Object类型的Equals,ReferenceEquals都有2个方法,静态方法和实例方法,两者的功能一样,只是实例方法要求实例不能为null。
比如 a.Equal(b)要求a不为null,object.Equal(a,b)则没有。
静态方法最终还是通过实例方法来实现的
1. ReferneceEqual
专用于引用类型的比较
对于值类型返回的永远是false
对于引用类型,会比较他们的引用是否相等,假如相等,返回true,否则返回false
对于string类型,也是比较其引用
2. Equal
对于值类型,先比较他们的类型,假如类型不同,返回false,假如类型相同则比较值,假如值相同返回true,不同返回false
对于引用类型,比较他们的引用是否相等,假如相等,返回true,否则返回false
对于string,Equal已经被改写,只会比较它们的值是否相等,不会比较引用
同样的,string.Equal(a1,a2)也是比较值是否相等
3. ==
对于值类型,先比较他们的类型,假如类型不同,就转换成同一类型,然后再比较值
对于引用类型,比较引用,等效于ReferenceEqual
对于string==已经被改写,只会比较它们的值是否相等,不会比较引用
4.泛型反射
对于获取类型的属性,使用getValue获取的属性是对类实例的引用,不管是使用==、Equal、ReferenceEqual都是跟原实例的属性相同
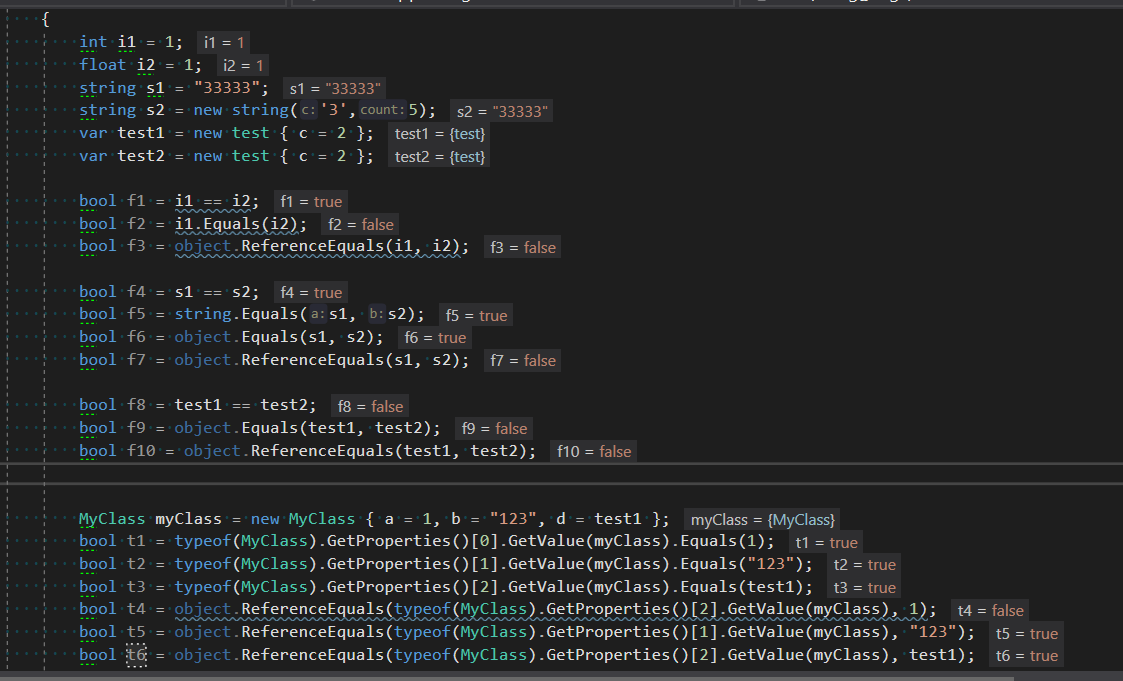
下面查看示例代码

1 class Program 2 { 3 static void Main(string[] args) 4 { 5 int i1 = 1; 6 float i2 = 1; 7 string s1 = "33333"; 8 string s2 = new string('3',5); 9 var test1 = new test { c = 2 }; 10 var test2 = new test { c = 2 }; 11 12 bool f1 = i1 == i2; 13 bool f2 = i1.Equals(i2); 14 bool f3 = object.ReferenceEquals(i1, i2); 15 16 bool f4 = s1 == s2; 17 bool f5 = string.Equals(s1, s2); 18 bool f6 = object.Equals(s1, s2); 19 bool f7 = object.ReferenceEquals(s1, s2); 20 21 bool f8 = test1 == test2; 22 bool f9 = object.Equals(test1, test2); 23 bool f10 = object.ReferenceEquals(test1, test2); 24 25 26 MyClass myClass = new MyClass { a = 1, b = "123", d = test1 }; 27 bool t1 = typeof(MyClass).GetProperties()[0].GetValue(myClass).Equals(1); 28 bool t2 = typeof(MyClass).GetProperties()[1].GetValue(myClass).Equals("123"); 29 bool t3 = typeof(MyClass).GetProperties()[2].GetValue(myClass).Equals(test1); 30 bool t4 = object.ReferenceEquals(typeof(MyClass).GetProperties()[2].GetValue(myClass), 1); 31 bool t5 = object.ReferenceEquals(typeof(MyClass).GetProperties()[1].GetValue(myClass), "123"); 32 bool t6 = object.ReferenceEquals(typeof(MyClass).GetProperties()[2].GetValue(myClass), test1); 33 34 35 36 } 37 } 38 39 class MyClass 40 { 41 public int a { get; set; } 42 public string b { get; set; } 43 public test d { get; set; } 44 } 45 46 class test 47 { 48 public int c; 49 }
结果如下: