一:NIO与IO的区别
1.NIO面对的是缓冲区,IO面对的是流
2.NIO是非阻塞的,IO是阻塞的
3.NIO中引入了选择器
二:既然NIO面对的是缓冲区,那就先来了解缓冲区
1.NIO中Buffer负责存储,Buffer底层采用的是数组,可以存储不同数据类型,提供了相应的缓冲区(ByteBuffer,IntBuffer......),对于缓冲区的管理一致,通过allocate获取缓冲区
2.缓冲区存取数据的2个方法,put()存入,get()取出
3.缓冲区的4个核心属性
a.capacity:容量,最大存储数据的容量,一旦声明不能改变
b.limit:界限,表示缓冲区中可以操作数据的大小,(limit后面的数据不能进行读写)
c.limit:界限,表示缓冲区中可以操作数据的大小,(limit后面的数据不能进行读写)
d.position:位置,(表示缓冲区中正在操作数据的位置)
e:规则:position<=limit<=capacity
@Test public void test1(){ String str="abcde"; //1.分配指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); System.out.println("allocatt................................."); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); //通过put存入缓冲区 buf.put(str.getBytes()); System.out.println("put......................................."); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); //切换成读数据模式 buf.flip(); System.out.println("flip......................................."); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); //读取缓冲区中的数据 byte[] dst=new byte[buf.limit()]; buf.get(dst); System.out.println(new String(dst)); //获取完之后 System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); //rewide(),可重复读数据 System.out.println("rewinde....................."); buf.rewind(); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); //clear(),清空缓冲区,但是缓冲区中的数据依然存在,但是处于“被遗忘状态”(三个属性变为最初状态,不能正确的读取数据) buf.clear(); System.out.println("clear............................."); System.out.println(buf.position()); System.out.println(buf.limit()); System.out.println(buf.capacity()); }

allocatt................................. 0 1024 1024 put....................................... 5 1024 1024 flip....................................... 0 5 1024 abcde 5 5 1024 rewinde..................... 0 5 1024 clear............................. 0 1024 1024
说明:上面的程序是解释Buffer的基本属性,下面是其图解

4.mark。标记,记录当前position的位置,通过reset恢复到mark位置
@Test public void test2(){ String str="abcde"; ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); buf.put(str.getBytes()); buf.flip(); byte[] dst=new byte[buf.limit()]; buf.get(dst,0,2); System.out.println(new String(dst)); System.out.println(buf.position()); //标记一下 buf.mark(); buf.get(dst,2,2); System.out.println(new String(dst)); System.out.println(buf.position()); //恢复 buf.reset(); System.out.println(buf.position()); }

ab 2 abcd 4 2
5.直接缓冲区与非直接缓冲区
* 非直接缓冲区:通过allocate()方法分配缓冲区,缓冲区建立再JVM内存中
* 直接缓冲区:通过allocateDirect()方法分配缓冲区,可以将缓冲区建立在操作系统的物理内存中.在某种情况下可以提高效率
@Test public void test3(){ //直接缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024); }
图解直接缓冲区和非直接缓冲区:
非直接缓冲区:

