Amr loves Geometry. One day he came up with a very interesting problem.
Amr has a circle of radius r and center in point (x, y). He wants the circle center to be in new position (x', y').
In one step Amr can put a pin to the border of the circle in a certain point, then rotate the circle around that pin by any angle and finally remove the pin.
Help Amr to achieve his goal in minimum number of steps.
Input consists of 5 space-separated integers r, x, y, x' y' (1 ≤ r ≤ 105, - 105 ≤ x, y, x', y' ≤ 105), circle radius, coordinates of original center of the circle and coordinates of destination center of the circle respectively.
Output a single integer — minimum number of steps required to move the center of the circle to the destination point.
2 0 0 0 4
1
1 1 1 4 4
3
4 5 6 5 6
0
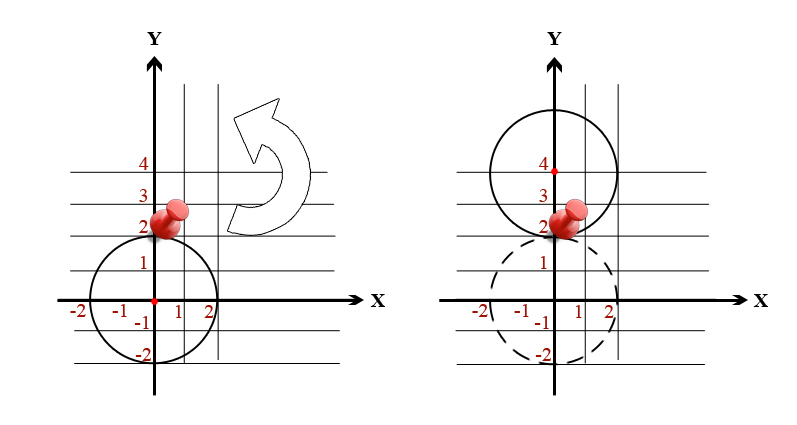
In the first sample test the optimal way is to put a pin at point (0, 2) and rotate the circle by 180 degrees counter-clockwise (or clockwise, no matter).
直接用两点之间的距离除以圆的直径就可以了,需要注意如果有小数点向前取整就可以了.
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double x1,y1,x2,y2;
int r;
cin>>r>>x1>>y1>>x2>>y2;
r*=2;
double sub=sqrt((y2-y1)*(y2-y1)+(x2-x1)*(x2-x1));
if(sub-(int)sub>0)
sub+=1;
if((int)sub%r==0)
cout<<(int)sub/r<<endl;
else
cout<<(int)sub/r+1<<endl;
return 0;
}