GitHub项目地址
https://github.com/1721819634/WC
1.Word Count 项目要求:
wc.exe 是一个常见的工具,它能统计文本文件的字符数、单词数和行数。这个项目要求写一个命令行程序,模仿已有wc.exe 的功能,并加以扩充,给出某程序设计语言源文件的字符数、单词数和行数。
实现一个统计程序,它能正确统计程序文件中的字符数、单词数、行数,以及还具备其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。
具体功能要求:
程序处理用户需求的模式为:
wc.exe [parameter] [file_name]
基本功能列表:
wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数
wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的词的数目
wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的行数
扩展功能:
-s 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件。
-a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)。
空行:本行全部是空格或格式控制字符,如果包括代码,则只有不超过一个可显示的字符,例如“{”。
代码行:本行包括多于一个字符的代码。
注释行:本行不是代码行,并且本行包括注释。一个有趣的例子是有些程序员会在单字符后面加注释:
} //注释
在这种情况下,这一行属于注释行。
[file_name]: 文件或目录名,可以处理一般通配符。
高级功能:
-x 参数。这个参数单独使用。如果命令行有这个参数,则程序会显示图形界面,用户可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、行数等全部统计信息。
需求举例:
wc.exe -s -a *.c ===> 返回当前目录及子目录中所有*.c 文件的代码行数、空行数、注释行数。
2.预计开发时间 PSP
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
5 |
|
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
10 |
|
|
Development |
开发 |
300 |
|
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
45 |
|
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
10 |
|
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
0 |
|
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
10 |
|
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
120 |
|
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
60 |
|
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
30 |
|
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
120 |
|
|
Reporting |
报告 |
60 |
|
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
30 |
|
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
20 |
|
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
10 |
|
|
合计 |
|
830 |
|
3.解题思路
编程语言:python
预计要学习的知识:I/O流、GUI图形编程、正则表达式
设计结构分析:
字符数、单词数、行数等都可以看做是从一个文本中可获得的属性,因此把他们的获得方法封装成一个类会很方便调用。最后设计一个主函数根据传入的命令调用他们。
遇到的困难:
由于之前对I/O流接触得比较少,在实现文件的读入时常发现如编码出错等小错误。对于python的GUI设计,现学现做,单是学习并搞懂基本操作就花了我挺多的时间。
在实现完基本功能去实现扩展功能的时候,比较烦恼如何不把代码设计得太繁杂。
4.设计实现过程
编写功能类,在初始化时需传入文件路径和命令符。每个功能对应类中的一个函数,除此之外还有一个主调用函数
函数功能如下:
chars_count: 实现计算文本字符个数的函数
lines_count:实现文本行数计数,返回代码行、注释行、空行以及总行数
words_count:实现文本单词计数
recur_files:用于递归处理文件目录。具体实现为获取传入路径所有的子文件,逐一判断个子文件是否为文件夹;若是文件夹则递归处理,否则调用主函数
主调用函数:根据命令符调用以上函数
GUI类:用于实现图形界面操作
函数调用关系:

5.代码说明
WC功能类
