子查询:
子查询是将一个查询语句嵌套在另外一个查询语句中,内层查询语句的查询结果,可以作为外来层查询语句提供查询条件。
因此在特定条件下,一个查询语句的条件,需要另外一个查询语句来获取。
前期准备表:
create table employee ( num int(50), d_id int(50), name varchar(50), age int(50), sex varchar(50), homeadd varchar(50) );
insert into employee values(1,1001,'zhangsan',26,'nan','beijing'); insert into employee values(2,1001,'lisi',24,'nv','hunan'); insert into employee values(3,1002,'wangwu',25,'nan','jiangsu'); insert into employee values(4,1004,'aric',15,'nan','yingguo');
select * from employee;
create table department ( d_id int(50), d_name varchar(50), functione varchar(50), address varchar(50) );
insert into department values(1001,'keyanbu','yanfachanpin','3lou5hao'); insert into department values(1002,'shengchanbu','shengchanchanp','5louyiceng'); insert into department values(1003,'xiaoshoubu','cehuaxiaoshou','1louxiaoshoudating');
select * from department;
一、带in关键字的子查询
select * from employee where d_id in (select d_id from department );

select * from employee where d_id not in (select d_id from department );

二、带exists关键字的子查询
exists关键字表示存在,使用exists关键字时,内层查询语句不用返回查询的记录。而是返回一个真假值。
如果内层查询语句查询到满足条件的记录,就返回一个真值(true);否则,返回一个假值(false);
当返回值为true时,外层查询语句将进行查询;而返回false时,外层查询语句不进行查询或者查询不出任何记录。
select * from employee where exists (select d_name from department where d_id = 1003);

select * from employee where exists (select d_name from department where d_id = 1004);

其它:
exists关键字可以与其他查询条件一起使用。条件表达式与exists关键字之间用and或者or来连接。 select * from employee where age > 24 and exists (select d_name from department where d_id = 1003); select * from employee where age > 24 and exists (select d_name from department where d_id = 1004); not exists与exists相反。 select * from employee where age > 24 and not exists (select d_name from department where d_id = 1003); select * from employee where age > 24 and not exists (select d_name from department where d_id = 1004);
===================================================================
准备语句:
create table schoarship ( levela int(50), score int(50) );
insert into schoarship(levela,score) values(1,90); insert into schoarship values(2,80); insert into schoarship values(3,70);
select * from schoarship;
create table computer_stu ( id int(50), name varchar(50), score int(50) );
insert into computer_stu(id,name,score) values (1001,'lily',85); insert into computer_stu(id,name,score) values (1002,'tom',91), (1003,'jim',87), (1004,'aric',77), (1005,'lucy',65), (1006,'andy',99), (1007,'ada',85), (1008,'jeck',70);
select * from computer_stu;
select * from schoarship;

select * from computer_stu;

3、带比较运算符的子查询
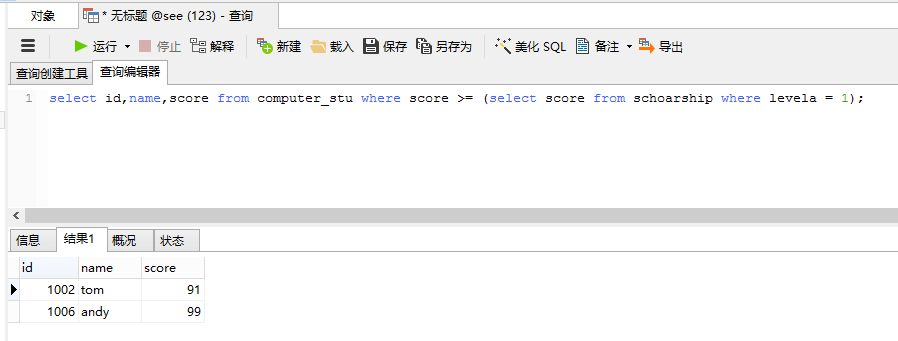
select id,name,score from computer_stu where score >= (select score from schoarship where levela = 1); /* 查询获得一等奖学金的学生有哪些,第一个表为奖学金等级和最低分数*/
select d_id,d_name from department where d_id != (select d_id from employee where age = 24); /*只有生产部和销售部没有年龄等于24岁的员工*/

4、带any关键字的子查询
any关键字表示满足其中任何一个条件。使用any关键字时,只要满足内查询语句返回的结果中的任何一个,就可以通过该条件来执行外层查询语句
select * from computer_stu where score >= any ( select score from schoarship ); /*结果显示,有7个人获得奖学金,只有id为1005的人没有,因为分数为65,不高于奖学金指定最低分数的任何一个*/

5、带all关键字的子查询
all关键字表示满足所有条件。使用all关键字时,只有满足内层查询语句返回的所有结果,才可以执行外层查询语句。
select * from computer_stu where score >= all ( select score from schoarship ); /*结果显示,只有两个人获得奖学金。因为这两个人的分数比所有奖学金要求的分数都高*/
