Jupyter All In One
Jupyter Architecture
https://jupyter.readthedocs.io/en/latest/projects/architecture/content-architecture.html
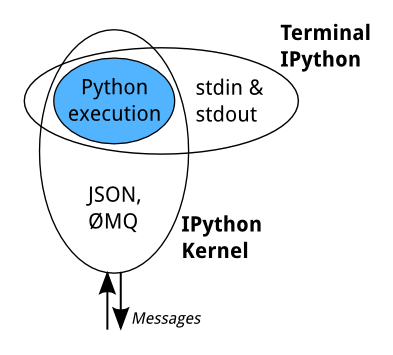
iPython
Jupyter Notebook Interface
https://ipython.org/index.html
Jupyter Notebook
https://jupyter.readthedocs.io/en/latest/install.html
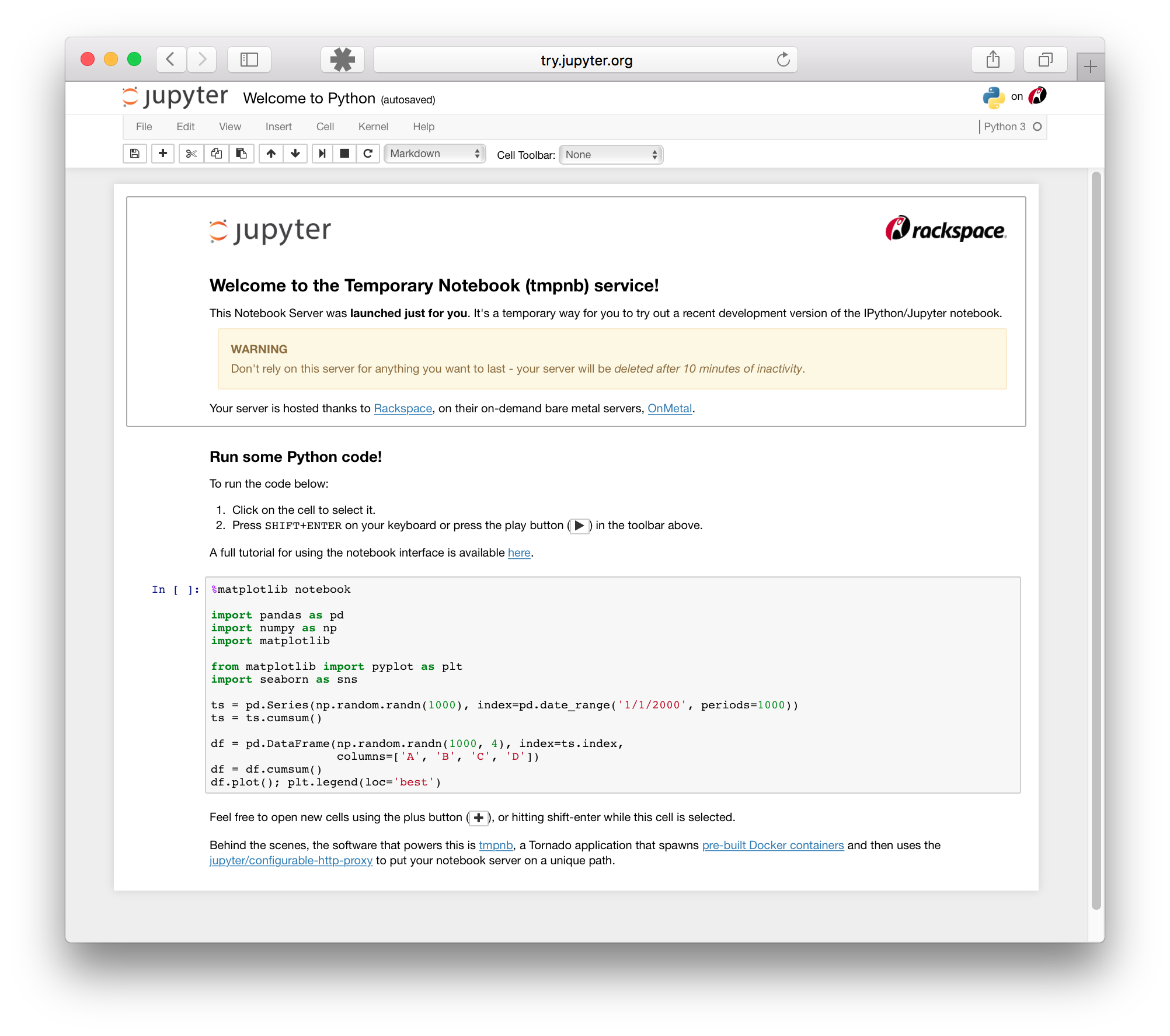
Python REPL online

REPL & playground
https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/ipython/ipython-in-depth/master?filepath=binder/Index.ipynb
https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/jupyterlab/jupyterlab-demo/try.jupyter.org?urlpath=lab
Python enumerate()
enumerate() is a built-in function to iterate through a sequence and keep track of both the index and the number.
>>> list(range(11))
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
>>> list(enumerate([1, 2, 3]))
[(0, 1), (1, 2), (2, 3)]
>>> list(enumerate([1, 2, 3], start=10))
[(10, 1), (11, 2), (12, 3)]
list = [45, 22, 14, 65, 97, 72].
for i, num in enumerate(numbers):
if num % 3 == 0:
numbers[i] = "fizz"
if num % 5 == 0:
numbers[i] = "buzz"
if num % 5 == 0 and num % 3 == 0:
numbers[i] = "fizzbuzz"
for i, num in enumerate(numbers):
if num % 5 == 0 and num % 3 == 0:
numbers[i] = "fizzbuzz"
elif num % 3 == 0:
numbers[i] = "fizz"
elif num % 5 == 0:
numbers[i] = "buzz"
refs
https://realpython.com/lessons/python-coding-interview-tips-overview/
https://realpython.com/courses/python-range-function/
https://realpython.com/lessons/use-enumerate-keep-running-index/
©xgqfrms 2012-2020
www.cnblogs.com 发布文章使用:只允许注册用户才可以访问!