class WC: def __init__(self, file_dict, order): self.file_dict = file_dict self.order = order # 计算字符个数 def chars_count(self, in_dict=None): f_dict = self.file_dict if in_dict is None else in_dict file = open(f_dict, mode='r', encoding='UTF-8') chars = len(file.read()) file.close() return chars # 计算行数 def lines_count(self, in_dict=None): f_dict = self.file_dict if in_dict is None else in_dict file = open(f_dict, mode='r', encoding='UTF-8') read = file.readlines() space_lines = 0 # 空行行数 code_lines = 0 # 代码行行数 comment_lines = 0 # 注释行行数 comment_flag = False # 注释行判断标志,用于判断多行注释 start_comment_line = 0 # 多行注释的起始位置 total_lines = 0 # 总行数 for line in read: total_lines += 1 line = line.strip() if not comment_flag: if line.startswith('"""') or line.startswith("'''"): comment_flag = True start_comment_line = total_lines elif line.startswith('#'): comment_lines += 1 elif len(line) <= 1: space_lines += 1 else: code_lines += 1 else: if line.endswith('"""') or line.endswith("'''"): comment_flag = False comment_lines += (total_lines - start_comment_line + 1) file.close() return [code_lines, comment_lines, space_lines, total_lines] # 计算词语数目 def words_count(self, in_dict=None): f_dict = self.file_dict if in_dict is None else in_dict file = open(f_dict, mode='r', encoding='UTF-8') read = file.readlines() words = [] # 存储单词,得到单词并且存入列表中 for line in read: # 用空格代替一串非数字和字母 word = re.sub(r'[^0-9a-zA-Zu4E00-u9FFF]+', ' ', line) # 用空格代替一串非数字和字母 word = word.strip() word = word.split(' ') # 若该行为空或没有任何单词,word = [''] if word != ['']: words.extend(word) file.close() return len(words) def main_function(self, in_dict=None, in_oredr=None): from gui import WcFrame as WF f_dict = self.file_dict if in_dict is None else in_dict order = self.order if in_oredr is None else in_oredr is_file = False # 若目录不为文件,只能与'-s'搭配 if os.path.isfile(f_dict): is_file = True if order == '-c' and is_file: charco = self.chars_count(f_dict) print("字符数:", charco) elif order == '-w' and is_file: wordco = self.words_count(f_dict) print("单词数:", wordco) elif order == '-l' and is_file: lineco = self.lines_count(f_dict) print("总行数:", lineco[3]) elif order == '-a' and is_file: lineco = self.lines_count(f_dict) print("代码行行数:", lineco[0]) print("注释行数:", lineco[1]) print("空行数:", lineco[2]) elif order == '-s' and not is_file: self.recur_files() elif order == '-x': app = wx.App() frame = WF(None) frame.Show() app.MainLoop() elif order == '-g' and is_file: # 输出全部信息 lineco = self.lines_count(f_dict) print("字符数:", self.chars_count(f_dict)) print("单词数:", self.words_count(f_dict)) print("代码行行数:", lineco[0]) print("注释行数:", lineco[1]) print("空行数:", lineco[2]) print("总行数:", lineco[3]) else: print("输入命令有误,请重新输入!") def recur_files(self, in_dict=None): f_dict = self.file_dict if in_dict is None else in_dict path_list = os.listdir(f_dict) # 获取当前目录下的文件名 result = [] result.extend(path_list) for path in path_list: new_dict = os.path.join(f_dict, path) # 将获取的文件名拼接到原目录后面,组成新目录 if os.path.isfile(new_dict): # 判断是否为文件 print('----------------') print('文件', path) self.main_function(new_dict, '-g') else: result.extend(self.recur_files(new_dict)) return result # 返回所有文件名,用于测试函数
GUI图形类
class WcFrame(wx.Frame): def __init__(self, parent): super(WcFrame, self).__init__(parent, title="Word Count", pos=(1000, 200), size=(500, 190)) self.path_test = wx.TextCtrl(self, pos=(5, 5), size=(350, 24)) self.open_button = wx.Button(self, label="打开", pos=(370, 5), size=(50, 24)) self.open_button.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnOpenFile) # 绑定打开文件事件到open_button按钮上 # wx.TE_MULTILINE可以实现以滚动条方式多行显示文本,若不加此功能文本文档显示为一行 self.content_text = wx.TextCtrl(self, pos=(5, 39), size=(475, 100), style=wx.TE_MULTILINE) self.cal_button = wx.Button(self, label="计算", pos=(430, 5), size=(50, 24)) self.cal_button.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.word_count) def OnOpenFile(self, event): # 打开文件事件 wildcard = 'All files(*.*)|*.*' dialog = wx.FileDialog(None, 'select', os.getcwd(), '', wildcard, wx.FD_OPEN | wx.FD_FILE_MUST_EXIST) if dialog.ShowModal() == wx.ID_OK: self.path_test.SetValue(dialog.GetPath()) dialog.Destroy def word_count(self, event): wc = WC(self.path_test.GetValue(), '-g') chars = wc.chars_count() words = wc.words_count() lines =wc.lines_count() result = '字符数:{}, 单词数:{},代码行行数:{},注释行行数:{},空行行数:{} 总行数:{}'.format(chars, words, lines[0], lines[1], lines[2], lines[3]) self.content_text.SetValue(result)
6. 测试运行
程序实现功能
本程序实现了高级功能的支持通过图形界面选取文件;-c、-l、-w、-s指令以及-a的全部指令(为了方便测试,我多设计了一个输出全部结果的指令-g)
支持各种文本文档文件,
测试使用样例
import numpy as np from sympy import * from numpy import random ''' this file is used to test wc. Here is the parameters chars: 407 words: 75 code_lines: 11 space_lines: 1 comment_lines: 10 total_lines: 22 ''' sst = random.randint(10, 30, size=(10, 10)) s = sst.ravel() long = len(s) mean = sum(s) / long std = np.sqrt(sum((s - mean) ** 2 / long)) print(np.pi) print(math.sqrt(4)) print(std) # print(net)
测试过程
① 打开编译器,编译代码,弹出窗口
② 输入命令符和文件路径
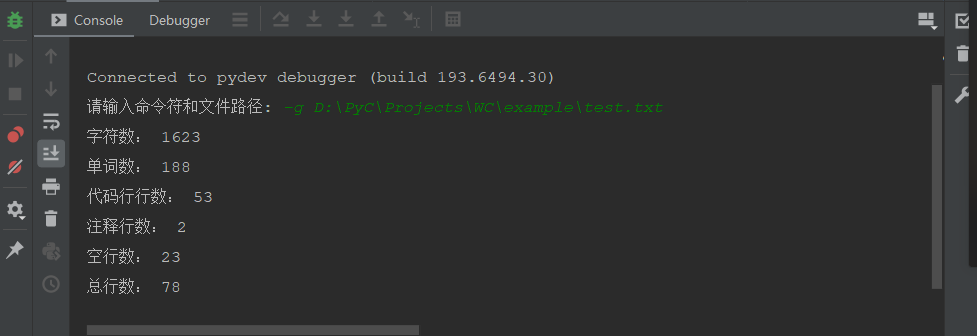
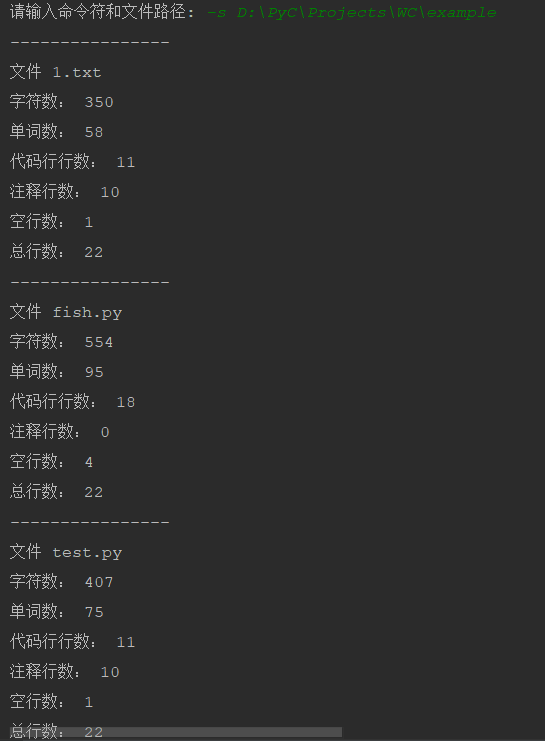
