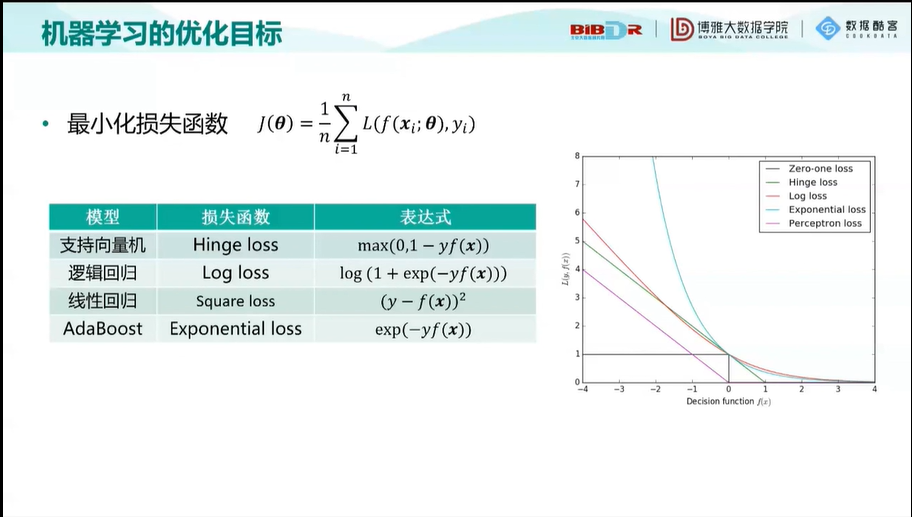
机器学习的优化目标
batch和mini-batch梯度下降

机器学习中常用优化算法的 Python 实践
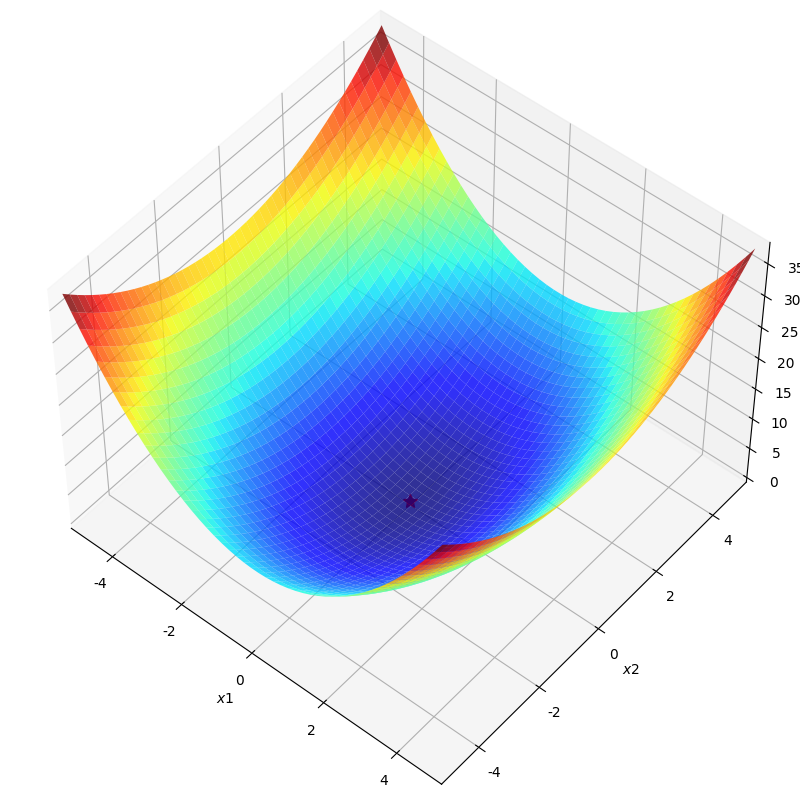
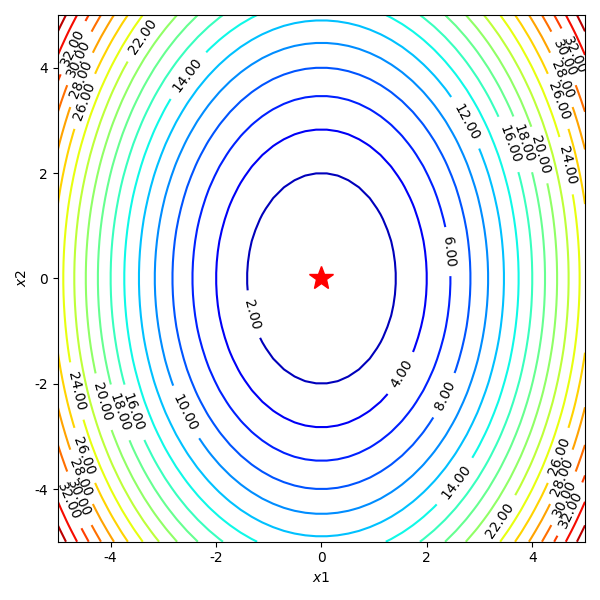
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D from matplotlib import animation from autograd import elementwise_grad, value_and_grad,grad from scipy.optimize import minimize from scipy import optimize from collections import defaultdict from itertools import zip_longest plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False # 用来正常显示负号 f1 = lambda x1,x2 : x1**2 + 0.5*x2**2 #函数定义 f1_grad = value_and_grad(lambda args : f1(*args)) #函数梯度 def gradient_descent(func, func_grad, x0, learning_rate=0.1, max_iteration=20): path_list = [x0] best_x = x0 step = 0 while step < max_iteration: update = -learning_rate * np.array(func_grad(best_x)[1]) if(np.linalg.norm(update) < 1e-4): break best_x = best_x + update path_list.append(best_x) step = step + 1 return best_x, np.array(path_list) best_x_gd, path_list_gd = gradient_descent(f1,f1_grad,[-4.0,4.0],0.1,30) x1,x2 = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-5.0,5.0,50), np.linspace(-5.0,5.0,50)) z = f1(x1,x2 ) minima = np.array([0, 0]) #对于函数f1,我们已知最小点为(0,0) fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8)) ax = plt.axes(projection='3d', elev=50, azim=-50) ax.plot_surface(x1,x2, z, alpha=.8, cmap=plt.cm.jet) ax.plot([minima[0]],[minima[1]],[f1(*minima)], 'r*', markersize=10) ax.set_xlabel('$x1$') ax.set_ylabel('$x2$') ax.set_zlabel('$f$') ax.set_xlim((-5, 5)) ax.set_ylim((-5, 5)) plt.show() dz_dx1 = elementwise_grad(f1, argnum=0)(x1, x2) dz_dx2 = elementwise_grad(f1, argnum=1)(x1, x2) fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6)) contour = ax.contour(x1, x2, z,levels=20,cmap=plt.cm.jet) ax.clabel(contour,fontsize=10,colors='k',fmt='%.2f') ax.plot(*minima, 'r*', markersize=18) ax.set_xlabel('$x1$') ax.set_ylabel('$x2$') ax.set_xlim((-5, 5)) ax.set_ylim((-5, 5)) plt.show()