直接缓冲区:
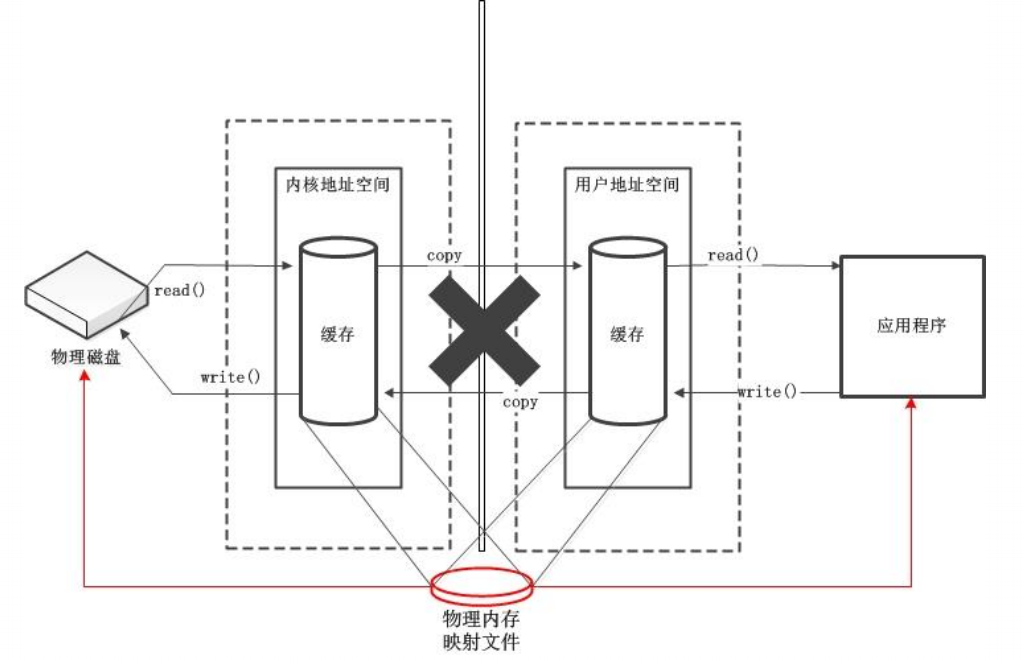
区别:直接缓冲区是直接在物理内存上面开辟空间,非直接缓冲区是在JVM上面开辟空间,在一定程度上面提高了效率
直接缓冲区的坏处:
a.创建和销毁开销大
b.数据进入直接缓冲区后,后续写入磁盘等操作就完全由操作系统决定了,不受我们控制
三:通道
1.负责源节点和目标节点的连接,在NIO中负责缓冲区中数据的传输,不能存储数据,配合缓冲区使用(理解为铁路(通道)和火车(缓冲区))
2.主要实现类
java.nio.channels.Channel接口:
FileChannel--本地
SocketChannel--TCP
SertverSocketChannel-TCP
DatagramChannel-UDP
3.获取通道的三种方式*
1.getChannel()方法
本地
FileInputStream/FILEOut
网络
Socket
ServerSocket
DatagramSocket
2.在JDK1.7中的NIO.2针对各个通道提供了静态方法open()
3.在JDK1.7中的NIO.2的Files的工具类的newByteChannel()
4.通道之间的数据传输
1.transferForm()
2.transferTo()
5.分散与聚集
1.分散读取(将通道中的数据分散到多个缓冲区)
2.聚集写入(将多个缓冲区中的数据聚集到通道中)
6.字符集
编码:将字符串转换成字符数组
解码:字符数组转换成字符串
下面举几个例子:
通过通道完成文件的复制
@Test public void test1() throws IOException { FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("1.jpg"); FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("2.jpg"); //1.获取通道 FileChannel inChannel = fis.getChannel(); FileChannel outChannel = fos.getChannel(); //2.分配指定大小缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //3.将通道中的数据存入缓冲区 while(inChannel.read(buf)!=-1){ buf.flip();//切换到读取模式 //4.将缓冲区中的数据写入通道 outChannel.write(buf); buf.clear();//清空缓冲区 } //5.关闭通道 inChannel.close(); outChannel.close(); fis.close(); fos.close(); }
使用直接缓冲区完成文件的复制
//使用直接缓冲区 @Test public void test2() throws IOException { FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ); FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("3.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.CREATE); //内存映射文件 MappedByteBuffer inMapBuf = inChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inChannel.size()); MappedByteBuffer outMapBuf = outChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inChannel.size()); //直接堆缓冲区堆数据进行读写操作 byte[] dst=new byte[inMapBuf.limit()]; inMapBuf.get(dst); outMapBuf.put(dst); inChannel.close(); outChannel.close(); }
通道之间的数据传输(使用直接缓冲区)
//通道之间的数据传输(直接缓冲区) @Test public void test3() throws IOException { FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ); FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("3.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.CREATE); inChannel.transferTo(0,inChannel.size(),outChannel); inChannel.close(); outChannel.close(); }
分散与聚集
说明:分散读取是将通道里面的数据依次读到多个缓冲区里面,聚集写入是将多个缓冲区里面的数据依次写入通道里面
//分散与聚集 @Test public void test4() throws IOException { RandomAccessFile raf1=new RandomAccessFile("1.txt","rw"); //获取通道 FileChannel channel = raf1.getChannel(); //分配指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer bf1=ByteBuffer.allocate(100); ByteBuffer bf2=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //分散读取 ByteBuffer[] bufs={bf1,bf2}; channel.read(bufs); for (ByteBuffer byteBuffer:bufs) { byteBuffer.flip(); } System.out.println(new String(bufs[0].array(),0,bufs[0].limit())); System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------"); System.out.println(new String(bufs[1].array(),0,bufs[1].limit())); //聚集写入 RandomAccessFile raf2=new RandomAccessFile("2.txt","rw"); FileChannel channel2 = raf2.getChannel(); channel2.write(bufs); }
console:

abvc dse fds gfdgfd gfdg gfdg gfdghytj fgdgfcv gfdr xzcas c fds aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa -------------------------------------------------- aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
字符集
@Test public void test5(){ SortedMap<String, Charset> map = Charset.availableCharsets(); Set<Map.Entry<String, Charset>> set = map.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry<String, Charset> entry:set) { System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"="+entry.getValue()); } }
编码和解码
****使用哪种字符集编码就要使用哪种字符集解码
@Test public void test6() throws CharacterCodingException { Charset cs1 = Charset.forName("GBK"); //获取编码器和解码器 CharsetEncoder ce = cs1.newEncoder(); //获取解码器 CharsetDecoder cd = cs1.newDecoder(); CharBuffer cbuf = CharBuffer.allocate(1024); cbuf.put("xhww!!"); cbuf.flip(); //编码 ByteBuffer bBuf = ce.encode(cbuf); for (int i=0;i<12;i++){ System.out.println(bBuf.get()); } //解码 bBuf.flip(); CharBuffer cBuf = cd.decode(bBuf); System.out.println(cBuf); }