③ -s命令测试

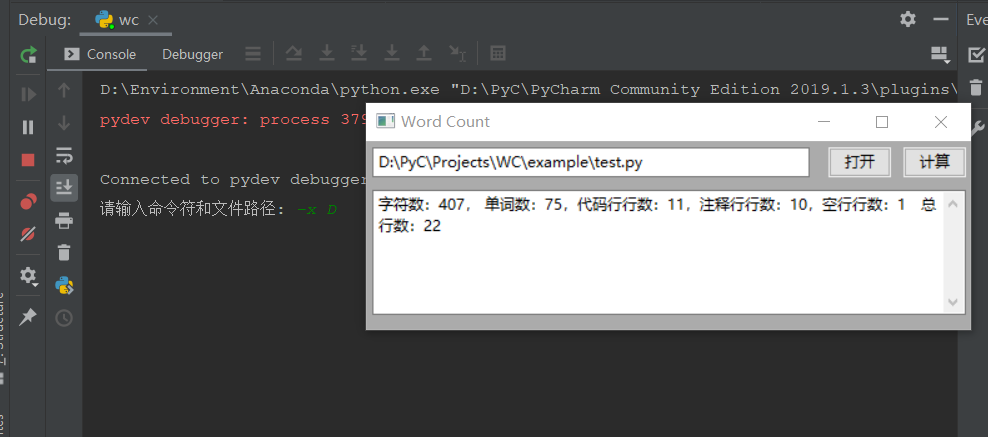
④ GUI测试
单元测试文件及结果
import unittest from wc import WC class TestWC(unittest.TestCase): def test_wc(self): wc = WC('D:/PyC/Projects/WC/example/test.py', '-c') self.assertEqual(wc.file_dict, 'D:/PyC/Projects/WC/example/test.py') self.assertEqual(wc.order, '-c') def test_chars_count(self): wc = WC('D:/PyC/Projects/WC/example/test.py', '') chars = wc.chars_count() self.assertEqual(chars, 407) def test_lines_count(self): wc = WC('D:/PyC/Projects/WC/example/test.py', '') lines = wc.lines_count() self.assertEqual(lines[0], 11) self.assertEqual(lines[1], 10) self.assertEqual(lines[2], 1) self.assertEqual(lines[3], 22) def test_words_count(self): wc = WC('D:/PyC/Projects/WC/example/test.py', '') words = wc.words_count() self.assertEqual(words, 75) def test_recur_files(self): test = ['1', 'test.py', 'test.txt', '1.txt', 'fish.py'] wc = WC('D:/PyC/Projects/WC/example', '') result = wc.recur_files() for i in range(len(test)): self.assertEqual(result[i], test[i]) def test_main_function(self): for order in ['-c', '-w', '-l', '-a', '-s', '-x', '-a', '-g', ' ']: wc = WC('D:/PyC/Projects/WC/example/test.py', order) wc.main_function() if __name__ == '__main__': unittest.main()

7.实现完程序后,实际花费时间
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
5 |
6 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
10 |
8 |
|
Development |
开发 |
300 |
480 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
45 |
120 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
10 |
5 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
0 |
0 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
10 |
10 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
120 |
80 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
60 |
80 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
30 |
35 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
120 |
150 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
60 |
50 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
30 |
45 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
20 |
30 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
10 |
15 |
|
合计 |
|
830 |
1114 |
8.项目小结
在开发项目前,以为这个程序并不会花很多时间。但在实际上手后发现并非如此。虽然花在代码实现的时间并没有那么多,但我
的时间大部分花在代码调试以及学习新知识上。由于开发经验并不是很多,我在开发前并没有很严格的进行需求分析和设计分析,
导致在添加功能的时候由于没搞清一些代码的关系而出现bug的情况。这让我重新审视了需求分析的重要性。在实现-x功能时,由
于时间关系我并没有做很好的优化,导致这功能任然要输入一个路径作为参数,算是一个缺陷。同时,在开发后期,我想到了更为
方便的设计结构,但由于代码已成型不便修改。这再次让我重新认识到的项目前分析的重要性。