherwise lead // to a spin loop if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) { unsafe.read(); } } catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) { unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise()); } }
NioMessageUnsafe.read();
public void read() { assert eventLoop().inEventLoop(); final ChannelConfig config = config(); final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline(); final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle();//缓冲区分配器 allocHandle.reset(config); boolean closed = false; Throwable exception = null; try { try { do { int localRead = doReadMessages(readBuf);//读取连接的数据到readBuf,封装为NioSocketChannel,进行管道的事件传递 if (localRead == 0) { break; } if (localRead < 0) { closed = true; break; } allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead);//总共消息数+1 } while (allocHandle.continueReading()); } catch (Throwable t) { exception = t; } int size = readBuf.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) { readPending = false; pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));//遍历传播读事件,参数是NioSocketChannel } readBuf.clear(); allocHandle.readComplete(); pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();//传播读完成事件 if (exception != null) { closed = closeOnReadError(exception); pipeline.fireExceptionCaught(exception); } if (closed) { inputShutdown = true; if (isOpen()) { close(voidPromise()); } } } finally { // Check if there is a readPending which was not processed yet. // This could be for two reasons: // * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelRead(...) method // * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelReadComplete(...) method // // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2254 if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) { removeReadOp(); } } }
NioServerSocketChannel.doReadMessages(List<Object> buf);
protected int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception { SocketChannel ch = SocketUtils.accept(javaChannel());//进行接收,返回SocketChannel try { if (ch != null) { buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));//创建NioSocketChannel return 1; } } catch (Throwable t) { logger.warn("Failed to create a new channel from an accepted socket.", t); try { ch.close(); } catch (Throwable t2) { logger.warn("Failed to close a socket.", t2); } } return 0; }
SocketUtils.accept(final ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel);
public static SocketChannel accept(final ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel) throws IOException { try { return AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<SocketChannel>() { @Override public SocketChannel run() throws IOException { return serverSocketChannel.accept(); } }); } catch (PrivilegedActionException e) { throw (IOException) e.getCause(); } }
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i))
管道传递读事件,参数就是刚封装的NioSocketChannel,首先调用了通道上下文的invokeChannelRead方法,传入了头上下文head,也就是初始化时候的HeadContext,也就是从头开始传递。
public final ChannelPipeline fireChannelRead(Object msg) { AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRead(head, msg); return this; }
AbstractChannelHandlerContext的invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg)
可以传入上下文对象和消息体,让上下文对象去传递消息体。
static void invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg) { final Object m = next.pipeline.touch(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(msg, "msg"), next);//看msg是不是引用计数接口ReferenceCounted类型,不是就直接返回msg,其实是做资源泄露检测 EventExecutor executor = next.executor();//获取next的执行器,如果为null就是通道的NioEventLoop if (executor.inEventLoop()) { next.invokeChannelRead(m);//如果执行器线程就是当前线程,就调用invokeChannelRead,传入NioSocketChannel } else { executor.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { next.invokeChannelRead(m); } }); } }
HeadContext的invokeChannelRead(Object msg)
直接的上下文对象传递消息体。
private void invokeChannelRead(Object msg) { if (invokeHandler()) {//是否已经被添加到管道 try { ((ChannelInboundHandler) handler()).channelRead(this, msg);//调用处理器的channelRead方法 } catch (Throwable t) { invokeExceptionCaught(t); } } else { fireChannelRead(msg);//直接传递到下一个可以处理消息的通道上下文 } }
handler();

HeadContext的channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
直接调用父类的方法,传递到下一个去:
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);//直接传递到下一个可以处理消息的通道上下文 }
AbstractChannelHandlerContext的fireChannelRead(final Object msg)
public ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRead(final Object msg) { invokeChannelRead(findContextInbound(MASK_CHANNEL_READ), msg); return this; }
AbstractChannelHandlerContext的findContextInbound(int mask)
mask为标记位,响应不同的事件。
// Using to mask which methods must be called for a ChannelHandler. static final int MASK_EXCEPTION_CAUGHT = 1; static final int MASK_CHANNEL_REGISTERED = 1 << 1; static final int MASK_CHANNEL_UNREGISTERED = 1 << 2; static final int MASK_CHANNEL_ACTIVE = 1 << 3; static final int MASK_CHANNEL_INACTIVE = 1 << 4; static final int MASK_CHANNEL_READ = 1 << 5; static final int MASK_CHANNEL_READ_COMPLETE = 1 << 6; static final int MASK_USER_EVENT_TRIGGERED = 1 << 7; static final int MASK_CHANNEL_WRITABILITY_CHANGED = 1 << 8; static final int MASK_BIND = 1 << 9; static final int MASK_CONNECT = 1 << 10; static final int MASK_DISCONNECT = 1 << 11; static final int MASK_CLOSE = 1 << 12; static final int MASK_DEREGISTER = 1 << 13; static final int MASK_READ = 1 << 14; static final int MASK_WRITE = 1 << 15; static final int MASK_FLUSH = 1 << 16; static final int MASK_ONLY_INBOUND = MASK_CHANNEL_REGISTERED | MASK_CHANNEL_UNREGISTERED | MASK_CHANNEL_ACTIVE | MASK_CHANNEL_INACTIVE | MASK_CHANNEL_READ | MASK_CHANNEL_READ_COMPLETE | MASK_USER_EVENT_TRIGGERED | MASK_CHANNEL_WRITABILITY_CHANGED; private static final int MASK_ALL_INBOUND = MASK_EXCEPTION_CAUGHT | MASK_ONLY_INBOUND;//入站总mask static final int MASK_ONLY_OUTBOUND = MASK_BIND | MASK_CONNECT | MASK_DISCONNECT | MASK_CLOSE | MASK_DEREGISTER | MASK_READ | MASK_WRITE | MASK_FLUSH; private static final int MASK_ALL_OUTBOUND = MASK_EXCEPTION_CAUGHT | MASK_ONLY_OUTBOUND;//出站总mask
skipContext
private static boolean skipContext( AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx, EventExecutor currentExecutor, int mask, int onlyMask) { // Ensure we correctly handle MASK_EXCEPTION_CAUGHT which is not included in the MASK_EXCEPTION_CAUGHT return (ctx.executionMask & (onlyMask | mask)) == 0 || // We can only skip if the EventExecutor is the same as otherwise we need to ensure we offload // everything to preserve ordering. // // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/10067 (ctx.executor() == currentExecutor && (ctx.executionMask & mask) == 0); }
executionMask在通道上下文初始化的时候创建
AbstractChannelHandlerContext(DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline, EventExecutor executor, String name, Class<? extends ChannelHandler> handlerClass) { this.name = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(name, "name"); this.pipeline = pipeline; this.executor = executor; this.executionMask = mask(handlerClass); // Its ordered if its driven by the EventLoop or the given Executor is an instanceof OrderedEventExecutor. ordered = executor == null || executor instanceof OrderedEventExecutor; }
mask(handlerClass)
static int mask(Class<? extends ChannelHandler> clazz) { // Try to obtain the mask from the cache first. If this fails calculate it and put it in the cache for fast // lookup in the future. Map<Class<? extends ChannelHandler>, Integer> cache = MASKS.get(); Integer mask = cache.get(clazz); if (mask == null) { mask = mask0(clazz); cache.put(clazz, mask); } return mask; }
mask0(clazz)
最终处理方法,默认入站和出站是全部的标记
private static int mask0(Class<? extends ChannelHandler> handlerType) { int mask = MASK_EXCEPTION_CAUGHT; try { if (ChannelInboundHandler.class.isAssignableFrom(handlerType)) { mask |= MASK_ALL_INBOUND; if (isSkippable(handlerType, "channelRegistered", ChannelHandlerContext.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_CHANNEL_REGISTERED; } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "channelUnregistered", ChannelHandlerContext.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_CHANNEL_UNREGISTERED; } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "channelActive", ChannelHandlerContext.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_CHANNEL_ACTIVE; } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "channelInactive", ChannelHandlerContext.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_CHANNEL_INACTIVE; } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "channelRead", ChannelHandlerContext.class, Object.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_CHANNEL_READ; } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "channelReadComplete", ChannelHandlerContext.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_CHANNEL_READ_COMPLETE; } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "channelWritabilityChanged", ChannelHandlerContext.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_CHANNEL_WRITABILITY_CHANGED; } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "userEventTriggered", ChannelHandlerContext.class, Object.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_USER_EVENT_TRIGGERED; } } if (ChannelOutboundHandler.class.isAssignableFrom(handlerType)) { mask |= MASK_ALL_OUTBOUND; if (isSkippable(handlerType, "bind", ChannelHandlerContext.class, SocketAddress.class, ChannelPromise.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_BIND; } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "connect", ChannelHandlerContext.class, SocketAddress.class, SocketAddress.class, ChannelPromise.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_CONNECT; } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "disconnect", ChannelHandlerContext.class, ChannelPromise.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_DISCONNECT; } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "close", ChannelHandlerContext.class, ChannelPromise.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_CLOSE; } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "deregister", ChannelHandlerContext.class, ChannelPromise.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_DEREGISTER; } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "read", ChannelHandlerContext.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_READ; } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "write", ChannelHandlerContext.class, Object.class, ChannelPromise.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_WRITE; } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "flush", ChannelHandlerContext.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_FLUSH; } } if (isSkippable(handlerType, "exceptionCaught", ChannelHandlerContext.class, Throwable.class)) { mask &= ~MASK_EXCEPTION_CAUGHT; } } catch (Exception e) { // Should never reach here. PlatformDependent.throwException(e); } return mask; }
isSkippable是个判断函数,是否要略过,根据反射出的方法和类的标注,声明了Skip标注,才会去除某个mask事件
private static boolean isSkippable( final Class<?> handlerType, final String methodName, final Class<?>... paramTypes) throws Exception { return AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Boolean>() { @Override public Boolean run() throws Exception { Method m; try { m = handlerType.getMethod(methodName, paramTypes); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug( "Class {} missing method {}, assume we can not skip execution", handlerType, methodName, e); } return false; } return m != null && m.isAnnotationPresent(Skip.class); } }); }
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.findContextInbound(int mask)
寻找下一个能不能处理这个事件的入站上下文,找不到就返回自己。
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextInbound(int mask) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
EventExecutor currentExecutor = executor();
do {
ctx = ctx.next;
} while (skipContext(ctx, currentExecutor, mask, MASK_ONLY_INBOUND));//寻找下一个能处理相应事件的
return ctx;
}
executor()
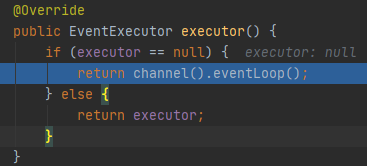
这里就会去找HeadContext的下一个,也就是我们放进去的含有ServerBootstrapAcceptor的上下文DefaultChannelHandlerContext。继续执行AbstractChannelHandlerContext的invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg)方法。next为DefaultChannelHandlerContext。执行DefaultChannelHandlerContext的invokeChannelRead(Object msg)方法。这次处理器为ServerBootstrapAcceptor。
ServerBootstrapAcceptor的channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
这里就是将NioSocketChannel注册到worker组。
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { final Channel child = (Channel) msg;//得到NioSocketChannel child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);//在得到NioSocketChannel的管道中添加我们自定义的初始化处理器 setChannelOptions(child, childOptions, logger);//设置选项 setAttributes(child, childAttrs);//设置属性 try {//向workerGroupt注册NioSocketChannel并添加完成监听 childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { if (!future.isSuccess()) { forceClose(child, future.cause()); } } }); } catch (Throwable t) { forceClose(child, t); } }
boss组接受连接的事结束,后续就是work组了。